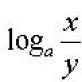What is inverse proportion? Inverse proportionality
Basic goals:
- introduce the concept of direct and inverse proportional dependence of quantities;
- teach how to solve problems using these dependencies;
- promote the development of problem solving skills;
- consolidate the skill of solving equations using proportions;
- repeat the steps with ordinary and decimals;
- develop logical thinking students.
DURING THE CLASSES
I. Self-determination for activity(Organizing time)
- Guys! Today in the lesson we will get acquainted with problems solved using proportions.
II. Updating knowledge and recording difficulties in activities
2.1. Oral work (3 min)
– Find the meaning of the expressions and find out the word encrypted in the answers.
14 – s; 0.1 – and; 7 – l; 0.2 – a; 17 – c; 25 – to
– The resulting word is strength. Well done!
– The motto of our lesson today: Power is in knowledge! I'm searching - that means I'm learning!
– Make up a proportion from the resulting numbers. (14:7 = 0.2:0.1 etc.)
2.2. Let's consider the relationship between the quantities we know (7 min)
– the distance covered by the car at a constant speed, and the time of its movement: S = v t ( with increasing speed (time), the distance increases);
– vehicle speed and time spent on the journey: v=S:t(as the time to travel the path increases, the speed decreases);
–
the cost of goods purchased at one price and its quantity:
C = a · n (with an increase (decrease) in price, the purchase cost increases (decreases));
– price of the product and its quantity: a = C: n (with an increase in quantity, the price decreases)
– area of the rectangle and its length (width): S = a · b (with increasing length (width), the area increases;
– rectangle length and width: a = S: b (as the length increases, the width decreases;
– the number of workers performing some work with the same labor productivity, and the time it takes to complete this work: t = A: n (with an increase in the number of workers, the time spent on performing the work decreases), etc.
We have obtained dependences in which, with an increase in one quantity several times, another immediately increases by the same amount (examples are shown with arrows) and dependences in which, with an increase in one quantity several times, the second quantity decreases by the same number of times.
Such dependencies are called direct and inverse proportionality.
Directly proportional dependence– a relationship in which as one value increases (decreases) several times, the second value increases (decreases) by the same amount.
Inversely proportional relationship– a relationship in which as one value increases (decreases) several times, the second value decreases (increases) by the same amount.
III. Setting a learning task
– What problem is facing us? (Learn to distinguish between direct and inverse dependencies)
- This - target our lesson. Now formulate topic lesson. (Direct and inverse proportional relationship).
- Well done! Write down the topic of the lesson in your notebooks. (The teacher writes the topic on the board.)
IV. "Discovery" of new knowledge(10 min)
Let's look at problem No. 199.
1. The printer prints 27 pages in 4.5 minutes. How long will it take it to print 300 pages?
27 pages – 4.5 min.
300 pages - x?
2. The box contains 48 packs of tea, 250 g each. How many 150g packs of this tea will you get?
48 packs – 250 g.
X? – 150 g.
3. The car drove 310 km, using 25 liters of gasoline. How far can a car travel on a full 40L tank?
310 km – 25 l
X? – 40 l
4. One of the clutch gears has 32 teeth, and the other has 40. How many revolutions will the second gear make while the first one makes 215 revolutions?
32 teeth – 315 rev.
40 teeth – x?
To compile a proportion, one direction of the arrows is necessary; for this, in inverse proportionality, one ratio is replaced by the inverse.
At the board, students find the meaning of quantities; on the spot, students solve one problem of their choice.
– Formulate a rule for solving problems with direct and inverse proportional dependence.
A table appears on the board:
V. Primary consolidation in external speech(10 min)
Worksheet assignments:
- From 21 kg of cottonseed, 5.1 kg of oil was obtained. How much oil will be obtained from 7 kg of cottonseed?
- To build the stadium, 5 bulldozers cleared the site in 210 minutes. How long would it take 7 bulldozers to clear this site?
VI. Independent work with self-test against standard(5 minutes)
Two students complete task No. 225 independently on hidden boards, and the rest - in notebooks. They then check the algorithm's work and compare it with the solution on the board. Errors are corrected and their causes are determined. If the task is completed correctly, then the students put a “+” sign next to them.
Students who make mistakes in independent work can use consultants.
VII. Inclusion in the knowledge system and repetition№ 271, № 270.
Six people work at the board. After 3-4 minutes, students working at the board present their solutions, and the rest check the assignments and participate in their discussion.
VIII. Reflection on activity (lesson summary)
– What new did you learn in the lesson?
-What did they repeat?
– What is the algorithm for solving proportion problems?
– Have we achieved our goal?
– How do you evaluate your work?
I. Directly proportional quantities.
Let the value y depends on the size X. If when increasing X several times the size at increases by the same amount, then such values X And at are called directly proportional.
Examples.
1 . The quantity of goods purchased and the purchase price (with a fixed price for one unit of goods - 1 piece or 1 kg, etc.) How many times more goods were bought, the more times more they paid.
2 . The distance traveled and the time spent on it (at constant speed). How many times longer is the path, how many times more time will it take to complete it.
3 . The volume of a body and its mass. ( If one watermelon is 2 times larger than another, then its mass will be 2 times larger)
II. Property of direct proportionality of quantities.
If two quantities are directly proportional, then the ratio of two arbitrarily taken values of the first quantity is equal to the ratio of two corresponding values of the second quantity.
Task 1. For raspberry jam we took 12 kg raspberries and 8 kg Sahara. How much sugar will you need if you took it? 9 kg raspberries?
Solution.
We reason like this: let it be necessary x kg sugar for 9 kg raspberries The mass of raspberries and the mass of sugar are directly proportional quantities: how many times less raspberries are, the same number of times less sugar is needed. Therefore, the ratio of raspberries taken (by weight) ( 12:9 ) will be equal to the ratio of sugar taken ( 8:x). We get the proportion:
12: 9=8: X;
x=9 · 8: 12;
x=6. Answer: on 9 kg raspberries need to be taken 6 kg Sahara.
The solution of the problem It could be done like this:
Let on 9 kg raspberries need to be taken x kg Sahara.
(The arrows in the figure are directed in one direction, and up or down does not matter. Meaning: how many times the number 12 more number 9 , the same number of times 8 more number X, i.e. there is a direct relationship here).
Answer: on 9 kg I need to take some raspberries 6 kg Sahara.
Task 2. Car for 3 hours traveled the distance 264 km. How long will it take him to travel? 440 km, if he drives at the same speed?
Solution.
Let for x hours the car will cover the distance 440 km.
 Answer: the car will pass 440 km in 5 hours.
Answer: the car will pass 440 km in 5 hours.
Task 3. Water flows from the pipe into the pool. Behind 2 hours she fills 1/5 swimming pool What part of the pool is filled with water in 5 o'clock?
Solution.
We answer the question of the task: for 5 o'clock will be filled 1/x part of the pool. (The entire pool is taken as one whole).
I. Directly proportional quantities.
Let the value y depends on the size X. If when increasing X several times the size at increases by the same amount, then such values X And at are called directly proportional.
Examples.
1 . The quantity of goods purchased and the purchase price (with a fixed price for one unit of goods - 1 piece or 1 kg, etc.) How many times more goods were bought, the more times more they paid.
2 . The distance traveled and the time spent on it (at constant speed). How many times longer is the path, how many times more time will it take to complete it.
3 . The volume of a body and its mass. ( If one watermelon is 2 times larger than another, then its mass will be 2 times larger)
II. Property of direct proportionality of quantities.
If two quantities are directly proportional, then the ratio of two arbitrarily taken values of the first quantity is equal to the ratio of two corresponding values of the second quantity.
Task 1. For raspberry jam we took 12 kg raspberries and 8 kg Sahara. How much sugar will you need if you took it? 9 kg raspberries?
Solution.
We reason like this: let it be necessary x kg sugar for 9 kg raspberries The mass of raspberries and the mass of sugar are directly proportional quantities: how many times less raspberries are, the same number of times less sugar is needed. Therefore, the ratio of raspberries taken (by weight) ( 12:9 ) will be equal to the ratio of sugar taken ( 8:x). We get the proportion:
12: 9=8: X;
x=9 · 8: 12;
x=6. Answer: on 9 kg raspberries need to be taken 6 kg Sahara.
The solution of the problem It could be done like this:
Let on 9 kg raspberries need to be taken x kg Sahara.
(The arrows in the figure are directed in one direction, and up or down does not matter. Meaning: how many times the number 12 more number 9 , the same number of times 8 more number X, i.e. there is a direct relationship here).
Answer: on 9 kg I need to take some raspberries 6 kg Sahara.
Task 2. Car for 3 hours traveled the distance 264 km. How long will it take him to travel? 440 km, if he drives at the same speed?
Solution.
Let for x hours the car will cover the distance 440 km.
 Answer: the car will pass 440 km in 5 hours.
Answer: the car will pass 440 km in 5 hours.
Solving problems from the problem book Vilenkin, Zhokhov, Chesnokov, Shvartsburd for 6th grade in mathematics on the topic:
§ 4. Relations and proportions:
22. Direct and reverse proportional dependencies
1 For 3.2 kg of goods they paid 115.2 rubles. How much should you pay for 1.5 kg of this product?
SOLUTION
2 Two rectangles have the same area. The length of the first rectangle is 3.6 m and the width is 2.4 m. The length of the second is 4.8 m. Find its width.
SOLUTION
782 Determine whether the relationship between the quantities is direct, inverse, or not proportional: the distance covered by the car at a constant speed and the time of its movement; the cost of goods purchased at one price and its quantity; the area of the square and the length of its side; the mass of the steel bar and its volume; the number of workers performing some work with the same labor productivity, and the time of completion; the cost of the product and its quantity purchased at a certain amount money; the age of the person and the size of his shoes; the volume of the cube and the length of its edge; the perimeter of the square and the length of its side; a fraction and its denominator, if the numerator does not change; a fraction and its numerator if the denominator does not change.
SOLUTION
783 A steel ball with a volume of 6 cm3 has a mass of 46.8 g. What is the mass of a ball made of the same steel if its volume is 2.5 cm3?
SOLUTION
784 From 21 kg of cotton seed, 5.1 kg of oil was obtained. How much oil will be obtained from 7 kg of cottonseed?
SOLUTION
785 For the construction of the stadium, 5 bulldozers cleared the site in 210 minutes. How long will it take 7 bulldozers to clear this site?
SOLUTION
786 To transport the cargo, 24 vehicles with a carrying capacity of 7.5 tons were required. How many vehicles with a carrying capacity of 4.5 tons are needed to transport the same cargo?
SOLUTION
787 To determine the germination of seeds, peas were sown. Of the 200 peas sown, 170 sprouted. What percentage of the peas sprouted (germinated)?
SOLUTION
788 During the city greening Sunday, linden trees were planted on the street. 95% of all planted linden trees were accepted. How many of them were planted if 57 linden trees were planted?
SOLUTION
789 There are 80 students in the ski section. Among them are 32 girls. What percentage of section participants are girls and boys?
SOLUTION
790 According to the plan, the plant was supposed to smelt 980 tons of steel in a month. But the plan was fulfilled by 115%. How many tons of steel did the plant produce?
SOLUTION
791 In 8 months, the worker completed 96% of the annual plan. What percentage of the annual plan will the worker complete in 12 months if he works with the same productivity?
SOLUTION
792 In three days, 16.5% of all beets were harvested. How many days will it take to harvest 60.5% of the beets if you work at the same productivity?
SOLUTION
793 V iron ore For 7 parts of iron there are 3 parts of impurities. How many tons of impurities are in the ore that contains 73.5 tons of iron?
SOLUTION
794 To prepare borscht, for every 100 g of meat you need to take 60 g of beets. How many beets should you take for 650 g of meat?
SOLUTION
796 Express each of the following fractions as the sum of two fractions with numerator 1.
SOLUTION
797 From the numbers 3, 7, 9 and 21, form two correct proportions.
SOLUTION
798 The middle terms of the proportion are 6 and 10. What can the extreme terms be? Give examples.
SOLUTION
799 At what value of x is the proportion correct.
SOLUTION
800 Find the ratio of 2 min to 10 sec; 0.3 m2 to 0.1 dm2; 0.1 kg to 0.1 g; 4 hours to 1 day; 3 dm3 to 0.6 m3
SOLUTION
801 Where on the coordinate ray should the number c be located for the proportion to be correct.
SOLUTION
802 Cover the table with a sheet of paper. Open the first line for a few seconds and then, closing it, try to repeat or write down the three numbers of that line. If you have reproduced all the numbers correctly, move on to the second row of the table. If there is an error in any line, write several sets of the same number of two-digit numbers yourself and practice memorizing. If you can reproduce at least five two-digit numbers without errors, you have a good memory.
SOLUTION
804 Is it possible to formulate the correct proportion from the following numbers?
SOLUTION
805 From the equality of the products 3 · 24 = 8 · 9, form three correct proportions.
SOLUTION
806 The length of segment AB is 8 dm, and the length of segment CD is 2 cm. Find the ratio of the lengths AB and CD. What part of AB is the length CD?
SOLUTION
807 A trip to the sanatorium costs 460 rubles. The trade union pays 70% of the cost of the trip. How much will a vacationer pay for a trip?
SOLUTION
808 Find the meaning of the expression.
SOLUTION
809 1) When processing a casting part weighing 40 kg, 3.2 kg was wasted. What percentage is the mass of the part from the casting? 2) When sorting grain from 1750 kg, 105 kg went to waste. What percentage of grain is left?
g) the age of the person and the size of his shoes;
h) the volume of the cube and the length of its edge;
i) the perimeter of the square and the length of its side;
j) a fraction and its denominator, if the numerator does not change;
k) a fraction and its numerator if the denominator does not change.
Solve problems 767-778 by composing.
767. A steel ball with a volume of 6 cm 3 has a mass of 46.8 g. What is the mass of a ball made of the same steel if its volume is 2.5 cm 3?
768. From 21 kg of cotton seed, 5.1 kg of oil was obtained. How much oil will be obtained from 7 kg of cottonseed?
769. For the construction of the stadium, 5 bulldozers cleared the site in 210 minutes. How long will it take 7 bulldozers to clear this site?
770. To transport the cargo, 24 vehicles with a lifting capacity of 7.5 tons were required. How many vehicles with a lifting capacity of 4.5 tons are needed to transport the same cargo?
771. To determine the germination of seeds, peas were sown. Of the 200 peas sown, 170 sprouted. What percentage of the peas sprouted (germination percentage)?
772. During the city greening Sunday, linden trees were planted on the street. 95% of all planted linden trees were accepted. How many linden trees were planted if 57 linden trees were planted?
773. There are 80 students in the ski section. Among them are 32 girls. Which section members are girls and which are boys?
774. According to the plan, the collective farm should sow 980 hectares with corn. But the plan was fulfilled by 115%. How many hectares of corn did the collective farm sow?
775. In 8 months, the worker completed 96% of the annual plan. What percentage of the annual plan will the worker complete in 12 months if he works with the same productivity?
776. In three days, 16.5% of all beets were harvested. How many days will it take to harvest 60.5% of all beets at the same productivity?
777. In iron ore, for every 7 parts of iron there are 3 parts of impurities. How many tons of impurities are in the ore that contains 73.5 tons of iron?
778. To prepare borscht, for every 100 g of meat you need to take 60 g of beets. How many beets should you take for 650 g of meat?
P 779. Calculate orally:

780. Present each of the following fractions as the sum of two fractions with numerator 1: ![]() .
.
781. From the numbers 3, 7, 9 and 21, form two correct proportions.
782. The middle terms of the proportion are 6 and 10. What can the extreme terms be? Give examples.
783. At what value of x is the proportion correct:
784. Find the relation:
a) 2 min to 10 s; c) 0.1 kg to 0.1 g; e) 3 dm 3 to 0.6 m 3.
b) 0.3 m 2 to 0.1 dm 2; d) 4 hours to 1 day;
1) 6,0008:2,6 + 4,23 0,4;
2) 2,91 1,2 + 12,6288:3,6.
D 795. 20 kg of apples yield 16 kg applesauce. ^^ How much applesauce will you get from 45 kg of apples?
796. Three painters can finish the job in 5 days. To speed up the work, two more painters were added. How long will it take them to finish the job, assuming that all painters will work with the same productivity?
797. For 2.5 kg of lamb they paid 4.75 rubles. How much lamb can you buy at the same price for 6.65 rubles?
798. Sugar beets contain 18.5% sugar. How much sugar is contained in 38.5 tons of sugar beets? Round your answer to tenths of a ton.
799. The new variety of sunflower seeds contain 49.5% oil. How many kilograms of these seeds must be taken so that they contain 29.7 kg of oil?
800. 80 kg of potatoes contain 14 kg of starch. Find the percentage of starch in such potatoes.
801. Flax seeds contain 47% oil. How much oil is contained in 80 kg of flax seeds?
802. Rice contains 75% starch, and barley 60%. How much barley do you need to take so that it contains the same amount of starch as is contained in 5 kg of rice?
803. Find the meaning of the expression:
a) 203.81:(141 -136.42) + 38.4:0.7 5;
b) 96:7.5 + 288.51:(80 - 76.74).
N.Ya.Vilenkin, A.S. Chesnokov, S.I. Shvartsburd, V.I. Zhokhov, Mathematics for grade 6, Textbook for high school