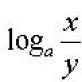Mainland Australia large rivers lakes. Rivers of Australia, lakes of Australia, Great Artesian Basin
Large rivers and lakes of Australia
Largest rivers: Murray - Darling
This system is Australia's main river and lake system. The Murray is the most famous, but there is more than one river. Murray and Darling two different rivers: Darling tributary of the Murray.
Other famous rivers Australia:
The Flinders River (the longest in Queensland), the Diamantina River and Cooper Creek, which run through western Queensland, eventually emptying into Lake Eyre.
The Lachlan River, which flows into the Murrumbidgee River, which in turn flows into the Murray. Lachlan is essentially one of the main irrigation systems in the state of New South Wales.
The Culgoa, Balonne, Warrego and Condamine rivers feed the Darling River.
The Gascoyne River is the longest in Western Australia.
Goulburn River (Victoria)
The Hunter River, which frequently floods in New South Wales, as well as the Clarence and Richmond.
The Dumaresque, McIntyre and Tweed rivers form part of the border between Queensland and New South Wales.
The Burdekin River, forms the main dams in northern Queensland.
Each of Australia's cities and capital is built on a river:
Sydney - Hawkesbury and Parramatta Rivers
Melbourne - Yarra
Adelaide - Torrens
Brisbane - Brisbane
Perth - Swan (Swan)
Hobart - Derwent
Capital of the Commonwealth of Australia, Canberra, on the Molonglo River
Lakes of Australia
There are 800 lakes in Australia. The basins of most of them were formed in early geological eras and are relics. Many of the lakes (Amadies, Frome, Torrens) are filled only during periods of heavy rainfall, which occur every few years. In normal times they are dry basins.
Lakes of the Australian Capital Territory
Burley Griffin
An artificial lake in the center of Canberra, the capital of Australia. The structure was completed in 1964 after the Molonglo River was dammed between the city center and the Parliamentary Triangle. The site is located in the approximate geographic center of the city, and, in accordance with Griffin's original design, was the central point of the capital. The buildings of many central institutions were built on its banks, such as National Gallery Australia, National Museum Australia, National Library of Australia, Australian National University and the High Court of Australia, with the Australian Parliament House located nearby.
Lakes of Western Australia
Disappointment
Salt Lake in Western Australia. It dries out during the dry months. Yours modern name The lake received its name in 1897 and was named so by traveler Frank Hann, who made a significant contribution to the study of the Pilbara region. Spotting in the study area a large number of streams, he hoped to find a large freshwater lake.
Mackay
One of hundreds of dry lakes scattered across Western Australia and the Northern Territory. Lake Mackay covers approximately 100 kilometers from north to south and west to east.
Hiller
A lake in southwest Australia, notable for its pink. The lake is surrounded by sand and eucalyptus forest. The island and lake were discovered during the expedition of British navigator Matthew Flinders in 1802. Captain Flinders is said to have spotted the lake while climbing to the top of the island. For tourists, Lake Hillier is not the most convenient place. Due to the lack of water navigation in this area, the most convenient way to get there is by air, which is unaffordable for most people who want to see the unusual body of water.
Lakes of Queensland
Blue Lake
Lake in Queensland. Located 44 km east of Brisbane on North Stradbroke Island. Located 9 km west of Dunwich. The lake is located in the Blue Lakes National Park. Maximum depth lakes - about 10 m. Rivers from the lake flow into the Mail swamp.
Ichem
A volcanic lake in the Australian state of Queensland, occupies one of the maars of the Atherton Plateau. Ichem is a former stratovolcano. Severely destroyed by powerful explosion 18,750 years ago. The last eruption dates back to 1292.
Kutaraba
A lake in the Sunshine Coast, Queensland, within the Great Sandy National Park.
Lakes of the Northern Territory
Amadius
A drying, endorheic salt lake in central Australia. Located approximately 350 km southwest of Alice Springs. Area - about 880 km². Due to the arid climate, Amadius is a completely dry lake for most of the year.
Anbangbang-Billabong
Billabong Lake in northern Australia, located between Nawurlandja Rock and Nourlangie Rock in Kakadu National Park, Northern Territory. The lake is about 2.5 km long and is home to many species of birds. In the morning, marsupial wallabies can be seen on the banks.
Lakes of Tasmania
Barbary
An artificial lake located in the western part of the island of Tasmania, slightly east of the city of Queenstown. It was formed as a result of the construction of the Crotty Dam, which blocked the King River. The area of the lake is 49 square kilometers. Thus, it is the sixth largest in area among natural and artificial reservoirs in Tasmania.
Great Lake
A lake located in the northern part of the Central Highlands of the island of Tasmania. It is a natural lake that was significantly enlarged by the construction of a dam. The area of the lake is 170 square kilometers. Thus, it is the third largest natural and artificial reservoir in Tasmania.
Dove
A lake located in the north of the Central Highlands of the island of Tasmania. The lake is located at an altitude of 934 m. The area of the lake is 0.86 km². Dove Lake is located in the northern part of Cradle Mountain-Lake St Clair National Park. This park is part of an area called " wild nature Tasmanian Wilderness, which is the subject World Heritage UNESCO.
Pedder
A lake located in the southwestern part of the island of Tasmania. Initially, on this site there was a lake of natural origin with the same name - the “old” Lake Pedder. In 1972, the installation of several dams flooded a much larger area, effectively turning the lake into a reservoir - the "new" Lake Pedder.
St. Clair
A lake located in the Central Highlands of Tasmania. The maximum depth of the lake is 200 m; thus, it is the deepest lake in Australia. The area of the lake is 30 square kilometers, the height of the water surface is 737 m above sea level. Lake St. Clair is located in the southern portion of Cradle Mountain-Lake St. Clair National Park.
Lakes of South Australia
Alexandrina
A lake in South Australia adjacent to the coast of the Great Australian Bight, which is part of Indian Ocean.
Bonnie
Coastal Lake in the south-eastern part of South Australia. This is one of the largest freshwater lakes in Australia. The lake is 450 km from Adelaide and 13 km southwest of Millicent. Kanunda National Park is located next to the lake shore. For over 60 years, large volumes Wastewater from neighboring pulp and paper mills had a negative impact on the condition of the lake.
Gairdner
A large endorheic lake in central South Australia, it is considered the fourth largest salt lake in Australia when flooded. The lake covers more than 160 kilometers in length and 48 kilometers in width with salt deposits reaching up to 1.2 meters thick in some places. It is located west of Lake Torrens, 150 km north-west of Port Augusta and 440 km north-west of Adelaide.
Torrance
The second largest saline endorheic rift lake in Australia, in the state of South Australia, located 345 km north of Adelaide. The indicated area of the lake is very arbitrary, since over the past 150 years it has been completely filled with water only once. The lake is now part of national park Lake Torrens, which requires special permission to enter.
Frome
A large endorheic lake in the Australian state of South Australia, located east of the Flinders Ranges. Frome is a large, shallow drying lake covered with a crust of salt. The lake is about 100 km long and 40 km wide. Most of the lake is below sea level. Area - 2596 km². Occasionally it fills with brackish water from dry creeks originating in the Flinders Ranges west of Frome, or exclusively with water from Strzelecki Creek to the north.
Air
A dry lake in South Australia. It is located in the center of the vast pool of the same name. Occasionally it fills to a level of 9 m below the sea level. Moreover, its area is 9500 square meters. km., making it Australia's largest lake. When dry, the lowest point of the lake bottom is at an altitude of -16 m, which is the lowest point in the country.
Great Artesian Basin:
Also known as "Canal Country", it is one of the largest artesian basins groundwater in the world and is an important source of water for Australian agriculture.
Lakes Eyre Basin
The Lake Eyre basin is the largest endorheic basin in Australia and one of the largest in the world, with an area of approximately 1,200,000 square kilometres, covering approximately one-sixth of the country, and is one of four sub-basins of the Great Artesian Basin.
The rivers here flow based on the amount of precipitation that falls, and therefore isolated reservoirs of water have vital important for the local population and wildlife.
This article was automatically added from the community
Australia is famous not only for its rare species marsupials, the most picturesque desert and mountain landscapes, but also its magnificent lakes. They vary in geological origin, water composition and even color. They also differ in the beauty of the coastal zone. But let's look at the largest water bodies and find out what the largest lake in Australia is, and also introduce several unusual bodies of water on the continent.
Disappointment
Our list opens, albeit small, with an area of only 330 km², but with interesting story openings, Lake Disappointment.
The famous traveler Frank Hann last quarter XIX century explored the western expanses of Australia in the hope of finding a freshwater lake. In 1897, having found freshwater streams, he went to the shore of the lake, but the water in it turned out to be salty, which greatly disappointed the researcher.
This is how the lake got its name, because “disappointment” in English language means disappointment.
TOP 10 largest Australian lakes
Alexandrina

Unique lake on south coast Australia is closely adjacent to the ocean bay, and its beautiful name received in honor of Princess Alexandrina, who reigned under the name Queen Victoria.
On its eastern side they flow into an amazingly beautiful lake. large rivers continent, but the lake is still shallow and there are many islands spread across its surface.
The aborigines worshiped the waters of the lake and believed that a monster lived in its depths. Now on the shores of Alexandrina there are many lizards, snakes and turtles.
By the way, in one of the articles we wrote about the most, we recommend reading!
Frome

One of the large endorheic reservoirs is located in the southern part of Australia near a mountain range, and the area of the lake is 2596 km².
Filling with water occurs due to small rivers flowing from the Flinders Ranges, and the mirror of the lake stretches for 100 km. The banks of the reservoir are varied in landscape. To the east it is adjoined by flat expanses of desert, and to the west there are beautiful landscapes national park.
Rarely do surveyors receive the honor of having lakes named after them, but Edward Frome, as surveyor general, received such an honor.
By the way, the site has a very interesting article about the city, which amazes with its magnificent landscapes.

Another drainless and very salty lake with the romantic name Amadius is located in the very center of the mainland, and its area is 1032 km². The climate in this part of the country is quite dry, which is why the lake is dry most of the year.
Europeans learned about it in 1872, and since then it has been named after the monarch of Spain. Although initially they insisted on the name in honor of Ferdinand Müller, who allocated funds for the study of the lake.
The length of the lake stretches for 180 km, which makes it one of the longest, but salt development is not carried out due to its remoteness from highways and markets.

One of the many drying lakes in the West of the Australian continent, distinguished from them by its large area of 3494 km². It’s interesting, but the lake is almost the same in both width and length, which are equal to 100 km.
The lake is a real natural attraction, because during the dry season the water completely leaves the reservoir, leaving a desert landscape with some areas of thickets.
Another interesting point. The depth of the lake directly depends on the time of year when the depths are measured. During the rainy season, the depth reaches up to 3 m, but during dry periods it does not exceed 50 cm.

Lake with picturesque shores of the national lake of the same name natural park state of South Australia. The area of the reservoir is 4700 km², which firmly places it in fourth place in size among the large lakes of the continent.
The length of Gairdner extends for 160 km, and the surface is covered with a salt crust, the thickness of which in some areas reaches 1.3 m. The lake is fed by six streams, which, however, also dry up.
The lake received its name in 1857, and State Governor Richard McDonnell personally gave it the name Gairdner.
A large dry lake with an area of 5714 km² is comfortably located within the Western Australian Plateau. It got its name in honor of David Carnegie, who explored the lake and its shores in the 80s of the last century.
The reservoir is located at an altitude of 439 m above sea level, and is surrounded mainly by desert plains. Only during the rainy season is Carnegie completely filled with water, and during the dry season it is a wetland with dense vegetation.
Its location on a plateau deprived the lake of natural inflows of water, so it only feeds during rainfall.
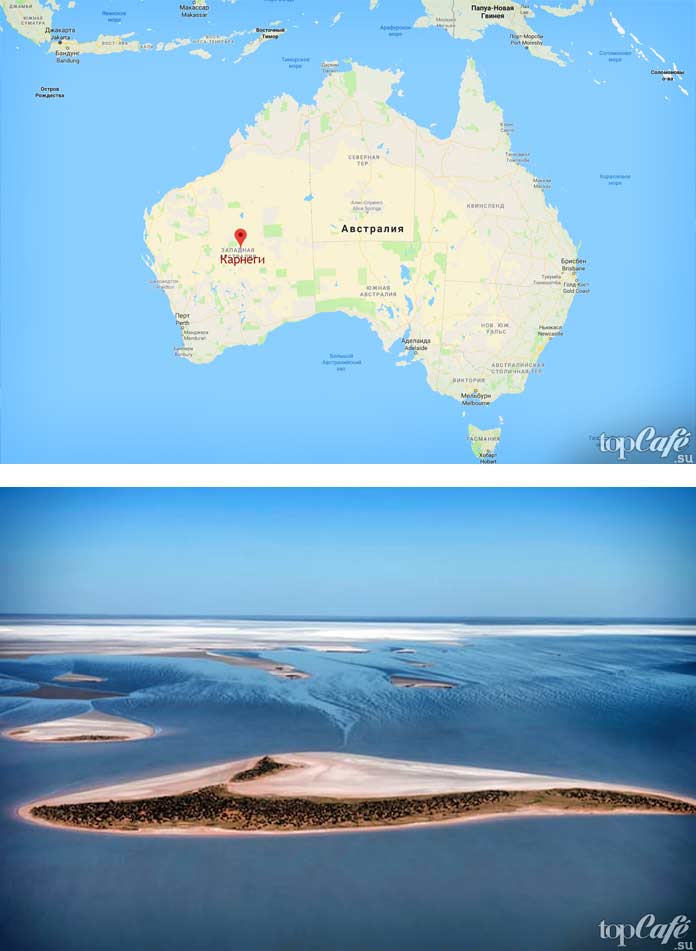
Torrance
In the state of South Australia, a beautiful and unusual lake called Torrens spreads out the mirror of its water surface. And they named the reservoir in honor of the founder of the British colony, Colonel Robert Torrance.
The lake area of 5698 km² stated in reference books and Wikipedia is very arbitrary. The reason is that the lake is not always filled with water within its shores, and in the last 150 years, only in 1989 during the rainy season heavy rainfall filled the bowl of the lake.
The geology of the lake dates back more than 40,000 years. The water in it is so salty that almost all the time the surface of the reservoir is covered with a thin crust of salt with small admixtures of clay.
Bonnie Riverland

Located off the very south-eastern coast, near the town of Millicent, the reservoir is Australia's largest freshwater lake.
It is noteworthy that there are no rivers flowing from it, and when the water is very full it goes straight into the ocean. Around the lake there is a magnificent natural Park Kanunda, famous for its rare plant species and rare representatives fauna.
Over the years, the lake ecosystem and coastal zone great harm was caused by nearby pulp mills, but today wastewater treatment plants have corrected the situation. TopCafe highly recommends visiting this place, especially since it is not so far from the largest Australian cities.
Hiller

Before moving on to the record holder for area, let’s go to a unique reservoir, the color of the water is pink.
It is located on the small island of Middle Island in Southwestern Australia. The shores of the lake are strewn with sand, and majestic eucalyptus trees grow nearby. Over the years, scientists have conducted research to determine why the waters of this unusual body of water are colored... pink color.
In 2016, pink Lake Hiller revealed its secret. It turned out that it was all about special algae growing in its waters.

Now the time has come to introduce the largest lake in Australia, whose surface area is 9500 km², and it is located in the very center of the basin of the same name, almost in the very center of the continent.
Kati Thanda, as it is also called by locals, is a drying pond. Very rarely the water level reaches 9m below sea level, and during dry periods the level drops to -16m, making the Eyre surface the lowest elevation in the country.
During heavy rains Flooding may occur in the area around Ayr. Despite such unusual conditions, a popular yacht club in the country operates on the lake.

The largest lake in Australia is truly amazing in its size, but just as the continent of Australia itself is the smallest of all the continents on the planet, so the largest lake located in its vastness is much smaller in size than the world record holders.
The large rivers and lakes of Australia make up the entire water system of the continent, have enormous recreational potential, and, what is especially interesting, every city in Australia is built on the banks of a river. If you have anything to add about the lakes of Australia, write comments on our article, we are very interested in your opinion.
Eyre (lake)
Lake Eyre (Kati Thanda-Lake Eyre) can hardly be called a lake. Set against a scorched landscape close to the rolling dunes of the Simpson Desert, it's more like two vast but shallow basins in Australia's thirsty heart.
Lake Eyre's lowest point is 16 meters below sea level - the lowest point in Australia.
During the rains, it receives water running down from distant mountains along river beds. Most of the water evaporates or goes into the sand. But if the rain is heavy, the water flows into Lake Eyre and it seems to explode with life. Plants appear, algae come back to life, birds (ducks, cormorants, seagulls) arrive.
However, with the cessation of water supply, the lake evaporates very quickly. What remains is a hard salt crust covering the wet mud.
Lake Hillier
Lake Hillier is located in Western Australia on Middle Island. This is the most unusual lake in Australia, main feature which is the pink color of water
Lake Amadeus (Amadies)
Amadeus – drying up drainage salt Lake.
In hot, arid climates, it is completely covered with a layer of hardened salt for most of the year. And only during the rainy season is it filled with water.
The lake is located in central Australia, 350 km from the city of Ellis Springs. It has an oblong shape, 180 km long and 10 km wide - it is the largest lake in the Northern Territory.
Lake Argyle
It is the second largest artificial lake in Australia and is located near East Camberia in Western Australia.
The lake currently irrigates approximately 150 km2 of agricultural land in the East Kimberia region.
Lake Burley Griffin
One of Canberra's iconic landmarks is Lake Burley Griffin, located in the center of the Australian capital. It bears the name of the American architect Walter Burley Griffin, who designed almost all of Canberra.
This fairly deep reservoir (up to 18 meters), with a diamond-shaped outline, up to 11 km long and up to 1.2 km wide, is very popular.
Gordon Reservoir
Reservoir on the Gordon River. Created in the early 1970s by the construction of the Gordon Dam. Located in South-West national park islands of Tasmania.
Largest rivers in Australia
Murray River
Australia's largest river is the Murray River.
Originates in the Australian Alps. The river, especially in its current state, is low in water; many of its tributaries dry up and are taken apart for irrigation.
The river flows slowly through the rubber forests. Further the river flows through desert lands called Malliland. Here the banks of the river are in places overgrown with malli trees, a type of eucalyptus. The river bed is easy to determine by looking at political map Australia. The river forms most of the borders between the states of New South Wales and Victoria. The Murray flows through lakes Alexandrina and Victoria (indigenous Australians call it Kinga)
The river flows into the Great Australian Bight of the Pacific Ocean.
Murrumbidgee River
The source of the Murrumbidgee River is in the Eastern Highlands of New South Wales in the Australian Alps, part of the Great Alps. Watershed Ridge.
The river's flow is regulated by the Tantangara Dam and also by a system of reservoirs, which limit the Murrumbidgee's natural annual flow by almost 50%.
The Lochlan River flows into the Murrumbidgee, after which the river continues to flow in a south-west direction.
Just adjacent to the New South Wales-Victoria border, the Murrumbidgee flows into the Murray River.
Darling River
A river in southeastern Australia, a right tributary of the Murray. It is the second longest river in Australia.
It originates on the western slopes of the New England ridge near the city of Bourke, in its lower reaches it flows through a semi-desert.
Lochlan River
A river in the central part of the Australian state of New South Wales, a right tributary of the Murrumbidgee River.
The source of the Lochlan River is in the Eastern Highlands of New South Wales.
Cooper Creek
A dry river flowing through the Australian states of Queensland and South Australia.
The source of Cooper Creek (at this point it is called the Barcoo River) is on the eastern slope of the Warrego Range in Queensland, in the Great Dividing Range.
After crossing the Queensland border, the river flows through the state of South Australia, where it flows into Lake Eyre (during wet seasons only).
Diamantina River
A river flowing through the Australian states of Queensland and South Australia. The source of the Diamantina is located northwest of settlement Longreach in Queensland, then the river flows in a south-westerly direction through central regions state and flows into the swamp - Goyder Lagoon, located in the north of the Strzelecki Desert.
During the high season, the river flows from the marsh to join the Georgina River to form Warburton Creek, which reaches Lake Eyre during the wet seasons.
Flinders River
The longest river in the Australian state of Queensland.
The source of the Flinders River is on the south-western slopes of the Gregory Mountains, part of the Great Dividing Range, near the town of Kargun.
eventually flowing into the Gulf of Carpentaria.
The Murray is considered a major river not only by the standards of its continent. The total length of the Murray is 2375 km, and together with the Darling it is almost two hundred kilometers longer than the Volga. But in terms of the abundance of water, the Murray is significantly inferior to most large European rivers.
Most long river Australia is fairly easy to find in the eastern part of the continent. Its path passes through a variety of natural landscapes: mountains, forests, swamps. The river flows past cities and agricultural land. Murray and his people attract the most different shapes lives that have successfully adapted to its peculiarities.
Murray has its origins in the most high mountains ah, the southern continent, the Australian Alps. Largest tributaries the rivers begin much further north. Flowing from east to west, the Murray receives less and less precipitation, but still remains a deep river. If you go downstream, you can get acquainted with all the diversity of the flora and fauna of Australia.
In the vast expanses of the lower reaches of the Murray you can find Australia's largest birds, the emu and the kangaroo.
Features of the Murray River
The Murray River has the distinction of being free for navigation throughout the year. The width of the river in some places reaches a kilometer. Passenger ships rise almost two thousand kilometers along its current. But the navigation characteristics of its tributary, the Darling, depend almost entirely on the amount of precipitation.
A very large proportion of the Murray's waters are used to irrigate the land. A carefully designed irrigation system serves this purpose. To properly distribute water resources Murray, dams have been built along the entire length of the river. The Murray Basin also has an artificial lake that collects rainwater.
It is the water resources of Australia’s longest and deepest river that make it possible to transform desert areas into lush plains.
There is a project that assumes that the waters of all the small rivers that flow down the eastern slopes will be released into the Murray mountain system. If the project can be implemented, the river beds could be turned in a westerly direction, after which they would bring their waters to Murray. Thanks to this, the capabilities of the irrigation system of the river complex will greatly increase.
Australia is a dry continent. A significant part of the precipitation that falls here evaporates. The rest is carried away by the rivers. Moreover, half of the total amount of sediment carried away by rivers falls on the largest river in Australia. For this reason, the importance of Murray in the life of the country can hardly be overestimated.
At 2,995 kilometers (1,861 miles) long, the Murray descends from the Australian Alps.
From the driest western side of the highest mountains of the Australian continent, and for most of its length, meanders through interior plains Australia, forming the border between the states of New South Wales and Victoria.
It flows northwest, turns south for a final journey of 500 kilometers (310 miles) and, upon reaching the ocean, falls into Lake Alexandrina.
Australia's largest river - Character of the river
Most Australian rivers are located close to the coast. The largest and longest of Australian rivers can be found in the eastern part of the country. They pass through various environments on their way to the sea: mountain forests, wetlands, farmland and cities.
Many different animals live in the Australian river area. Fish, frogs, crayfish, mussels, platypuses, swans, ducks, pelicans, kangaroos, lizards, snakes, turtles live in aquatic environment rivers.
Murray water flows through several lakes that fluctuate in salinity (and were freshwater until recent decades), including Lakes Alexandrina and Coorong before being drained through the mouth of the Murray River in the south-eastern Indian Ocean and, based on Australian maps, the Southern Ocean. near Goolwa.
Despite the river bed being filled with significant volumes of water, before the advent of irrigation systems, the mouth was always relatively small and shallow.
Since 2010, the river system receives 58% of the natural flow. This is Australia's most important irrigated region - the nation's feeding ground.
Less than one-fifth of rainwater goes to Australian rivers. Most rainwater evaporates, is used by trees and plants, or ends up in lakes, wetlands or the ocean. Due to this, Australian rivers have a very irregular flow.
This means that sometimes the river becomes wider, deeper and has fast current, and sometimes it becomes smaller, its channels become narrow, and the waters become slow.
River of life

The Murray River, and its associated tributaries, support a variety of unique river life forms adapted to its vagaries.
- This includes various breeds of fish such as the famous Murray cod, trout, golden perch, Macquarie perch, silver perch, eel, tailed catfish, Australian smelt and western gudgeon carp.
- Several other aquatic animals can be mentioned, such as Murray short-necked turtles, Murray River crayfish, broad-clawed yabbies and large-clawed Macrobrachium shrimp, water rats, Platypus. The Murray River supports forest corridors with its edging.
The health of the Murray River has declined significantly. Recent extreme droughts (2000-2007) have placed significant stress on coastal forests and there is growing concern about their long-term survival. The Murray also floods places on some occasions, the most significant being the flood of 1956 - it lasted six months and inundated many towns on the lower Murray.
The fish species represented - carp, gambusia, char, rudd perch and rainbow trout - also experienced serious Negative consequences changes. Deteriorated condition environment Murray River and its tributaries, destroys plants and constantly causes an increase in turbidity.