What are the main signs of a new attitude towards conflicts. Conflict concept, types, reasons, solution
Bipolarity as the presence and opposition of two principles is necessarily present in any psychological conflict. Whether we are talking about an intrapersonal conflict, interpersonal or intergroup - in any case, there are two instances in the conflict, opposing each other.
Bipolarity, or opposition, represents opposition and at the same time interconnectedness, contains the internal potential of contradiction, but in itself does not mean collision or struggle.
Activity aimed at overcoming contradictions is also characteristic of any conflict and is evidently present in various designations in all definitions of conflict (which is not surprising: remember that by its very origin the word “conflict” is a collision). This activity is called "collision", "incompatibility", "opposition", etc.
Activity is another sign of conflict, but only that activity that is synonymous with the concepts of "struggle" and "counteraction", activity is impossible without some impulse given by the awareness of the situation on the part of the subject of the conflict.
In the context of the problem of defining conflicts, this property can be designated as bipolarity, which means both interconnection and mutual opposition at the same time. A true point of view can exist only if a false one coexists with it. The confrontation of interests presupposes the presence of two conflicting or incompatible interests. The struggle of motives is also possible only with their multiplicity.
Bipolarity as a feature of the conflict, apparently, is also characteristic of cases of broader social confrontation. By itself, bipolarity does not mean a collision of two different principles. Their true opposite reveals itself not just in their comparison, but in their opposition, which presupposes "struggle", active interaction aimed at overcoming the contradiction separating them. The South and North Poles, for all their polarity, "poles" in the literal sense of the word, are not in conflict with each other.
The presence of subjects of the conflict is another sign, the subject is an active party capable of creating a conflict situation and influencing the course of the conflict, depending on its interests. As a rule, the subjects of the conflict have a special type of consciousness - conflict. You can only be in conflict with someone - with another group, with another person, with yourself. The fact that a conflict requires the presence of a subject or subjects representing its parties presupposes the possibility (at least potential) of active and conscious actions on the part of these subjects. This is how a conflict differs from a contradiction, the parties to which do not necessarily have to be represented by subjects.
Conflict situations often arise in our life - between friends, acquaintances, relatives, colleagues and loved ones. The soil can be very diverse - from a mismatch of interests to interracial hostility. The concept of conflict will be discussed in detail in our review. We will also talk about the main reasons for its manifestation, the need for its presence in everyday life, the rules of behavior during a conflict situation, and ways of solving it.
A conflict situation is a clash based on misunderstanding, rejection of other people's ideas, values and thoughts that arises between people, society, and individual states. Previously, it was believed that this should be avoided, try to find a compromise in everything, but modern psychology refutes this statement. Today, all sorts of collisions are not considered as purely negative, since, according to numerous studies, the conflict helps individuals and groups develop, thanks to it a person gains experience in communication.
The essence of situations of this kind is to defend your point of view and your own competitiveness. Faced with misunderstanding, injustice, a person gets involved in a conflict.
Structure
The structure of all conflict situations includes:
- Subject (object) provoking the development of the dispute. It can be both a thing and a person, thoughts, ideas, in which the parties to the conflict are interested.
- The subjects of the situation. They can be groups, organizations, individuals.
- The conditions in which the conflict proceeds. For example: work environment, family disputes, and so on.
- The scale of the situation: global, interpersonal, regional, localized.
- Behavioral features and tactics of behavior of the conflicting parties.
- The result is an understanding of the result of the conflict, its consequences.
Types and types of conflict situations in the business environment

The most common conflicts of interest are in organized groups, namely in collectives of workers, among teachers in schools, in organizations assembled from individuals of different ethnicity. In this case, these types of conflicts are considered:
- Intrapersonal. Formed in connection with the dissatisfaction of an individual with the requirements for his activities. That is, if a person is forced to do something against his will, or the performance of the task is contrary to the foundations and values of the individual, an intrapersonal conflict situation arises.
- Interpersonal. Most often, it is interpersonal conflicts that arise in groups. Their manifestation is directly related to the lack of any resources to achieve the goals set, the desire to "curry favor" with the authorities (higher positions), as well as with the character traits of each member of the group. Basically, "friction" in the team arises in connection with the cardinal dissimilarity of individuals, the difference in their worldview and different temperaments.
- Between an individual and a group. The emergence of a conflict of this kind is caused by defending the opinion of one individual in front of a group. That is, a person who does not agree with the opinion of the majority tries to defend his idea, while creating a conflict situation.
- Intergroup... Any team consists of at least 2 groups: formal and informal, between which conflicts arise from time to time. Basically, the basis for this is the unfair attitude of the bosses to the informal group, rallying to protect and defend their interests.
- Managerial. It develops during the workflow, when allocating resources. The managerial conflict arises in connection with the mismatch of the temperament of subordinates, the divergence of values and goals.
The most common types of conflicts
More often than others, interpersonal, intrapersonal collisions, as well as collisions between a group and an individual, are encountered in everyday life and daily activities of a person. An example of a conflict between two people can be found in any school class, team, family:
- Failure to accept a new group member based on external criteria. For example, a student came to the class who did not correspond to the group's concepts of appearance, he was not noticed, repulsed, not invited to participate in joint games and discussions. There is a conflict here between the group and the individual.
- A dispute about raising a child is an interpersonal conflict.
- An order from the authorities to increase the working time for a specific specialist. This is fraught with the emergence of an intrapersonal conflict situation.
Characters

The parties to the conflict are the parties directly involved in the formation and completion of the conflict of interest. There are 2 types of actors: indirect and direct participants in the conflict.
Indirect ones include:
- Provocateur. A person (state, group, society) provoking another person into a collision, while in some cases not taking part in the conflict situation itself.
- The provocateur's ally, or "support group". A person who provides assistance (material, moral) to the development of the collision.
- The organizer (creator) of the conflict.
- Judge (mediator, mediator). A person who is a third party in a conflict situation.
Direct ones include:
- The instigator. Sometimes it is a provocateur.
- Subject.
- Collision sides.
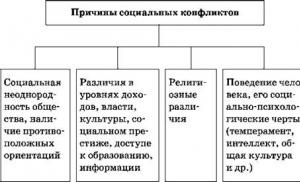
Causes of occurrence
Sources of conflicts are unfavorable conditions, coincidence of circumstances, personal qualities of individuals that provoke the development of a collision. Of all the sources, the following are more common: unstable financial situation, lack of resources, character traits and excessive emotionality of a person, as well as features of his mental development, values, morality, and personality ethics.
The family as one of the small groups where conflict situations occur periodically
Family conflicts are among the most common. According to statistics, almost every family member has to face misunderstanding from one of the close relatives. The reasons for the development of conflicts in this group of individuals are:
- Strong differences in character and temperament both among spouses and among children and relatives.
- Everyday problems. In most cases, for couples, a conflict situation is brewing precisely on the basis of a lack of funds.
- Unjustified expectations. The clash arises in connection with the unjustified hopes placed on the marriage by one of the spouses.
- Dissatisfaction with sex life.
- Treason. Due to dissatisfaction with sex, often one of the spouses (less often both) begins to look for warmth and affection on the side. As a result - the development of a conflict situation leading to a break. However, some try to add "spice" to the relationship, thereby saving them.
- Lack of personal space. Most couples constantly spend time together, without having the opportunity to retire, which leads to the "recapture" of certain areas of the house.
- Jealousy, heightened sense of ownership. Some types of people tend to overprotect their partner, limiting his communication with the opposite sex, while constantly suspecting the spouse of non-existent infidelity. An example of a conflict, the development of which is due to jealousy: one of the spouses constantly read the personal correspondence of his partner, when the latter saw this, a scandal erupted.
- Abuse of one of the partners of alcohol and drugs, smoking.
- Different views on the educational process. If there are children in the family, then often a conflict can arise in connection with the dissatisfaction of one of the parents about their upbringing by the other.
The main "symptoms" of the development of a conflict situation in the family
The first signs of conflict often remain latent until the peak. How to understand that it is necessary to make any efforts to prevent a conflict situation?
Not a single confrontation arises without reason. The concept of a conflict implies the presence of certain prerequisites: frequent disputes, misunderstandings, silence and inability to properly build a dialogue. Example: A spouse returned from work upset and in need of support. And his wife, in turn, thought that he was tired and did not "bother" him with conversations, although now he just needed a dialogue with her. Gradually, omissions are superimposed on each other, and an invisible abyss arises between the partners, and later signs of conflict appear:
- Communication tension.
- A sharp reaction to any stimulus.
- Attempts to call a partner into a conversation end with his withdrawal into himself.
- Detachment from what is happening around.
As a result, due to unresolved issues in the family, a conflict situation is formed, for a successful resolution of which both parties must make every effort.
Human behavior during conflict
You should know what should be the behavior in the conflict. This will allow avoiding mistakes during forced collisions of interests, as well as influencing the opponent (initiator or other side of the conflict). In psychology, the following options for the behavior of an individual in a conflict situation are distinguished:
- Evasive (passive). It is used both on a subconscious level and consciously. Features of conflicts in which this option of behavior is used: the opponent does not defend his interests and the interests of the group, he is unable to defend himself, while trying to avoid further development of the conflict. Experts do not recommend resorting to frequent use of passive behavior, as this can lead to a decrease in personal self-esteem. Its use is justified only in those situations where a person, thanks to avoidance of collision, can achieve success, increase.
- Compliant, opportunistic. This form of behavior allows you to survive conflicts in relationships without resorting to complete confrontation. That is, when one of the opponents concedes during a conflict in something to another participant, this allows you to keep the relationship at the same level, relieve tension and quickly, without loss, close the dispute. However, compliance in a conflict situation does not provide an opportunity to fully defend your opinion and achieve what you want.
- Dominant (overwhelming). A person who chooses domination in a conflict rigidly defends his point of view, regardless of the wishes and needs of the other side. Thanks to this, he easily persuades the opponent to retreat, forcing him to make concessions. The advantages of this demeanor: quick achievement of the desired goal, stimulation of personal growth. Cons: due to the constant use of dominance, a person becomes a conflict person for others, while his mental strength is significantly expended, which can lead to severe stress.
- Compromise. This option of behavior allows you to resolve the conflict with partial satisfaction of the needs of both parties. Nevertheless, its frequent use cannot guarantee the absence of a repetition of the conflict situation, since the desires of the opponents are not fully satisfied, which can cause a new "wave" of collisions.
- Integration (cooperation). It represents the interaction of both parties in resolving the current situation. Such behavior is possible only with a full analysis of what the concept of conflict is, and the desire of opponents to achieve what they want without significant losses, taking into account their interests.
The impact of conflict on a person
How a particular conflict situation affects an individual depends on several factors:
- The goal and the desired result.
- The significance of the conflict for both parties.
- The option of behavior chosen by the participant in the conflict of interest.
Each of the above factors is strongly associated with the next, and only their combination can show how an individual is affected by the problem of conflict. For example, a person has set a task (goal) for himself, which is especially important for him, while his opponent is absolutely indifferent to this goal. As a result, with the dominant behavior chosen by the opponent, a person will not be able to achieve what he wants, acutely experiencing his failure.
What not to do during the settlement
It is worth remembering that excessive emotionality can only aggravate the current situation, and the calmness and coldness in the voice will allow you to quickly eliminate the conflict. To resolve any collision, restraint and respect for the opponent are necessary, no matter from which side he manifests himself. It is important to know that negativity in response to negativity can escalate psychological conflict and make it practically insoluble without additional help.

A conflict situation requires a special approach, its resolution should be brought to the end, otherwise it may arise again.
Basic rules for positive resolution
- You need to be able to listen to your opponent and take into account his desires.
- Do not use intimidation in resolving a dispute.
- You need total control over your own emotions.
- A well-formulated dialogue facilitates a quick transition to consensus.
- Understanding that each person resolves problems in their own way helps to resolve the conflict.
How to overcome a conflict situation in the family
The group most susceptible to the negative influence of conflicts is the family. There are three ways to prevent and eliminate conflicts of interest in family relationships. These include: destructive (destructive marriage), permanent (the state of the family at the present time), constructive (contributing to rapid recovery).
The structure of family relations during a conflict implies 2 types of behavior:
- Rivalry. One of the spouses (sometimes both) puts their desires and goals above family values. This selfish behavior further escalates the conflict and makes it more difficult to resolve.
- Cooperation. Here the interests of each family member are taken into account, which helps to quickly and painlessly eliminate the conflict situation.
In any existing family confrontation, each of the partners should strive to resolve it, in which both conflicting parties win (gain-win). The result, where one of the opponents loses, can provoke a new conflict, exacerbated by the oppressed pride and the previous fiasco of the partner.
The solution to the conflict is a direct conversation-explanation, where everyone can speak in a calm manner about a particular problem. In addition, compliance of both partners can become another solution.

Moments to help combat conflict:
- Supporting your own dignity without compromising your partner.
- Demonstrating appreciation and respect for your spouse.
- Containment of negative emotions.
- Lack of reminders about the mistakes that your partner has already made from the past.
- Restraint of jealousy, suspiciousness, elimination of possible thoughts about betrayal of a spouse.
- Patience, acceptance of a person for who he is.
- Transferring the conversation to another channel in order to exclude the possibility of an escalation of a conflict situation.
The joint pastime of spouses, communication on abstract topics helps to prevent family conflicts. The more and more often partners can talk, the stronger their family's protection from conflict. You should not put pressure on a person, try to re-educate him - this will be a big mistake, since each person is individual and has the right to defend his individuality in any situation.
There are different options for classifying conflicts. They divide all types of conflicts into classes according to some specific criterion: according to the composition of the participants in the conflict, according to the duration of the conflict, for its reasons, according to the forms of the conflict, etc.
So let's take a closer look at each classification.
1. By duration:
- short-term(from several minutes to several hours);
- long(from several hours to several days);
- lingering(indefinite, until a constructive solution is found).
2. By manifestation:
- hidden(visible manifestations of the conflict are not enough to judge its presence and characteristics);
- partially hidden(visible manifestations of the conflict do not allow to adequately judge its causes, depth, actions of the participants);
- open(all manifestations of the conflict are not hidden by the participants, and sometimes even take on a demonstrative character).
3. By conflict generators:
- conflicts of interest,
- conflicts of goals,
- conflicts of values,
- conflicts of approaches, etc.
4. Due to the occurrence:
- natural(arising without targeted impact);
- intentional(resulting from targeted exposure).
5.
By the nature of the reasons:
- objective(generated by objective reasons, resolved most often constructively);
- subjective(generated by objective, personal reasons and, as a rule, are resolved destructively).
6. Organizational structure:
- vertical (boss-subordinate);
- horizontal (without hierarchical relationships);
- mixed.
7.
By the level of evidence:
- hidden;
- masked;
- explicit.
8. By values:
- "plus-plus" (choice of two favorable options);
- "minus-minus" (choice of two unfavorable options);
- "plus or minus" (choice from unfavorable and favorable options).
9. Openness:
- Open conflict- disagreements relate to the production area and express different paths leading to the same goal. Open conflict most often unfolds on a business basis and is relatively harmless.
- Hidden conflict based on human relationships and is the most dangerous, as it can complicate relationships in a team.
10. By spheres of manifestation:
- economic conflicts;
- ideological conflicts;
- social conflicts;
- family and household conflicts.
11. By the degree of duration and intensity:
- violent fast-paced conflicts(arise on the basis of individual psychological characteristics of the personality, are distinguished by aggressiveness and extreme hostility of the conflicting parties);
- acute long-term conflicts(arise in the presence of deep contradictions);
- mild and sluggish conflicts(associated with non-acute contradictions or passivity of one of the parties);
- mild and fast-paced conflicts(associated with superficial reasons, are of an episodic nature).
12.
By subject:
- realistic (subject) conflicts(have a clear subject);
- unrealistic (pointless) conflicts(do not have an item or have an item that is vital for one or both of the subjects of the conflict).
13. On the sides of the conflict:
- intrapersonal
- interpersonal
- between the individual and the group
- intragroup
- intergroup
Intrapersonal conflict- it is carried by an individual. The content of this conflict is expressed in acute negative feelings of the individual. The reasons for the feelings are conflicting aspirations, motives, interests, and personal values. Those. intrapersonal conflict is a problem between the real and the desired state of a person, between reality and possibility.
Interpersonal conflict- this is a collision between people in the process of their interaction. For example: the contradiction between the boss and the subordinate about the size of the salary; confrontation between passengers in public transport, etc. The causes of conflicts can be very different. Personal qualities of people, their mental, socio-psychological and moral characteristics are of great importance here.
For the emergence of an interpersonal conflict, the simultaneous presence of 3 conditions is necessary: contradictions in interpersonal interaction, opposition of opponents, their experience of expressed negative emotions in relation to each other.
Conflict between the individual and the group- very similar to interpersonal. But at the same time, the potential for conflict is high here, because the group is organized in a certain way, has a formal or informal leader, has a structure. If the conflict is constructive, then the connection between the individual and the group is strengthened. If the conflict is destructive, then personality disidentification and group disintegration occur.
Intra-group conflict- this is a conflict between microgroups in a team, or an individual and a microgroup, or an individual and the whole team. The reasons for the conflict are the opposite of the goals of the parties, the preservation or strengthening of their social and group status, group domination, personal hostility to each other, prestige, authority, etc.
Intergroup conflict- this is a clash of interests of various groups. Causes of the conflict: economic, political, religious, class, ethnic, etc.
14. According to the results:
- Dysfunctional conflicts- the consequence of such conflicts is the complication of interpersonal relations and the lack of results on problematic issues.
- Functional conflicts help participants in the labor process to better understand the goals of the organization, turn to their unused reserves and do much of what seems impossible under normal conditions.
15. For social consequences:
- constructive conflicts(they are based on objective contradictions, such conflicts contribute to the development of the organization);
- destructive conflicts(they are based on subjective reasons, such conflicts create social tension and lead to the destruction of the social system).
From a practical point of view, the classification of conflicts is important, since it allows you to navigate in their specific manifestations and, therefore, helps to assess possible ways to resolve them.
The main signs of a conflict are: the presence of a situation perceived by the participants as a conflict; the object of the conflict, which cannot be divided fairly between the participants in the conflict interaction; the desire of the participants to continue conflict interaction to achieve their goals, and not to look for a way out of this situation.
Conflict = conflict situation + incident.
A conflict situation is the conflicting positions of the parties on any occasion, the pursuit of opposite goals, the use of various means to achieve them.
Quite often, a conflict situation is based on objective contradictions, but sometimes some trifle is enough: an unsuccessfully spoken word, opinion, that is, an incident - and the conflict can begin.
The main reasons for the conflict in the organization:
Resource allocation. Even in the largest organizations, resources are always limited, management needs to allocate materials, human resources and finances among various groups in order to most effectively achieve the goals of the organization, which often leads to conflict.
Interdependence of tasks. Since all organizations are systems consisting of interdependent elements, with inadequate work of one department or person, the interdependence of tasks can cause a conflict (a conflict between different departments - the head of the production repair service in the low productivity of his department, which, in turn, the personnel service, in the absence of new workers; between line and staff personnel, between an individual and a group if others think that one works worse).
Differences in purpose. As organizations grow, they become more specialized and broken down into divisions, and the specialized divisions formulate their own goals and may focus more on achieving them than the goals of the entire organization.
Differences in beliefs and values(a very common cause of conflict). Instead of objectively assessing the situation, people can only consider those views, the alternatives that, in their opinion, are favorable for their group and personal needs. In healthcare organizations, between administrative staff (strives for efficiency and cost-effectiveness) and medical staff (quality of care provided to patients); the subordinate may think that he always has the right to express his opinion, the leader - only when asked).
Differences in demeanor and life experience. Differences in life experience, education, seniority, age, social characteristics reduce the degree of mutual understanding and increase the possibility of conflict.
Poor communications. Poor communication of information is both a cause, a catalyst and a consequence of conflict (ambiguous quality criteria, inability to accurately define job responsibilities and functions, presentation of mutually exclusive job requirements).
Model of the conflict process. Stages and phases of the conflict.
Conflict is a process consisting of several stages, within which the collision is only one of them.
The development of a conflict goes through three stages - pre-conflict, conflict and post-conflict. The phases of the conflict are directly related to its stages and reflect the dynamics of the conflict, primarily from the point of view of the real possibilities of its resolution.
1. Pre-conflict stage: No social conflict arises instantly. Emotional stress, irritation, and anger usually build up over time.
1. phase: The emergence and development of a conflict situation.
A conflict situation is created by one or more subjects of social interaction and is a prerequisite for a conflict.
A characteristic feature of the conflict at the moment of its inception is the presence of an object that must be fundamentally indivisible or seem to be such in the eyes of rivals and the possession of which (or the achievement of which) is fundamentally necessary - the cause of the conflict. The presence and size of such an object must be at least partially realized by its participants. The existence of one or more sources of conflict increases the possibility of a conflict situation in the management process.
2.Phase: Awareness of the conflict situation at least one of the participants in the interaction and his emotional experience of this fact. The consequences and external manifestations can be: a change in mood, critical and unfriendly statements about the enemy, limitation of contacts with him, etc. During this period, the conflicting parties evaluate their resources before deciding on aggressive actions, look for ways to achieve goals, form a strategy behavior, but there is no open collision yet ..
2. Stage. Direct conflict: It is characterized by the presence of an incident, i.e. social actions aimed at changing the behavior of opponents - an active, active part of the conflict.
1. The beginning of open conflict interaction. One of the participants proceeds to active actions, the other, realizing that the actions are directed against him, in turn, takes active response actions.
At this stage, two phases are possible: constructive and destructive.
Parties may be reluctant to react in a way that further aggravates the situation. People do not always respond to conflict situations that entail small losses or are considered low-risk, or understand that the potential benefits of participating in a conflict are not worth the cost ("This time I will let him do his own thing").
2. Development of open conflict.
It is expressed in various types of conflicting behavior aimed at preventing the opposite side from realizing their interests, achieving the desired goal. Conflict often manifests itself when trying to persuade the other party or a neutral intermediary to accept their point of view or to block the other's point of view using primary means of influence: such as coercion, reward, tradition, peer review, charisma, persuasion, or participation.
The next stage of the conflict as a process is control them.
3. Stage Conflict resolution: Depending on the content of the conflict, it can be achieved by two means: pedagogical (conversation, persuasion, request, explanation) and administrative (transfer to another job, dismissal, order of the head, court decision, etc.).
An external sign of conflict resolution can be the end of the incident, conflict interaction between the conflicting parties ceases (the elimination of the incident, often, having stopped active conflict interaction, people continue to experience the conflict to look for its cause, and then the extinguished conflict flares up again).
Everyone knows what a conflict is. This concept has many synonyms: quarrel, dispute, scandal, etc. It is quite natural for people to conflict, which is why conflicts are of various types. Depending on the number of participants and the issues that are discussed during the quarrel, they can be social, intrapersonal, interpersonal, political, etc.
Many people have faced intrapersonal and interpersonal conflicts. Only at the level of groups or an entire state can one enter into a social or political conflict.
A feature of conflicts is that they can be observed from the outside, you can enter them when they are already flaring up, and also leave when they do not stop. Conflict can arise between two people and between entire states, which number millions of people.
At all times, people have had conflicts. What kind of "beast" is this? This will be discussed in the article, which will also consider the topic of how to resolve conflicts, which is also necessary for every person to be able to.
What is conflict?
The most important question is: what is conflict? All people know what it is, because they could have been in it more than once. Conflict has many concepts:
- Conflict is a method of resolving disagreements in goals, worldview, ideas that arise during interaction with society.
- Conflict is an emotional dispute where participants express negative feelings towards each other outside the norm.
- A conflict is a struggle between its participants.
On rare occasions, a fight starts on an impartial basis. Usually, a conflict is an emotional state when a person begins to experience negative emotions, which push him to raise his voice and express rude words to other people. Thus, conflict is a mental state of a negative and subjective nature.
What is a dispute, a quarrel, a conflict between people? This is a war of opinions. A man and a woman do not quarrel, but each try to prove his innocence. Friends do not conflict, but try to defend each of their opinions. People do not argue, but provide evidence and arguments for their points of view.
Everyone has their own opinion on a particular issue. This is fine. There is some exact knowledge that does not require proof. So, for example, everyone agrees to unconditionally accept knowledge of mathematics, physics or anatomy. No one argues with this knowledge or refutes, if there is no compelling evidence. And there is an opinion, a view, which is often confirmed by what a person has gone through. This is due to the fact that events can occur for various reasons.
Each of the parties to the dispute is right. Surprisingly, the two opposing opinions are correct, although the disputants themselves do not think so. When you are in conflict with someone, you consider your behavior and look to be the only correct one. The opponent thinks the same way. The most striking thing is that you are both right.
The same situation can be formed for different reasons. Everyone has their own experience of experiencing certain situations. People are different, as well as their attitude to what is happening. That is why everyone has a personal opinion on the same event. And all these opinions will be correct.
Conflict is a war of opinions. It's just that each of the opponents wants to prove their case. And the important thing to remember in the moment of a quarrel with another person is that you and your opponent are right, despite the fact that your opinions do not coincide. You're right! Your opponent is right! If you remember this, the war will end. No, you will not change your point of view. You will simply have a chance not to fight for whose opinion is more correct, but to start having a conversation in order to find a solution to the problem that has arisen, which takes into account the interests of both parties.
As long as the war is waged, the problem will not be solved. Once you admit that both are right, then there is a chance to start a conversation that aims to find a solution to your common problem.
Conflict functions
A person usually sees only the negative side of conflicts. However, the personality is naturally given a tendency to conflict. This is dictated by the functions to which conflict situations lead. The negative side becomes apparent only when people do not reach the goal, because of which, in principle, the dispute flared up.
Conflict functions can be called:
- The pursuit of excellence. Only through the struggle between the old and the new, where the new triumphs, can you achieve something better.
- Survival drive. There are a limited number of material resources. A person who is struggling tries to get as many resources as possible for himself in order to survive.
- Striving for progress. Only through a conflict of interest, where some want to preserve and others want to change, is progress possible when something new is created.
- Striving for truth and stabilization. A person is not yet fully moral and highly spiritual. This is why there is much debate about what is moral and immoral. Such discussions are capable of finding the truth.
Not every conflict brings positive results. There are numerous cases where the outcome has been negative. The positive result of any conflict is finding a solution to the problem, which is realized and helps the participants to become better, stronger, more perfect. A negative result of a conflict is observed when the participants cannot find a common solution, their actions lead to destruction, decline, degradation.
An unsuccessful conflict can be called any dispute when people tried to agree on something, but did not agree. There are many reasons why people just scandal, and as a result of this action they get emptiness.
Is conflict helpful in and of itself? For the conflict to be useful, you need to set a goal when entering the dispute - what do you want to achieve as a result of the conflict? After that, act only within the framework of this goal. Since people rarely set themselves a goal that they want to come to, they simply express their emotions, resentment, wasting their energy and time.
Often times, people just want to show their displeasure. But what after that? What do you want to receive or hear from the other person? It is not enough just to displease and criticize, you also need to argue your discontent and say what you want to get from a person.
People quite often do not agree, but force them to accept their point of view. Each of the opponents thinks that his opinion is the only correct one. But all the participants in the process think so. And while people are trying to get their opponents to go over to their side, it will be like a tug of war, where everyone will be a winner and a loser. People will scandalize, and it will not end with anything big.
The reason for the unsuccessful conflict is sometimes the habit of conflict. A person is used to communicating with others in a raised tone, which is perceived by them as an attack. A person speaks loudly with other people, they perceive this as an attack against them, which causes an unreasonable conflict. And all because a person simply does not understand that you can express your thoughts and desires in a calm tone.
People often conflict with each other. But what is the use of conflict? It does not exist, because sometimes people simply conflict, discussing a certain problem, without any clear goal to solve it.
The main types of conflicts
The classification of conflicts can be very diverse. This includes the number of participants, and the topic of the conversation, and the consequences that occur, and the ways of conducting the conflict, etc. The main types of conflicts are intrapersonal, interpersonal and group (according to the number of conflicting ones):
- Intrapersonal conflicts are a struggle of several opinions, desires, ideas within a person. This raises the question of choice. A person must sometimes choose between equally attractive or unattractive positions, which he cannot do. This conflict can still arise when a person cannot find a solution, how to please himself and other people (their requirements). Another factor is getting used to one role, when a person cannot switch to another.
- Interpersonal conflicts are mutually directed arguments and reproaches of people against each other, where everyone wants to defend their needs and desires. They have their own classification:
- By spheres: household, family, property, business.
- By consequences and actions: constructive (when opponents achieve goals, find a common solution) and destructive (the desire of opponents to defeat each other, take a leading position).
- According to the criteria of reality: genuine, false, hidden, accidental.
- Group conflicts are confrontations between individual communities. Each of them considers itself exclusively from the positive side, and opponents from the negative side.
A genuine conflict is a quarrel that really exists and the participants perceive it adequately. A false conflict occurs when there is no reason for a dispute. There is no contradiction.
Displaced conflict occurs when people are fighting for a reason other than the reason they actually have conflict. So, they may quarrel about what furniture to buy, although in fact they do not like the lack of a lot of money.
An incorrectly attributed conflict develops when a person argues about what the opponent did, although he himself asked him to do it, but forgot.
Types of intrapersonal conflicts

Sometimes a person doesn't need a partner for a conflict to arise. Often people begin to conflict within themselves. This is the surest way to become unhappy - not being able to choose, not knowing what to do, doubting and hesitating. The types of intrapersonal conflicts are as follows:
- Role-playing is a conflict of roles that a person can and should play. Sometimes a person is required to behave that he cannot or does not want to play, but is forced to. Sometimes a person has more opportunities, but he is forced to limit himself, because this does not fit into social norms of behavior. Sometimes it is difficult to switch roles, for example, from work to family.
- Motivational - often it is about the opposition of instinctive desires and moral needs. Tension is relieved when a person finds a solution to how to satisfy both sides.
- Cognitive is a clash of two knowledge, perceptions, ideas. A person is often faced with the contradiction between the desired and the actual, the real. When a person does not receive what he wants, based on the ideas that he is guided by, then it becomes necessary to study other knowledge that contradicts the existing one. It is sometimes difficult for a person to accept what is contrary to his views.
The surest way to become an unhappy person is to have internal conflicts, that is, to conflict with yourself in views, opinions, desires. Often, such a person who is incapable of making decisions succumbs to the influence of public opinion, which is ready to say what to do in a given situation. However, this will not solve his problem, but will only allow for a while to reduce the level of tension within himself.
Types of interpersonal conflicts
The most common conflict is interpersonal. A person interacts with individual members of society, where one can inevitably face conflicting beliefs, desires, needs, interests. This type of conflict flares up very often, which forces people to avoid it even more. However, this is not possible. Between people, as between holistic individual systems, disputes will always arise, since everyone has their own opinion, needs, aspirations, etc.
Quarrels and scandals in the family are normal in society. Of course, spouses may be unhappy with the current state of affairs. However, if this discontent comes to screaming and even assault, it only means that the partners do not have constructive communication. They are focused on achieving only their desires, which they defend, and not on finding a compromise that will take into account the interests of both parties.
No one is clearly worried about quarrels and scandals in the family. However, all these conflict situations do not go unnoticed. They leave a wound in the soul of each partner, give rise to doubts, insecurity in feelings and union. No need to cut, itch, grumble. When this happens, the spouse is not nagging his opponent, but his own relationship. You need to learn to be more calm and sometimes even positive about what happens.
One of the reasons that generates discontent is ingratitude. Spouses focus on what they don't like, rather than on the positive aspects of each other and what they had. They want to achieve the relationship that appears to them in their heads. And each of them represents something different. It is the clash of these ideas that leads to quarrels. They are not grateful for the union that they have built in reality, because they want to live in the relationship that they imagine.
Please note that if you consider your spouse to be bad, then soon you may not have any spouse at all. If you love your wife (husband) and strive to create a strong family, then only you owe, and your wife (husband) owes nothing. Train to demand from yourself, not from your partner. Quarrels and scandals are usually based on this: you want some changes and actions on the part of your loved one, but you yourself are not going to do or change anything. Learn not to demand anything from your partner, let him decide what he should do for your relationship. Demand only from yourself. Otherwise, you will not cut your spouse, but your relationship with him.
Types of interpersonal conflicts:
- Values, interests, normative - what is involved in the quarrel?
- Sharp, lingering, sluggish - how quickly does the quarrel develop? Acutes occur here and now in direct confrontation. Prolonged ones last for several days, months, years and touch on significant values and topics. Sluggish are low-intensity, occur periodically.
Types of conflicts in the organization
Conflicts that arise in an organization can be perceived both positively and negatively. Much depends on the level at which they occur and how they are resolved. If conflicts arise between colleagues who try to harm each other, then the collision can lead to a decrease in the efficiency and productivity of people. If the conflict occurs in the process of solving a labor issue, then it can become productive due to the expression of different points of view and the possibility of finding a solution. Types of conflicts in the organization:
- Horizontal, vertical and blended. Horizontal conflicts arise between colleagues of equal status. Vertical conflicts, for example, occur between subordinates and superiors.
- Business and personal. Business concerns only business issues. Personal affects the personalities of people and their lives.
- Symmetrical and asymmetrical. In symmetrical conflicts, the parties equally lose and gain. In asymmetric conflicts, one of the parties loses, loses more than the other.
- Hidden and open. Latent conflicts arise between two people who may not express their dislike for a long time. Open conflicts are often manifested and even managed by management.
- Destructive and constructive. Destructive conflicts develop when the result, development, progress of work is not achieved. Constructive conflicts lead to progress, development, progress towards the goal.
- Intrapersonal, interpersonal, between employee and group, intergroup.
- Violent and non-violent.
- Internal and external.
- Intentional and spontaneous.
- Long term and short term.
- Recurring and one-off
- Subjective and objective, false.
The essence of social conflicts
Why do people conflict? People have already found the answer to this question, but they continue to conflict, since the problem often lies not in "why?", But in "what contributes?" The essence of social conflicts lies in the fact that each person has his own established system of views, opinions, ideas, interests, needs, etc. When an interlocutor meets who contradicts these values with his views, then a hostile attitude towards him arises, due to which a conflict flares up ...
A quarrel is not a clash of two opinions, but the desires of opponents to win in their views.
Quarrels, scandals, disputes, wars, conflicts - we are talking about the confrontation of two or more parties, where each is trying to defend their opinion, prove their case, gain power, force rivals to submit, etc. Peace-loving readers may have a question: is it possible can we live without such collisions at all? Psychologists note that everything is possible, but not in the situation that develops in society.
First, you should decide on the mechanism by which any conflict situations occur. A topic arises, a question, people can get some useful resource. If people have different goals, opinions and plans, then they begin to conflict with the intention to prove their superiority and get a useful resource for themselves or force others to live by their direction. A conflict is a confrontation between different opinions, where everyone is trying to achieve something beneficial for themselves.
Quarrels may not exist among people only in one case: when everyone begins to think the same way, when collective thinking reigns.
The modern world is the era of individualization. Selfishness, "life for your own good", freedom are actively promoted. Each person is individual, and he must cultivate this in himself. It is the individual person who can think differently from everyone else. There is no collectivism, compromise, submissiveness.
Quarrels happen because each person thinks about himself. In a scandal, each side strives to prove that it is the best, correct, and intelligent one. In the era of individuality, no relationship is complete without quarrels and scandals.
Things are very different when people think the same way. They have nothing to defend. There is no "mine", there is only "our". Here everyone is equal, the same. In such a society, there simply cannot be confrontation. Collectivism leads to the creation of one large organism, which is stronger than any individual person. However, here a person must abandon individuality, egoism, self and desires.
Take the family as an example. If partners act together, make concessions, think the same way, strive for one goal, then quarrels rarely occur in their relationship. They live for the sake of a common family. If the partners each take care of themselves, insist on their righteousness, strive for different goals, then here conflicts become an obligatory attribute. Each partner will try to "bend under himself", to adjust. Here, everyone will want to win back power and force the other to live for the sake of personal desires.
The conflict begins when external circumstances speak of the impossibility of realizing a certain human need. Participants in the conflict can:
- The witnesses are those who are watching the quarrel.
- Instigators - those who prod, inflame the quarrel even more.
- Aides are those who inflame a quarrel through advice, tools, recommendations.
- Mediators are those who try to resolve, pacify the conflict.
- Participants in the conflict are those who directly argue.
Types of political conflicts
Various types of political conflicts have existed at all times. People waged wars, conquered foreign lands, plundered and killed other peoples. All this is part of the conflict, which, on the one hand, is aimed at the development and strengthening of one state, on the other hand, at the infringement of the freedom and rights of another country.
Conflicts between countries arise at the level that one state in one way or another begins to infringe on the existence and activities of another. When mutual understanding is not achieved, then political wars begin.
Types of political conflicts:
- Interstate, domestic, foreign.
- The struggle of totalitarian regimes, democratic systems.
- Status-role-playing struggle, confrontation between values and identification, clash of interests.
Sometimes states can argue over the different state structures that they adhere to, as well as the goals and directions of their activities.
Conflict Management

Conflicts have always been and will continue to arise. There are no two like-minded people, groups, states, which would not collide with opposing opinions or needs. That is why conflict management becomes important if participants want to get out of the current situations with the least losses for themselves.
The resolution of the conflict is understood as the fact that all parties came to a common conclusion, decision or opinion, after which they calmly got out of the situation. Often this is either agreeing an opinion, reaching a compromise, or understanding that it is necessary to disagree and not cooperate further. These methods can be called positive ways to resolve the conflict. A negative way to resolve a dispute is the destruction, degradation, destruction of one or all of the parties to the conflict.
The site of psychological assistance, the site insists that people learn to resolve conflict situations, do not delay their elimination and do not develop. This can be done in the following ways:
- Negotiation.
- Avoiding confrontation.
- Finding a compromise.
- Smoothing issues.
- Solution.
Answer the question: do you want to quarrel or solve a problem? This gives an understanding that a person begins to behave differently when he seeks to quarrel or when he wants to solve a problem.
When you strive to quarrel, then you try to find flaws in your interlocutor in order to criticize them and make them guilty. You start doing only those things that will offend your interlocutor. You scream with pleasure, because emotions are raging in you.
When you want to solve a problem, you are deliberately calm. You do not shout even if you are shouted at. You are ready to listen to the interlocutor, to be silent in order to think over his words. You are nervous, but you understand that emotions will not help you right now. You should try to think as soberly as possible, realizing what you want and hearing the opinion of your opponent.
Observe yourself or your partner - and notice what the person is striving for. The one who quarrels only "muddies the waters": there is no conversation, there is only a verbal competition - who will win? Someone who is trying to solve a problem behaves calmly in a stressful situation, because he wants to think about the issue and solve it. When will the dispute be resolved faster? Only when both you and your opponent strive to solve the problem, and not to win verbally, any issues will be resolved quickly and without serious losses.
How to end a fight quickly? There are many options for how to do this. But often the question is not how to do this, but whether at least one of the disputing parties wants to end the useless conversation.
The fact that a quarrel is a useless dialogue has to be said. People often forget that when they are under the influence of negative emotions and indignation, they do not seek to solve the problem, but want to prove their opinion, action, point of view. It seems to them that they did everything right, so they enter into a loud conversation, trying to prove it. Their opponents prove that they were right in their actions and decisions, and everyone else was wrong. Thus, a quarrel is a conversation where everyone considers himself right, tries to achieve only this goal and does not seek to hear the other person.
People don't always want to end a fight. Until they achieve their goal, that is, the recognition of their innocence, they will not back down. Therefore, you first need to want to get away from the quarrel, and then take the appropriate steps.
How to end a fight quickly?
- You can go to another place where your opponent will not be.
- You can say: "Do as you know" or "Do as you want." Thus, you do not agree with the correctness of your interlocutor, but you also do not deny that he is right.
Other methods are less effective because your opponent may not want to end the argument with you. Your task is to be at a distant distance from your interlocutor, so that neither you see him, nor he you.
Outcome
Conflict is inherent in all people. Everyone knows how to quarrel with others. However, managing and resolving conflicts is an art that not everyone is taught. If a person knows how to calm conflicts, then he knows how to manage people, which requires a lot of knowledge and effort. The result is the ability to organize your own life, make it happier and more orderly.
People have already ruined many relationships due to the fact that they did not want to stop the quarrel. Often people died due to conflicts that flared up between groups and even entire states. The prognosis becomes unpredictable when people start to conflict. However, the result depends entirely on what decisions and actions they will take.
You can lead the dialogue in a constructive direction if you want to solve the problem, and not prove your case. You can lead a dispute in a destructive direction when there is no desire to cooperate and find a compromise. People often refuse to accept responsibility for the results achieved as a result of the conflict. Although in reality they achieved everything themselves.