Drawing up and maintaining management accounting of the company. Implementation of a management accounting system
We continue to understand the “1C: Retail 2.1” configuration for the “1C: Enterprise 8” platform. In previous articles we have already dealt with, and now let's see how to add information about individual items of the item to the database. In order to do this, we need to go to the “Nomenclature” directory.
Right now our directory is still empty. New items can be added directly to the root of the directory, but for convenience it is better to create a separate group for each type of item. From the article on types of items, you already know that items can belong to one of three types: goods, services and gift certificates. As examples, we will work with product items, so we will create a group “Products”, and in it another group - “Buckets”.
In order to create a new item group, you need to press the icon with the image of a yellow folder or the key combination Ctrl+F9.

In the window that opens, write the name of the new group in the “Name” line. We do not indicate anything in the “Group” line.

Now a new group appeared in the directory. To create another group inside it, you need to double-click on it or select it, and then press Enter. Let's do this and create a "Buckets" group inside the "Products" group in exactly the same way.
Please note that the “Group” line is automatically filled with the name of the group that is in this moment we have it open. If we were to create a nested group without first opening the parent group, we would have to specify the name of the parent group manually or select it by clicking on the button with the ellipsis symbol.

You can also nest one group within another by simply dragging it with the mouse, but it’s more convenient to immediately create it where you need it.
Now, in exactly the same way, we will create the groups “Bolts” and “Concrete Mixers”, which will also be nested in the “Products” group. The result should be the following picture.

To create a new position, you need to go to the desired group and click the “Create” button in the “1C: Retail” interface or use the Insert key on the keyboard. In principle, it is not necessary to join a group, since the same rules apply here as for groups, but it is much more convenient.
There are many fields in the nomenclature card, but only those underlined with a red line are required to be filled out.
The first item we will add will be called “Enameled Bucket”. I would like to note that when entering a product name consisting of several words, you should put a noun at the beginning and always adhere to this rule, even if the name is written differently on the label. Otherwise, accounting errors may occur when the same product is entered into the directory twice under different names. For example, “Enameled bucket” and “Enameled bucket.”
When, after specifying the name, we move to another line, the “Print Name” field will be filled in automatically. This is done for the convenience of the user. If necessary, the printed version of the name can be changed manually.

Next, another pleasant surprise awaits us. As soon as we specify the type of item, the main part of the fields will be filled in automatically, in accordance with the settings specified for this type. As you can see in the next screenshot, the card is almost completely filled.
At this point, you can save and close the card, but I want to show you one more important feature. First, let’s save the new position without closing it by clicking on the icon with the image of a floppy disk, and then click on the “Characteristics” link in the navigation panel.

Here we will see that our new nomenclature already has a number of characteristics. They appeared because, when creating the “Buckets” item type in one of the previous lessons, we indicated that products with this item type would have General characteristics. Then we created these characteristics.

Now, in the same way, we will create another item of the nomenclature - “Bolt” and indicate the corresponding type for it. For the “Bolts” nomenclature type, the use of characteristics is also indicated, but if we go into the characteristics, we will see that there is nothing here yet. After all, for this type we have chosen individual characteristics, which means that for each position of this type they will need to be specified manually. This is done using the same “Create” or Insert buttons.
The characteristics can be as complex and detailed as you like, but for simplicity, we will distinguish bolts by thread diameter: 6, 8 and 10 mm.

If the use of characteristics is specified for an item in an item, then at least one characteristic must be filled in. Otherwise, such a product cannot be added to any document. In other words, the final object for selection in this case will not be a name, but a characteristic.
If the nomenclature does not have characteristics, the choice will be limited by the name.
Let's see what the product looks like without specifications. We still have one more type of nomenclature - “Concrete mixers”. But when creating it, we specified individual characteristics for it. Now you need to change these settings taking into account the fact that the characteristics will not be used. We have already looked at the editing procedure, so I won’t write about it here.
Let’s create the position “Concrete mixer B-1”. If we now open the window with its characteristics, we will see that the list is empty, and the buttons for creating, editing and deleting characteristics have become inactive.

The first step in setting up the 1C: Retail 2.2 program will be to create Organizations. To do this, go to point Regulatory Reference Information (RNI), in the navigation panel select Organization details.
In the window that opens, select Entity or Individual entrepreneur. After this, fill in the appropriate details: Name in the program, Abbreviated name, Full name, TIN and others. 
The next step is to create Types of prices. Go to the section Marketing, in the navigation panel select Types of prices and press the key Create.
We will need to create two types of prices: Purchasing And Retail.
First let's create Purchasing To do this, fill in the window that opens: Name, Method of setting the price and Data layout scheme. Purchasing the price will be filled in from the goods receipt document. 
After adding Purchase price need to be added Retail price, that is, the price at which we will sell. Fill in new price: Name, Use when selling, Method of setting price and Calculation rules. IN in this case, we will receive an automatic price calculation, that is, Product Receipt Price + 50% markup = Retail Price. In the future, you can change the price manually. 
The next step is to create Pricing Rules, come in Marketing Pricing Rules and press Create.
In the window that opens, fill in Name And Type of prices.
Program 1C: Retail requires creation to work Store who will release the goods. Let's go to Regulatory Reference Information (RNI), in the navigation panel select The shops and press Create. 
In the window that opens, fill in the basic details: Name, In the shop here you need to choose either to work with one warehouse or with several, Warehouse name, Sales organization this is the organization with which sales will be made, Pricing Rule, Type of minimum selling prices this is the same purchase price, it will be impossible to sell below this price, so as not to work at a loss, The procedure for rounding the check amount This item will allow you to round up the amount of the check, so as not to bother with pennies, if you think that you will already have equal prices and this is not required, then you are mistaken, because when you apply discounts, pennies will still appear in the item Rounding type choose Round the total This item will allow you to lose less money on rounding. After filling in all the details, click the button Save and close.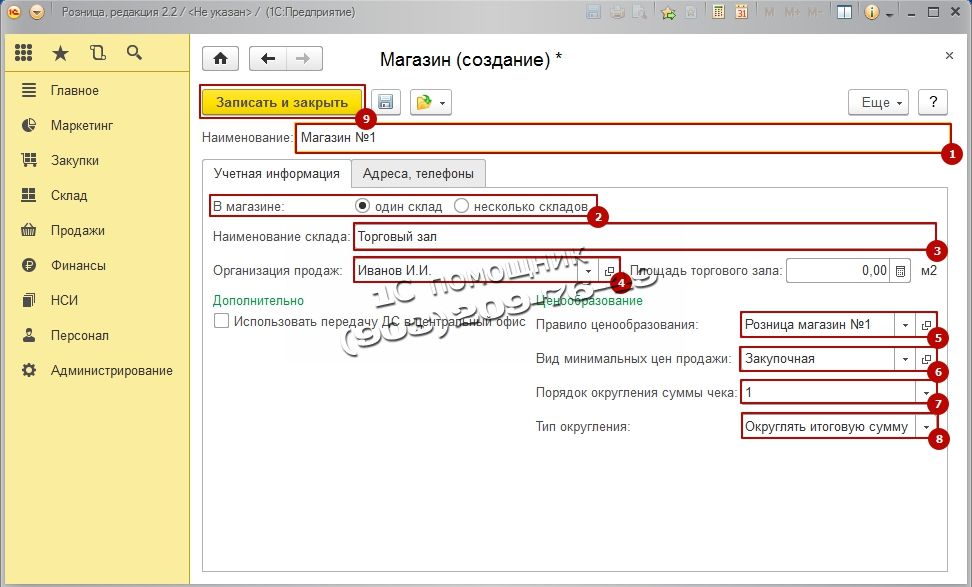
RMK (Cashier Workplace) cannot function without a Fiscal Registrar, so the next step is to add a fiscal registrar to the system. In our case we will add emulation of a fiscal registrar. Go to the section Administration, select in the navigation menu Connected equipment.
Next, check the box Use connected equipment and go to Connected equipment.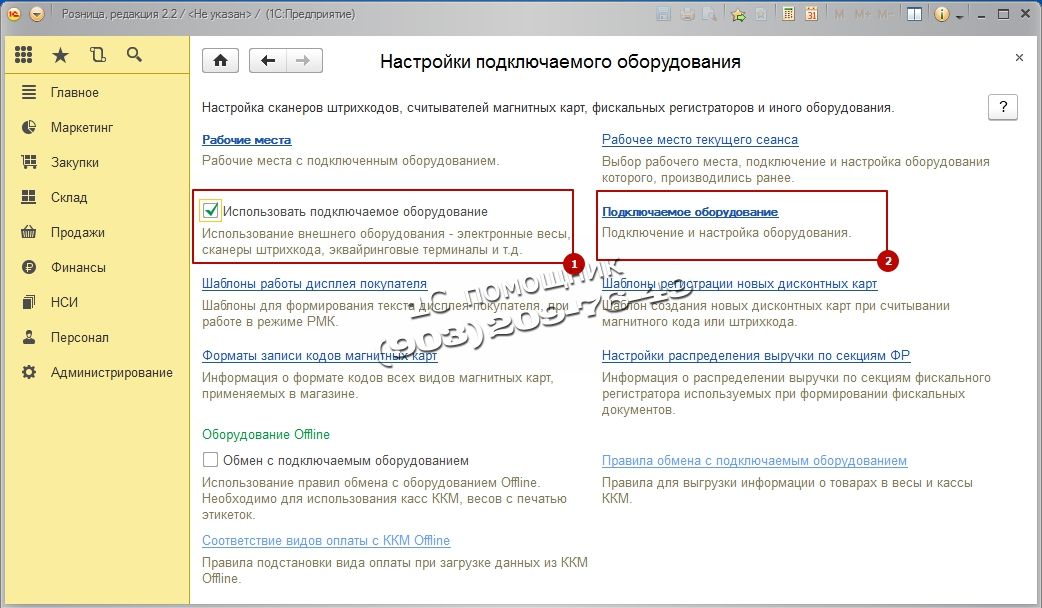
The equipment list is empty, add new equipment. Press the key Create.
Fill out the form that opens: Type of equipment select Fiscal registrars, Hardware Driver select 1C: Fiscal registrar (emulator), check the box Device in use, click on Record button an object and go to Tune…
If the device driver is not installed on the computer, click: Functions and choose Install the driver. If the driver is installed, then setting the check parameters will appear. They can be changed at your discretion or left as default. 
The next step is to configure KKM cash registers which will punch receipts in your Store. Go to the section Regulatory reference Information(NSI), KKM cash registers and press Create.
Fill in the main points. Cash register type, Store, Name, Workplace, Connected equipment The Fiscal Registrar that we created earlier should appear in the field. Then presses Record and close.
Now we need to add rights to our user to use all the functions of the RMK. This point is very important. Let's go to Administration, Users and rights and choose Additional user rights.  First, let's give the user all rights. Click on Button with green check mark and press Write it down. All necessary rights will be given to the user.
First, let's give the user all rights. Click on Button with green check mark and press Write it down. All necessary rights will be given to the user. 
Next, we need to receive the goods into the warehouse; for this we need to create a document Receipt of goods. We take the data to fill out from the supplier’s invoice. Let's go Procurement, select the item Receipts of goods.

A list of all documents will appear Receipts of goods previously created in order to create new document press Create.
We will not consider in detail how the Goods Receipts document is created; this can be found in the article
To sell goods, we must have installed Retail prices for goods. To do this, after creating and filling out the Goods Receipts document, select Create based on next we choose Setting item prices.
The document will open. This document forms the Purchase and Retail prices. The program itself calculates the price based on the formula we set earlier. Purchasing equal to the receipt price of 50 rubles, and Retail equal Purchasing +50% markup amounted to 75 rubles. You can change the calculated prices manually; to do this, you need to double-click in the price field and then enter your price. To save the document, click Swipe and close.
So we have made the basic settings of the RMK, now we go directly to the Cashier’s Workplace. To do this, go to the section Sales and choose RMK (controlled mode).
The RMK panel opens, initially we need to Open shift, click Opening Shift, and then press Sales registration.
In the window that opens, click the button Menu(F10) When you click on it, the bottom menu will appear, then press the button Search (F11) to select a product from the list. 
In the window that opens Search and selection of goods in RMK turn on the display additional information at prices and balances. To do this, click the button below Show Information.
In the next window, select two checkboxes Show: Remainings and Prices. The current stock balances and retail price will appear at the bottom of the selection. 
Select the product with two mouse clicks and close the product selection window. In the RMK window, enter quantity of goods sold press the button Cash (F6) to make a sale, enter the amount of money deposited, the program will calculate the change and press the button Enter.

Your sales receipt will appear at the bottom right. If you are not using an Emulator, but a real fiscal registrar, then your fiscal registrar will print a Receipt.
After you have worked a working day, you need to close the shift. To do this, exit the RMK by pressing the key Exit(F12). The RMK launch window will open. Now we need to close the cash register shift. Press the button Closing a shift.
The program will ask for confirmation of closing the shift. If you are ready to close the shift, click Yes.
If everything is in order and the sales amounts for the day coincide with sales, press the button Closing a shift.
The cash register is closed. The program will display an information window about the cash register shift. If you are using a real fiscal recorder (not an emulator), it will print you Z-REPORT. 
Product article - its definition, designation, which is a fixed, alphabetic or numeric value for classification certain type product: by manufacturer, color, composition and others distinctive characteristics. For example, a coat different colors will have a different article number, but differ only in color. Product SKU is a constant value and is assigned to the product upon receipt of it at the enterprise warehouse or retail outlet. Assignment occurs manually or using special programs for maintaining records of inventory items.
Programmatic entry of a product article into a common storage database, as a rule, occurs with the help of barcode reading devices. Write-off occurs in the same way. This process can often be observed in a grocery supermarket or a large industrial goods hypermarket.
What is the advantage of using a product SKU? It allows you to eliminate elementary misgrading of goods, correctly classify products and enter this data into the article table of this enterprise, and then implement quick search.
This is very convenient when the organization’s product range contains the same product from different suppliers. To search for a position, you need to find the product article in the catalog. Moreover, even a new employee who does not know the specifics of the product and its exact names can cope with such a simple operation.
The process of assigning an article number to goods begins with production, ending its technological chain at a temporary production warehouse, where the final article number of the product is formed. Each company develops its own articles. They can, of course, overlap with others trade organizations, but only if the same goods are traded and the European Article Number (ENA) is used. In it, the penultimate three digits are taken from the thirteen-digit code. This will be the product article, but basically it is assigned manually and each company has its own.
To a large extent, the article is needed for the correct circulation of goods within the organization, and not for maintaining. In the USSR, a common article system was used, approved by the Cabinet of Ministers and used by all trade and warehouse organizations. This made it possible to simplify trade relations in single state.
The printing house printed the article approved by the ministry in special catalogs that contained dozens of volumes printed edition. Every commodity expert in the country used these publications.
If accounting is kept within the enterprise, then the product article is assigned as desired as the warehouse is filled with item items, perhaps even in arithmetic order, special stickers are issued indicating the name, brief description and the article itself. If this is an external turnover of goods, then all this data is encoded into the barcode of the product, that is, into the same ENA.
If we have the 1C Enterprise Accounting program, in order to avoid duplicating products and entering identical positions, we should write the product article directly in the “Article” column, and not before the product name, as many do. What does this give? What this does is that when you write in the “Search by product name” column, exactly the position you are looking for is highlighted with the assigned article number in the adjacent line. Also, and vice versa, when you enter the article, the desired element and the desired product are found.
What happens when you write an article before? This is, of course, convenient, but only for those who know the articles by heart. Well, one person will not do this and have an impeccable memory. He may get sick, go on vacation, or get a promotion. A serial number written in front will block all system settings for searching by article, and searching by name will not bring results.
The system will not find “demi-season green coat” if it is written “1234 Green coat”, but will move this position to the top of the list. With this input error, a person will believe that such a position does not exist and will make a mistake by capitalizing and duplicating this product.
What is management accounting: definition and purpose + 10 differences management accounting from accounting + when it’s time to implement management accounting + how to implement it + how to automate management accounting + review of automation programs.
If you are reading an article about what is management accounting (MA), then most likely profitable, developing and expanding. We sincerely congratulate you on this achievement!
If not, apparently you work in such a company “at the helm”, which is also very good.
We made such simple conclusions because such accounting requires quite large organization, which has several departments, dynamic growth and funds for the implementation of management accounting.
Let's take a closer look at why and who needs a control system, what it “takes into account” and how to implement it in a company.
Definition, goals of management accounting and basic requirements for it
Details about what management accounting is
This is an enterprise accounting system that involves collecting information, presenting it and interpreting it in a special way.

The main feature of the management system is that it is configured and maintained in a way that is convenient for the company’s top managers. That is, there are no specific requirements for its implementation, but only recommendations on how to make it as effective as possible.
What is the purpose of management accounting?
Collect necessary and reliable information in as soon as possible and submit it in a form in which it is convenient to analyze it from the point of view of management, and after analysis, make the best and timely decision.
These decisions may concern:
- planning income and expenses both at the enterprise in general and in each of the divisions;
- distribution of funds;
- analysis of compliance between planning and actual results;
- analysis of the performance of departments and their individual products;
- control over the work of departments.
Basic requirements for information in a management report
- Brevity – only the main points.
- Credibility is much more important than accuracy.
- Efficiency - quick collection necessary information, mandatory readiness for the submission deadline.
- Comparability over time and across departments.
- Specificity – only the information requested.
- Detachment – dry facts without personal opinion and bias.
- Confidentiality – access to information exclusively for a strictly defined circle of persons.
The operation of the management accounting system has two main components:
- Process of collecting and transmitting information– appointment of responsible persons for collecting the necessary information, its grouping, evaluation and reporting; deadlines and ways of submitting reports.
- Reporting Process– methods for assessing and grouping information.
Before you take action, you need to carry out analysis and diagnostics.
First you need to understand what final result it should be clear what tasks management accounting should perform.
The next step is detailed studying the structure of the company and its work system.
You need to understand how reporting occurs at this stage, how information is collected from departments, what reports are executed and what questions they answer, what the hierarchy of reports looks like, what time frame they are prepared, how business processes occur in each department.
By collecting and evaluating the above information, you can understand what the “prototype” of accounting in the company currently looks like, how far it is from the desired result, and where its weaknesses are.
Compiled detailed plan it is necessary to document, appoint responsible persons for its implementation in each of the divisions, as well as the main person throughout the company. Next, calculate and allocate the necessary financial and labor resources, as well as premises and equipment.
When should management accounting be implemented?
It is believed that this system used in large and very large companies that this requires an urgent need, a certain status, financial and labor resources.
Some people mistakenly believe that this is just a fashionable feature.
In fact, it is better to implement a management accounting system early stages development of the company or when you feel that the existing system:
- does not provide answers to questions that arise or does not provide them in a timely manner;
- does not allow you to analyze the work of individual departments and their products;
- does not provide information about your company in terms of specific market realities;
- takes too long and labor resources.
In practice, it is worth thinking about management when you have several divisions (departments, points, etc.).
At first, this system will be quite simple, both in development and implementation, and in implementation. It can be supplemented, improved and customized.
This approach is certainly easier than designing and implementing it in a large and complexly structured company.
How to introduce management accounting into a company?
As mentioned earlier, the simpler an enterprise is organized, the easier it is to implement a management accounting system. But whatever the enterprise, there are a number mandatory conditions for a successful result.
Condition No. 1. Competent specialists
Usually, to organize the work of a control center, it is necessary to hire a separate employee, because this requires knowledge, experience and time.
At the same time, there is indeed a shortage good specialists, since in Russia only 10% of enterprises use management accounting.
It often happens that applicants for a position are more likely to be accounting specialists, so be careful when choosing a candidate. Some advise hiring university graduates in this specialty.
The services of third parties involved in setting up and maintaining control systems have become popular. Such freelancers and firms, of course, have enough experience. But the disadvantage of turning to a third party is that the system needs to be changed periodically, due to the growth of the company or changes in the internal structure.
Condition No. 2. Managers' participation
Since the system is being developed for efficient work top management, then its active participation is simply necessary at the development stage. Without a clear indication of accounting goals, all efforts may simply be pointless.
The participation of managers at the implementation stage is also important, since all involved employees, consciously or not, will resist innovations and additional responsibilities - this is the essence of a person.
It is important that immediate management, firstly, explains the need for such measures, and secondly, motivates employees to facilitate the process and strictly follow instructions.
Condition No. 3. Resources
Financial resources will be required to pay for specialists, for bonuses for employees taking part in its implementation, as well as for software.
Time resources should also be taken into account - setting up the process can take more than one month, on average it takes about six months.
How to automate management accounting?
Automation, no matter what it concerns, is very convenient.
It saves a lot of time and labor resources, reduces the impact human factor and attachment to specific employees. However, its cost is quite high.
It is worth thinking about automating management accounting and purchasing the appropriate software, if the company's staff exceeds 500 people.
In smaller companies, the “manual” management system is quite effective, and it is also easy to create your own program, for example, in Excel for accounting.
It is also important to say that automating unsystematic record keeping will not yield positive results. If your enterprise is in chaos, you first need to restore order and structure all accounting processes.
The choice of automated systems is quite large, both ours and foreign.
When choosing one of the automated systems, it is important to consider:
- The amount of information used at the moment and in the future, as more and more data grows every year.
Specifics of the company's field of activity.
It is advisable that the program be successfully implemented in an enterprise of the same type as yours, this will prevent it from being “cut down” for you.
Automation of management accounting does not pay for itself quickly due to its high cost, but the company’s profit after its implementation can increase by 30%.
This is the market average.
There are also different approaches to automation. Automating everything at once is far from the best solution.
In this regard, certain strategies are used:
Restructuring of financial statements.
This is a relatively simple path if the enterprise does not have gray accounting, all operations are reflected, and the structure of the business corresponds to the legal structure.
General database.
The most logical, convenient, but at the same time complex and expensive process.
The common database produces reports for management, accounting and operational accounting.
Two databases in one.
Based accounting generated separately by management, thanks to the transformation of accounting entries.
This option may be suitable for small businesses.
Introduction of an additional program.
It is understood that the existing accounting at the company remains unchanged, and another program is used for management.
In this case, it is necessary to configure data transfer between programs. This approach increases data security.
All management accounting automation programs are divided into:
- integrated;
- autonomous.
1) How to choose an automation program?
First you need to determine all the software requirements.
Then start analyzing the proposals. Make a list of all available proposals for control automation.
After that, correlate it with the following parameters:
- compliance with the requirements;
- price;
- developer reliability;
- support and administration.
Leave a few of the most suitable options from the entire list.
Arrange a presentation for all employees interested and participating in the automation process.
Contact users of the software in question, find out from them possible nuances in the operation of the program and its effectiveness.
2) Review of programs for automation of management accounting
There are a lot of offers on the market, and they are all designed for different requirements consumers.
It may not be easy to choose the option that is right for your company, but in any case, you need to make every effort, because the success of the business depends on the correct choice.
If you divide the software according to the approach to automation, you can create next list sentences (which of course is not complete):
- Introduction of an additional program– Excel, Sage, variations of 1C-Enterprise, Info-Accountant.
Accounting restructuring– Audit Expert program from Russian developers.
Its price ranges from 3 hundred to 1 thousand dollars.
Shared Database— Oracle App, SAP/R3, Baan (foreign and very expensive programs), Exact, Hansa, Scala (also foreign, but simpler), BOSS-Corporation, Galaxy, Parus, Magnat, Alpha, Etalon, Inotek (domestic).
The price of foreign developments is naturally higher - from $10,000, while our software costs several times less.
Two databases in one— BEST, variations of 1C Enterprise.
Their price is 1000 - 3000 dollars.
Differences between management accounting and accounting
- Accounting (AC) is provided to regulatory authorities, partners, and management only to company managers.
- Management management is structured in a way that is convenient for management, while accounting is formed according to strictly prescribed rules and is regulated by law.
- Often, an enterprise maintains double-entry bookkeeping, but there is only one scheme for management.
- In accounting, all parameters are measured in monetary or natural units, while in management accounting, any units of measurement are used.
- In accounting, costs are formed by item, in management accounting - by “cost tree”.
- In management accounting, the objects of accounting are divisions, in accounting - the enterprise as a whole.
- In BU it is necessary to adhere to the absolute accuracy of calculations; in CU approximate values are possible.
- Accounting is required to be carried out in any company, while management accounting is required or required.
- The BU has a clear reporting schedule; in the OU it can be carried out as needed.
- The management system allows you to use information about market conditions and competition.
What is management accounting?
How does it differ from other types of accounting? More details in this video:
In the article we provided answers to the questions: what is management accounting, why and who needs it, and also tried not to ignore the basic principles of its implementation in the enterprise and automation.
In conclusion of this topic, I would like to advise you, as a manager, to invest in the training and development of your own employees.
This will help save time and money when resolving issues related to management accounting, and especially its automation.
Useful article? Don't miss new ones!
Enter your email and receive new articles by email













