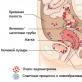
Types of aquifers and determination of the level of groundwater. Why groundwater is dangerous and how to deal with it
It is underground water resources, which lie at a shallow depth of the first water-resistant layer. Their resource is characterized by a large area and stable volumes of water. They always lie on weak or impermeable rock, which does not allow groundwater infiltration into lower layers. Groundwater belongs to the groundwater family and includes two main types: capillary water and upper water.
Exact definitions can only be given by hydrogeologists after an examination of a specific site. It is easiest to confuse groundwater with a performer. It differs in shallower depth and water surface area. Its bottom lies on random accumulations of water-resistant rocks (clay, etc.).
The image shows general scheme aquifers, only hydrological expertise can give an accurate picture
The groundwater layer is necessarily limited to the bottom, but usually does not have a roof. The rocks are porous, filled with water without pressure. Due to the water-permeable top layer groundwater very sensitive to precipitation, melting snow or just accidental water release. Depending on their quantity, the volume of groundwater constantly fluctuates, decreasing in drought and recovering in rainy seasons. In addition to volume, the chemical composition changes and average temperature... If groundwater occurs in close proximity to natural water bodies, then their level and composition is closely tied to dynamics surface waters... In relation to them, the exact proportionality is clearly observed - the amount of water supplied is equal to the amount of runoff water.
In conditions of large volumes of feeding infiltration, prolonged contact of groundwater with mineral rocks leads to the fact that all readily soluble salts are washed out, and the water itself becomes conditionally fresh. If groundwater is deposited in arid areas, the opposite process is observed: the mass of water does not drain, but evaporates, while the residues will gradually become saline.
Groundwater occurs in the vicinity of water bodies, shallow underground cracks and karst formations and rock fans. The composition of groundwater depends on the climate and flora terrain
The groundwater level affects its recharge and discharge. On the plains, they retain a static position, but if they find an outlet below the line of the surrounding relief, they form small springs, which are called springs. They are very important for the nutrition of natural bodies of water.
Groundwater can be unpredictable, especially if it occurs close to the surface
Use of groundwater for drinking and household
The main recharge of groundwater is precipitation... While the moisture drains down to the level of the groundwater, it is partially cleared of impurities. If the area is ecologically clean, there are no spills of harmful substances and are not used for farming chemical substances, then it can be considered conditionally suitable for drinking and watering plants.
The groundwater well will be subject to seasonal declines and rises. To make sure it's safe drinking water from a shallow horizon, you need to hand it over for analysis in a laboratory. If the composition of the water is normal, it can be eaten, but it is advisable to undergo additional filtration and boil disinfection.
It is forbidden to place garbage pits, cattle yards, sewers, and other sanitary facilities near an earth well. Water, passing through them, dissolves everything that is possible, and then the whole bouquet of microbes and chemicals will fall into the well and onto the table of the owners.
Low level the occurrence of groundwater and the absence of an upper watertight "floor" greatly facilitates pollution by rainfall or waste water... For eating, they are used as a last resort, but for other household needs they are quite suitable. Therefore, sometimes there are several water-bearing objects in the yard: an artesian well for drinking and a shallow well for irrigation, etc.
Only those groundwaters that are deeply buried and come to the surface in the form of springs are completely safe for drinking. There should be no motorways, production facilities and other polluting objects in the vicinity.
Negative effect of groundwater
Groundwater occurs at a depth of 2 to 20 meters. The smaller the distance from the surface of the soil to the water, the more trouble they cause to the owners of the sites. Situations are frequent when plants do not grow in the country, the root system of which goes into the ground for more than half a meter. Even ornamental plants dry and rot.
Groundwater is a great solution for irrigation
Drainage systems are used to drain the groundwater, and the soil level is raised by bringing in and filling additional soil.
The problems of gardeners and gardeners will seem like solvable little things if we compare the harm that groundwater can bring to residential and outbuildings, a drinking well or a well with good water. When building wells, they prefer to bypass the level of open groundwater, and reach deeper and protected aquifers (usually it is enough to get to the second water carrier). They lie between two water-resistant layers of rock, the first protects from the ingress of groundwater and upper water, and the second serves as the bottom.
The continuous structure of the well shaft is protected from the ingress of contaminated and runoff water. This is an ideal situation where the owners take good care of the well, regularly updating the waterproofing and the clay lock around the well. As you know, water wears away the stone, and the seams between the rings, even more so. They are weakened not only by groundwater, but also by quicksands, deep freezing of the soil, roots of nearby trees, and cracks appear in the mine.
Wells, the shafts of which are welded from plastic pipes... They are specially strengthened and reinforced to long time withstand loads and not crack.
V middle lane In Russia, the groundwater level (GWL) lies very close to the surface - 2-3 meters. This indicator is found even in large cities. This water must not be drunk! It is collected from showers and other drains and dissolves a lot of harmful substances and chemicals
How to understand that a well is flooded with a primer
If a well is built on a site using the traditional method of reinforced concrete rings or masonry, the risk of ingress of groundwater or storm water is very high.
During periods of heavy rains, floods or snowmelt, deep streams begin to drain into the well through the broken waterproofing dirty water... This process can be seen by the sharply increased water level and wet trickles on the walls of the mine. During such periods, experts from sanitary and epidemiological stations recommend switching to bottled water.
To understand through which area the water has leaked, you will need to pump out water to normal level and wait until the walls are dry. Leaky seams will remain moist, and if the pressure of the groundwater is strong, then water will spout through the cracks.
How to protect a well from groundwater
During the season of active feeding of groundwater due to rainfall or snow, tasty water from a well can turn into poison due to the ingress of groundwater or storm drains. Elimination of the consequences of flooding includes several procedures: cleaning, revision and thorough sealing of seams, disinfection of the well to destroy pathogens. Here the rule is true that prevention is cheaper and faster than elimination of consequences.
Of course, drains and outdoor toilets should be located away from the source of drinking water.
To prevent this from happening, you need to regularly conduct a preventive inspection of the integrity of the rings themselves and the waterproofing joints between them, and update them when damage is detected. You cannot use silicone sealant for sealing, after a short time it peels off. To protect against surface water, a high-quality clay castle around the well shaft is sufficient. It is laid to a depth of 70 cm to 2 meters and compacted in layers.
The company's specialists professionally eliminate the consequences and causes of wells flooding, and restore waterproofing so that this does not happen again.
Ground water is called the one that is located at a depth of 25 meters from the surface of the earth. It is formed due to various reservoirs and precipitation in the form of rain and snow. They seep into the ground and accumulate there. Groundwater differs from underground water in that it has no pressure. In addition, their difference is that groundwater is sensitive to changes in the atmosphere. The depth at which groundwater can be does not exceed 25 meters.
Ground water level
Groundwater is located in close proximity to the surface of the earth, however, its level can vary depending on the terrain and the season. It will rise in high humidity, especially when walking heavy rains and the snow melts. And also the level is influenced by nearby rivers, lakes, and other bodies of water. During dry periods, the groundwater level decreases. At this time, he is considered the lowest.
The groundwater level is divided into two types:
- low when the level does not reach 2 meters. Buildings can be built on such terrain;
- high - level over 2 meters.
If you make incorrect calculations of the depth of groundwater, then this threatens: flooding of the building, destruction of the foundation and other problems.
Groundwater occurrence
To find out exactly where the groundwater lies, you can first make simple observations. When the depth is shallow, the following signs will be visible:
- the appearance of fog in the morning, on certain plots of land;
- a cloud of midges "hovering" above the ground in the evening;
- a site where moisture-loving plants grow well.
And you can also apply another folk way... Put some kind of desiccant material (such as salt or sugar) into a clay pot. Then weigh it carefully. Wrap it in a piece of cloth and bury it in the ground to a depth of 50 centimeters. After a day - open, and weigh again. Depending on the difference in weight, it will be possible to know how close the water is to the surface of the earth.
You can also find out about the presence of groundwater from the hydrogeological map of the area. But the most effective method Is exploratory drilling. The most commonly used columnar method.
Specifications
When groundwater comes naturally, then it is drinkable. The contamination of the liquid is influenced by villages and cities located near, as well as the proximity of water to the surface of the earth.
Ground waters are divided into types that differ in their mineralization, so they are as follows:
- insipid;
- slightly saline;
- brackish;
- salty;
- brines.
The hardness of ground water is also distinguished:
- general. It is divided into five types: very soft water, soft ground water, moderately hard water, hard water, very hard ground water;
- carbonate;
- non-carbonate.
In addition, there is groundwater, which contains a lot of harmful substances. Such water is usually found near landfills, with dumps of chemical or radioactive waste.
Disadvantages of groundwater
Groundwater also has its drawbacks, for example:
- various microorganisms (and pathogenic ones too) in the composition of water;
- rigidity. This affects the decrease in the lumen of the pipes through which water is supplied, since specific deposits are deposited on them;
- turbidity, due to the fact that there are certain particles in the water;
- impurities in groundwater of various substances, microorganisms, salts and gases. All of them are able to change not only the color, but also the taste of water, its smell;
- large percentage mineral substances... It changes the taste of the water, so a metallic taste appears;
- seepage into groundwater of nitrates, ammonia. They are very dangerous to human health.
In order for the water to become much better quality, it must be carefully processed. This will help rid it of various contaminants.
Ground water groundwater of the first permanent aquifer from the Earth's surface. Formed mainly by infiltration (seepage) atmospheric precipitation and waters of rivers, lakes, reservoirs, irrigation canals; in some places G.'s reserves. are replenished by the rising waters of deeper horizons (for example, waters artesian basins), as well as due to condensation of water vapor. Top G. century. usually they are not overlapped by impermeable rocks, and they do not fill the permeable layer to their full capacity; therefore, the surface of the G.'s. is free, non-pressure. In some areas, where there is still a local waterproof overlap, G. century. acquire a local pressure (the value of the latter is determined by the position of the G.'s level of century in adjacent areas that do not have a waterproof overlap). When a borehole or a dug well reaches the geological point, their level (the so-called mirror of the geological point) is set at the depth where they were encountered. Areas of nutrition and distribution of G. of century. match. As a result of this, the conditions for the formation and regime of G. of century. possess characteristic features distinguishing them from deeper artesian waters: G. century. sensitive to all atmospheric changes... Depending on the amount of atmospheric precipitation, the surface of the G. of the century. undergoes seasonal fluctuations: in the dry season it decreases, in the wet season it rises, and the flow rate, chemical composition, and temperature of the gas flow also change. Near rivers and reservoirs, changes in level, discharge and chemical composition G. in. are determined by the nature of their hydraulic connection with surface waters and the regime of the latter. The value of the drainage of the gas. over a long-term period is approximately equal to the amount of water received by infiltration. In conditions humid climate intensive processes of infiltration and underground runoff develop, accompanied by soil leaching and rocks... In this case, readily soluble salts - chlorides and sulfates - are removed from rocks and soils; As a result of long-term water exchange, fresh water is formed, mineralized only at the expense of relatively little soluble salts (mainly calcium bicarbonates). Under conditions of an arid warm climate (in dry steppes, semi-deserts, and deserts), owing to the short duration of precipitation and the small amount of atmospheric precipitation, as well as to the poor drainage of the area, the underground runoff of the city of water. does not develop; in the expenditure part of the balance sheet of G. of century. evaporation prevails and salinization occurs. Differences in the conditions for the formation of G. of century. determine the zoning of their geographical distribution, which is closely related to the zoning of the climate, soil and vegetation cover. In forest, forest-steppe, and steppe regions, fresh (or low-mineralized) G. of century is widespread; within dry steppes, semi-deserts, and deserts on the plains, salty geological plants predominate, among which fresh water found only in some areas. The most significant reserves of G. in. are concentrated in alluvial deposits of river valleys, in fan cones of foothill areas, as well as in shallow massifs of fractured and karst limestones (less often in fractured igneous rocks). G. in. due to their relatively easy accessibility, they have great importance for National economy as sources of water supply industrial enterprises, cities, towns, rural settlements, etc. Lit .: Savarensky F.P., Hydrogeology, M., 1935; Lange O.K., Hydrogeology, M., 1969. P.P. Clement.
Great Soviet Encyclopedia. - M .: Soviet encyclopedia. 1969-1978 .
See what "Groundwater" is in other dictionaries:
Waters below the surface of the earth and circulating in rock strata. G. in. ch. arr. from the absorption of rain and melt water into the ground, and in some cases from the absorption of water brought by rivers or artificial canals. Under… … Technical Railway Dictionary
GROUND WATER, waters below the surface of the earth. Their source is mainly rain, although there are also waters of volcanic or sedimentary origin. They seep through porous sedimentary rocks and soils, accumulate in wells. ... ... Scientific and technical encyclopedic Dictionary
- (a. ground waters; n. Grundwasser; f. eaux de fond, eaux souterraines, eaux de terres; and. aguas subterraneas, aguas freaticas) gravitats. groundwater of the first permanent aquifer from the Earth's surface. Ch. arr. per … Geological encyclopedia
Subsoil waters, gravitational free-flowing waters of the first permanent aquifer from the earth's surface, which has a free surface, the pressure on which is equal to atmospheric. The groundwater is inhabited by a specific ... ... Ecological Dictionary
GROUND WATER- waters located on the waterproof soil layer closest to the surface. G. in. have a free surface, that is, do not have watertight rocks on top, water nutrition get from precipitation. In the depressions of the relief, there are ... ... Pond fish farming
Groundwater of the first permanent aquifer from the Earth's surface, which does not have a continuous roof of impermeable rocks on top; do not have pressure and are subject to seasonal fluctuations in level and flow rate ... Big Encyclopedic Dictionary
Groundwater lying on the first aquiclude from the earth's surface and representing a constant in time and significant in the area of distribution of the aquifer ... Geological terms
groundwater- The water below the earth's surface in the thickness of rocks and in the soil in any physical state. Syn .: groundwater ... Geography Dictionary
GROUND WATER- waters freely located on top of impermeable rocks (clay, marl, other non-fractured rocks), forming an aquifer and not having a continuous roof of impermeable rocks on top. Usually this is the name of the underground water of the first from ... ... Big Polytechnic Encyclopedia
Groundwater is water located in the rock mass of the upper part of the earth's crust in liquid, solid and gaseous state... Fizzle underground source of water supply Contents 1 Classification 2 ... Wikipedia
groundwater- 3.9 groundwater: Groundwater of the first aquifer from the surface, located above the first waterproof layer from the surface of the earth. A source … Dictionary-reference book of terms of normative and technical documentation
Books
- Soil and artesian wells, A.A. Krasnopolsky. St. Petersburg, 1912. P. P. Soikin's printing house. Illustrated edition. Typographic cover. The preservation is good. The purpose of this publication is to provide a summary of the theory of soil and ...
Most houses have a centralized water supply. But due to the remoteness from settlement or for other reasons in some country cottages, at the dachas it is not. The owners have to drill a well or equip a well.
To determine the horizon of the source, you have to resort to the help of a professional. His services will not come cheap. The depth of the groundwater table can be set independently. At the same time, it will be possible to significantly save money. family budget for the arrangement of the water supply system. For this, several simple approaches are used. Before starting work, you must consider the entire procedure in detail.
Groundwater type
The depth of the groundwater level is different. The type of source depends on this indicator. It is taken into account when conducting a water supply system. The layer closest to the surface is called the top water. It is located at a depth of 2-3 m. Such a source is applicable only for technical purposes.
This is followed by a free surface. There are also interstratal gravity and pressure artesian sources. The last variety is considered the cleanest, most drinkable. The chemical composition and quality are the highest among all sources. The water layer can pass in sandy, or in gravel.
Features of groundwater
Before determining the depth of groundwater, you need to learn about their features. First of all, their location is influenced by the type of terrain. In the steppe, where the surface is flat, the layers run evenly. At any point, their depth is the same.
But in the presence of bumps, slides, the water is also curved. Experts recommend taking into account such relief features when creating a well. If you need water for technical purposes, you can use the first layer. He comes closer than others to the surface.
For drinking purposes, it is necessary to use water from at least the second layer. If the terrain is hilly, it is better to drill a well on a hill. In this case, the soil layer filters out such water better.
In swampy areas, groundwater can approach the surface at a depth of only 1 m. When developing a well, you need to be prepared for this.
Ground waters of the Moscow region
Before the owners own home should inquire about the characteristics of the layers of underground sources. For example, the depth of groundwater in the Moscow region is characterized by heterogeneity.
There are 5 main layers here. They are all unequally located and have different powers. The first three layers are characterized by a low head. They are used for technical purposes. Water discharge takes place in small streams and rivers. This groundwater is replenished in the spring when the snow begins to melt.
Dolomite and limestone rocks have two lower layers. The depth of their occurrence is about 100 m. It is these springs that are suitable for drinking purposes. In the Moscow region, the central water supply is laid precisely from these sources.
Preparation for measurement
Moisture conditions and groundwater depth are closely related. When planning to take measurements, it is necessary to choose the right time. At the same time, there should be no drought or prolonged rains. Everything weather affect the measurement result.
To determine the depth of finding groundwater, you must use one of the simple methods. To do this, you need to prepare all the tools and materials at hand. Of the tools, you will need an ordinary drill, a tape measure. You also need to prepare a long rope.
In addition to tools, certain chemical elements... This is sulfur and copper sulfate. For different techniques, you will need one or another improvised means.
Drilling
Determination of the groundwater depth is possible using several methods. The most reliable of these is drilling. At the same time, it is possible to accurately determine what depth the underground source is, whether there are significant obstacles in the form of stones on the way to it.
For work will do an ordinary factory drill. If desired, additional blades are welded onto its blades. The tool cuts into soft ground. It is taken out together with the earth to the surface. To soften the soil, it is watered with water.
Using a threaded, sleeve connection, the drill is fastened to the pipes in order to go deeper to the desired level. Further, measurements are taken with the help of a rope. The well should be 0.5-1 m deeper than the paper is attached to the rope and it is checked at what level it gets wet.
Application of chemicals
If you don't want to drill a well, there is an easier way to find out the depth of groundwater. To do this, dig a hole with a shovel in the intended place. It can be about 0.5 m deep. An earthen pot is required to be installed in it.
In a vessel, quicklime, sulfur and copper sulfate are mixed in equal proportions. Next, the hole is buried and left for a day. After that, the pot is taken to the surface and weighed. The heavier it has become, the closer the groundwater comes to the surface. This method is not accurate enough, but it has been used since ancient times. Only now it has been improved.
Barometer
Another reliable way to determine the depth of groundwater in a given area is to use a barometer. However, it should be noted that its application requires the presence of a reservoir in the district.
If there is one, you can start measuring. Each barometer mark corresponds to 1 m depth. First, with the device, you need to go to the reservoir. Here, the barometer readings are recorded.
This method is also not very accurate. The error distorts the real picture. But general principle you can understand.
Folk way
The depth of the groundwater table can be determined folk methods... First of all, you need to pay attention to the vegetation. Where the source is close to the surface, it is greener, brighter. In such places, reeds, ivy, forget-me-not and other moisture-loving representatives of the flora love to grow.
The popular approach assumes the following. It is necessary to wash and dry the wool in a soapy solution. Vegetation is removed at the proposed site for the experiment.
Wool is laid on the ground. They lay on it a raw egg and cover everything with a frying pan. In the morning, evaluate the result of the experiment. If the egg and wool bedding are covered with dew drops, the water is close to the surface. But this procedure should be carried out in dry weather.
Having considered how the depth of the groundwater is determined, you can make measurements yourself. Depending on the method chosen, you can get a more accurate or approximate result. All the work can be done by yourself. At the same time, it will be possible to significantly save family budget funds.
Lecture number 7
Groundwater is formed by the percolation of water falling out in the form of precipitation (infiltration), sometimes groundwater is formed from water contained in magma (juvenile), sedimentary, groundwater captured from the surface by formed rocks and revived (formed during the metamorphism of minerals and rocks. Groundwater is classified according to the hydraulic characteristics - gravity and pressure, and according to the conditions of occurrence - upper water, groundwater and interstratal.
Verkhovodka is called temporary accumulations of water in the most upper layers of the earth's crust over local aquicludes or semi-aquicludes (lenses of clays and loams in the sand, interlayers of denser rocks). During the period of snow melting and heavy rains during infiltration, water is temporarily retained and forms an aquifer. Verkhovodka is a significant danger for urban areas. Lying within the underground parts of buildings and structures (basements, boiler rooms, etc.), it can cause flooding. V recent times As a result of significant leaks of water (water supply), the emergence of upstream horizons in the territories of industrial facilities and residential areas was noted.
Groundwater is called groundwater that occurs on the first aquiclude from the surface. Groundwater has a free surface called a mirror. Groundwater is fed by atmospheric precipitation and water inflow from surface water bodies and rivers. Ground water is open for the penetration of surface water into it, which leads to a change in its composition and pollution with harmful impurities. Groundwater is in motion and forms streams, which often leads to suffusion.
Interstratal waters are groundwaters occurring between two aquicludes. According to the conditions of occurrence, these waters can be free-flow and pressure-bearing, that is, artesian.
Over time, changes occur in the position of the level and nature of the surface of groundwater, their temperature and chemical composition. The combination of these changes is called the groundwater regime. Its study is the most important task, since the quantitative and qualitative changes in groundwater significantly affect the conditions for the construction and operation of structures and should affect the design. The reasons for fluctuations in the level of groundwater are:
1 meteorological factors(precipitation);
2 hydrological conditions (influence of rivers and reservoirs);
3 vibration of the earth's crust;
4 human construction activities (leaks from water supply and sewerage systems, reduction of water evaporation due to buildings, various pumping out of wells and boreholes).
To monitor the level of groundwater, boreholes are used, made in the required places singly or located in a certain order.
In each well, the depth of the appearance of water relative to the earth's surface is determined, which is then recalculated at an absolute elevation. To determine the depth of the level, use:
1 measuring rod (at shallow depths);
2 measuring ropes, at the ends of which floats, crackers, whistles are suspended);
3 level meters with electrical circuits;
4 float meters.