Whether at many tsmv comes to light. Cytomegalovirus (Inclusion disease, Viral disease of the salivary glands, Inclusive cytomegaly, Cytomegalovirus infection (CMV))
Cytomegalovirus infection- a widespread viral infection, characterized by a variety of manifestations from an asymptomatic course up to the most severe generalized forms with damage to internal organs and the central nervous system. During transplacental transmission of infection, the fetus may be affected.
The level of infection with cytomegalovirus infection and the degree of infection of the body depends on socio-economic conditions, ethnicity, health care practices for newborns and young children, and the time of sexual intercourse.
The proportion of CMV carriers in Russia is about 90%.
Once in the cells of the human body, cytomegalovirus is able to remain in it for life.
Pathogen(Cytomegalovirus hominis) belongs to the herpes viruses (family Herpesviridae)
Man is the only reservoir and source of infection. The virus can be found in saliva, milk, urine, feces, seminal fluid, and cervical secretions.
In 20-30% of healthy pregnant women, CMV is present in saliva, 3-10% in urine, 5-20% in the cervical canal or vaginal secretions.
The blood of about 1% of donors contains cytomegalovirus.
Although viral particles can be found throughout the body, cytomegalovirus is most often associated with the salivary glands.
Methods of transmission of infection
Previously, cytomegalovirus infection was called "kissing disease", as it was believed that it was transmitted only through kissing.
Cytomegalovirus infection spreads not only through saliva during close contacts, but also during sexual contact, through blood, from a pregnant mother to her fetus, as well as through household contact.
The greatest danger to the fetus is the primary infection in early pregnancy. The pathogen that entered the fetus through the blood in the early stages of pregnancy causes the formation of congenital malformations.
If there is an infection in the cervical canal in a pregnant woman, infection of the fetus can occur during childbirth, during the passage of the fetus through the birth canal.
The main route of infection for a child up to a year is the transmission of the virus through breast milk.
The source of infection for children under 5-6 years old are mothers who excrete the virus with saliva or urine.
Children who are in organized groups become infected more often by contact-household.
Infection at the age of 16-30 occurs, as a rule, through close contact through kissing and sexual contact.
Blood transfusions and other blood manipulations can also lead to infection with cytomegalovirus.
Symptoms of cytomegalovirus infection
In a healthy body, the virus does not manifest itself in any way, but it can be deadly for people with immunodeficiencies: for HIV-infected people, patients, after organ transplantation, as well as newborns awaiting transplantation.
With congenital cytomegalovirus infection, the nature of the damage to the fetus depends on the period of its infection. Especially dangerous is acute infection of the mother in the first 20 weeks of pregnancy.
What can infection in early pregnancy lead to?
Spontaneous miscarriage;
Intrauterine fetal death;
stillbirth;
Gross congenital malformations (anencephaly, microcephaly, hydrocephalus, violation of the structure of the lungs, bronchial tree, anomalies in the structure of the kidneys, etc.).
Congenital malformations in most cases are incompatible with life.
When infected with CMV in the later stages of pregnancy, the formation of malformations does not occur.
What causes the infection of a child with cytomegalovirus during childbirth?
Clinical signs usually appear 1-2 months after delivery.
Damage to the lungs (pneumonia);
Protracted jaundice;
Enlargement of the liver, spleen;
kidney disease;
Damage to the gastrointestinal tract;
The disease can be long-term relapsing.
The maximum lethality from cytomegalovirus infection falls on 2-4 months.
Prevention of cytomegalovirus infection
During counseling, pregnant women or those planning a pregnancy should be informed about the main sources and routes of infection (sexual contact with CMV-infected partners, physical contact during daily care of a child at home, or professional contact with young children in hospitals, orphanages, preschool institutions).
To reduce the risk of primary CMV infection in pregnant women, use barrier contraceptives during sexual intercourse, follow the rules of personal hygiene (wash hands after touching door handles, touching toys stained with saliva, urine of a child), it is not recommended to finish eating or drinking after children, use a joint dishes, you can not lick the nipple. Kissing on the lips of infants, who can excrete the virus in saliva, should be avoided.
When planning a blood transfusion for a premature baby or adult with a weakened immune system, it is necessary to test the blood and its components for the presence of CMV DNA.
A type: —
Class: —
Order: herpesvirales
Family: Herpesviridae (Herpesviruses)
Subfamily: Betaherpesvirinae (betaherpesviruses)
Genus: Cytomegalovirus, CMV
International scientific name: Cytomegalovirus
Cytomegalovirus (Cytomegalovirus, CMV, CMV)- a genus of herpesviruses belonging to the subfamily of betaherpesviruses, which is able to infect people, causing the development of the disease of the same name "cytomegalovirus infection", or as it is also called "cytomegaly".
The trickiness of CMV lies in its similarity to the tissues of the salivary glands and its latent stay in the body, which is why it is not immediately possible to identify it to the immune system and develop the necessary antibodies. In addition, together with the flow of lymph and blood, CMV is able to move almost throughout the body for a very long time, making itself felt only when the immune system is weakened or when the body is constantly infected with new portions from the carrier.
When entering a cell, CMV leads to an increase in its size, making it relatively gigantic.
According to medical statistics, the presence of antibodies to CMV in the body is detected in adolescents in 10-15% of cases, and in middle-aged people in 40% of cases. Also, higher infection rates were observed among the fair sex of childbearing age - up to 80%.
As S.C. wrote Dollard, S.A. Staras and other co-authors in the journal "Clinical Infectious Diseases" (11.2006, No. 43) in the USA from 1988 to 1994 among the population of 80 years and above, traces of cytomegalovirus were found in 90.8% of patients 1 .
Epidemiology, causes
Cytomegalovirus is not highly contagious. Infection usually occurs through prolonged and close contact with a virus carrier.
Infection with cytomegalovirus occurs in the following ways:
- Sexual way (with sexual intimacy, kissing) is the most common way to pick up a CMV infection,
- The airborne route is the second place among the routes of infection, which includes coughing or talking with the release of infected microdroplets into the external environment;
- Blood transfusion route - for blood transfusions and organ transplants;
- Transplacental route - the infection is transmitted from the mother to the unborn baby during its gestation.
The risk group includes:
- People working or studying in large groups;
- Persons leading a promiscuous sexual life;
- Persons who have chronic, constantly weakening immunity;
- Pregnant;
- people;
- People who are undergoing hemodialysis procedures;
- Persons who have had organ transplants or operations;
- Past courses of chemotherapy;
- Health workers.
Weakened immunity
A decrease in the reactivity of the immune system is secondary (after infection), but no less important factor in the spread of infection in the body and the development of the disease. If the immune system is strong, then a person, firstly, may not feel his infection, and secondly, if there are symptoms, then it is minimal, more like a cold.
Contribute to a decrease in immunity - smoking, uncontrolled intake of medications, the presence of chronic infections, irregular meals, a sedentary lifestyle.
Classification and characteristics
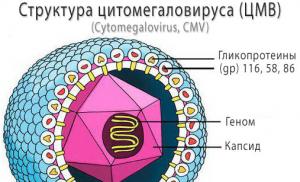
The size of the cytomegalovirus virion in diameter ranges from 150 to 200 nm, externally enclosed in an icosahendric, spherical or pleomorphic capsid (T=16), with 162 capsomeres. The CMV envelope is covered with glycoproteins (gp) 116, 58 and 86. The main protein of the viral matrix is pp65, and the capsid is p70.

As of 2019, scientists know 11 types of cytomegalovirus:
- Aotine betaherpesvirus 1 (Aotin betaherpesvirus 1, synonym - Aotine herpesvirus 1);
- Cebine betaherpesvirus 1 (Cebine betaherpesvirus 1, synonym - Cebine herpesvirus 1);
- Cercopithecine betaherpesvirus 5 (monkey betaherpesvirus 5, synonym - Cercopithecine herpesvirus 5);
- Human betaherpesvirus 5 typus (Human herpes virus type 5);
- Macacine betaherpesvirus 3 (Macacine betaherpesvirus 3, synonym - Macacine herpesvirus 3);
- Macacine betaherpesvirus 8 (Macacin betagrepesvirus 8, synonym - Macacine herpesvirus 8);
- Mandrilline betaherpesvirus 1 (Mandrilline begatherpesvirus 1);
- Panine betaherpesvirus 2 (Chimpanzee lichen virus 2, synonym - Panine herpesvirus 2);
- Papiine betaherpesvirus 3 (Papiin betaherpesvirus 3, synonym - Papiine herpesvirus 3);
- Papiine betaherpesvirus 4 (Papiin betaherpesvirus 4, synonym - Papiine herpesvirus 4);
- Saimiriine betaherpesvirus 4 (Seymirin betaherpesvirus 3, synonym - Saimiriine herpesvirus 4).
The disease "cytomegaly" is caused by a species - the human herpes virus type 5.
Symptoms
With weakened immunity- the infection negatively affects almost any of the organs or the entire body as a whole. The target organs are primarily the liver, kidneys, spleen, and pancreas. Moving from these "reservoirs" CMV contributes to inflammatory processes in the respiratory, digestive, genitourinary, gastrointestinal tract, causing diseases such as -, and others. In addition to the characteristic signs of the above diseases, salivary glands and localized pain are also noted.
Complications
The most serious consequence of CMV infection is death. This state of affairs is more typical for HIV-infected people and future babies, because. infection of the fetus often ends in miscarriage (especially infection before the 12th week of pregnancy).
Infection with cytomegalovirus of the fetus, even in the case of a timely birth, does not always guarantee the normal health of the newborn. With a congenital disease of cytomegalovirus infection, there are cases of damage to the brain, nervous system, mental and physical health disorders, and others.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of CMV includes:
- ELISA, which shows in the blood the presence of immunoglobulins M (IgM), G (IgG) and lymphocytes CD4, CD8;
- Cytological examination of biomaterials for the presence in the body of giant cells formed by cytomegaloviruses;
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) in saliva and urine.
Treatment
Treatment of cytomegalovirus includes antiviral therapy, symptomatic treatment and the use of drugs / means / procedures aimed at strengthening the body.
1. Drug treatment
1.1. Antiviral therapy
A mild course of cytomegalovirus infection in many cases is perceived by a person as a common ARVI, the symptoms of which quickly disappear with general strengthening therapy and do not require the use of specific antiviral drugs. Immunity takes control of the infection and prevents it from forming pathological processes. An exception may be pregnant women and children.
In general, specific antiviral therapy includes taking antiviral drugs that are effective in combating herpes virus infection.
Popular drugs against herpesviruses are Valaciclovir, Ganciclovir, Valganciclovir, Famciclovir, Penciclovir.
To increase the reactivity of the immune system, the doctor may prescribe interferon preparations.
Antibiotics for cytomegalovirus are used exclusively when a secondary is attached, because. in relation to CMV, they are ineffective, and even vice versa, they can harm, further lowering the reactivity of the immune system.
1.2. Symptomatic treatment
Symptomatic treatment is aimed at maintaining health, suppressing the acute inflammatory process and accelerating the recovery of a person.
To reduce body temperature, which for a long time and does not fall from high levels to apply - "", "", "", "Panadol". Wiping and compresses on a water-vinegar basis, which are recommended in this situation for children, have a milder effect against fever.
To improve nasal breathing when laying the nasal passages (sinuses), vasoconstrictors are used - Farmazolin, Nazivin, Otrivin. However, remember that these drops are very addictive, which is why many people sit on them for many, many years, because. mucous membranes get used and can no longer breathe without additional help. Children with a runny nose are recommended to rinse their nose with soda-salt solutions, which are already in convenient containers for use - Aquamaris.
In the fight against coughing, antitussives will help, which at the beginning will help to convert a dry cough into a wet form, thin the sputum and remove it from the respiratory tract - "", "Gerbion", "ACC".
If your ears are stuffed up, Otipax drops can be distinguished from the last, but effective means.
It is very important for viral, bacterial and other infections to drink plenty of fluids - mostly water. However, teas and infusions with raspberries are very useful.
1.3. Experimental Methods
Among the latest developments in specific antiviral therapy is the introduction into the body of a specific CRISPR associated protein 9 (Cas9) protein, which forms adaptive immunity that detects and destroys pathogenic infectious microorganisms even hidden for natural immunity.
2. Mode and special instructions
To speed up recovery and avoid spreading the infection to other people during illness, it is recommended to lie down at home, and also avoid sexual intercourse. By the way, if intimacy was within 2 months before the appearance of signs of cytomegaly, diagnosis, and when the diagnosis is confirmed, both partners must undergo a course of treatment.
For personal use, the patient is given separate dishes, and body care items, of course, and without this, each person should have their own.
It is extremely important to stop drinking alcohol and smoking.
Be sure to keep yourself from hypothermia!
In food, focus on eating foods rich in and.
Prevention
Prevention of cytomegalovirus includes the following preventive measures:
- Compliance;
- Complete nutrition;
- Avoidance of hypothermia;
- Maintaining an active lifestyle, moving more;
- When the first symptoms appear, consult a doctor in a timely manner to avoid chronic infections;
- Avoid stress, give up smoking and alcohol, incl. low alcohol products;
- During the period, avoid crowded places, and supply the body with an additional amount of vitamins and macro-microelements.
Which doctor should I contact if I have symptoms of cytomegalovirus?
Video
Character, the causative agent of which belongs to the herpes family. Pathology can proceed both asymptomatically and significantly worsen the well-being and quality of life of a person, affecting the internal organs and the central nervous system. According to statistics, almost half of the world's population are carriers of the virus. However, most people are not even aware of its presence.
What it is?
CMV infection is a disease, the development mechanism of which is as follows: a virus containing DNA molecules enters the human body and inserts its genome into the host cells. As a result of this process, the process of their pathological change is launched. The affected cells increase in size, that is, they become cytomegalic, and they themselves begin to produce the virus. Due to this, there is a violation of energy and synthetic processes. Unlike other viruses belonging to the herpes family, this pathogen has a rather long replication (reproduction) process, which prevents the formation of stable immunity.
You can only get infected from a sick person. It is important to know that in the body of both women and men, CMV infection remains forever. In the dormant form, it does not manifest itself in any way and does not have a negative impact. The transition to the acute phase occurs when the body's defenses are weakened.
In the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10), CMV infections are assigned the code B25.
Ways of infection
The degree of contagiousness of cytomegaly is not high. In order for the virus to be transmitted from a sick person to a healthy one, it is necessary to have long and close contact with the carrier of the infection.
You can become infected in the following ways:
- Airborne (during a conversation, when sneezing, coughing or kissing).
- Sexual (during sexual contact, the virus is contained in the female secret and in the semen of men).
- Hemotransfusion (during the transfusion of blood or its components, as well as during tissue and organ transplantation).
- Transplacental (during pregnancy from mother to child).
When CMV enters the body, the infection does not cause any symptoms only if the person has high immunity. In this case, the pathogen is found in the biomaterial of an infected person. As soon as the body's defenses are weakened, the disease can go into an active form. Most often in a person in the process of diagnosis (along with CMV infection) EBV - Epstein-Barr virus is detected. It also belongs to the herpes family and does not have a negative effect on high immunity.

Symptoms
CMV infection is persistent, that is, having a chronic character. It is characterized by a variety of clinical manifestations, the severity of which depends on the form of pathology.
Specialists subdivide CMV infection into the following types:
- Congenital. The main symptom of the disease is an increase in the size of the spleen and liver. Against the background of the development of the disease, jaundice and internal bleeding may occur. In addition, there are signs of disorders of the central nervous system.
- Sharp. It is characterized by the presence of symptoms similar to those of a common cold. Also on the tongue and gums of the patient, you can notice a white coating.
- Generalized. It is characterized by the development of inflammatory processes in the pancreas, kidneys and adrenal glands, spleen. As a rule, a bacterial infection is also detected during the diagnostic process.
Currently, it is extremely difficult to determine the duration of the course of CMV infection. The latent form is conditionally designated as an interval of 1-2 months, since it is impossible to determine the initial moment of the development of the disease.
Doctors identify several possible options for the development of pathology, each of which is characterized by a certain set of signs:
- The transition to the active phase occurs during the normal functioning of the body's defense system. It should be noted that such cases are extremely rare. The development of the disease is accompanied by fever, muscle weakness, deterioration in general well-being. In addition, a person's lymph nodes are enlarged. In most cases, the disease goes away on its own, which is a consequence of the powerful work of the body's defenses. As a rule, people do not even realize that they have suffered an acute phase of CMV infection, attributing everything to a cold.
- The active form of the disease passes when the immune system is weakened. In such cases, they speak of an illness. Pathology manifests itself in the defeat of the pancreas, liver, kidneys, lungs and retina. Most often it occurs in people with severe immunodeficiency, leukemia, hemoblastosis, as well as in those who have recently undergone transplantation of any internal organ.
- Symptoms appear shortly after the birth of a child who has been infected in utero. Signs of CMV infection in this case are: a delay in physical development, a violation of the formation of the jaws, poor hearing and vision. In addition, there is an increase in internal organs (usually the spleen, liver or kidneys).
In males, the infection in most cases is dormant. The transition to the active phase is carried out with a significant weakening of the body's defenses, which is the result of a cold or prolonged exposure to stress.
The symptoms are:
- increased body temperature;
- chills;
- nasal congestion;
- headache;
- rash;
- inflammatory processes in the joints.
Thus, the manifestations of infection are similar to those of acute respiratory infections and acute respiratory viral infections. The fundamental difference from colds is the duration of the preservation of the clinical picture. With cytomegaly, symptoms bother a person for about 1 month.

Diagnostics
If you experience anxiety symptoms, you should consult a therapist. If a specialist suspects the presence of cytomegalovirus, he will refer you to a venereologist or dermatovenereologist for a consultation.
During the reception, the doctor conducts a primary diagnosis of CMV infection, including a survey and examination. The specialist needs to provide information regarding the symptoms present and how long ago they occurred. After that, the doctor assesses the condition of the skin and palpates the internal organs to detect their increase in size.
If a cytomegalovirus infection is suspected, the specialist issues a referral for the following laboratory tests:
- cultural sowing. Biomaterial can be blood, urine, saliva or semen. During the study, it is possible not only to identify CMV infection in adults and children, but also to understand what degree of activity the disease has. In addition, this analysis is also prescribed after the course of treatment. With its help, it is possible to evaluate the effectiveness of the prescribed therapeutic regimen. The study is also informative for individuals with both CMV and HSV infection (herpes simplex virus).
- Light microscopy. The essence of the method lies in a thorough study of the biomaterial, during which pathologically altered cells of huge sizes with specific intranuclear inclusions are detected.
- enzyme immunoassay. This is a blood test that detects antibodies to CMV infection. The method is not informative for immunodeficiency. This is due to the fact that in this state, the process of producing antibodies does not occur.
- DNA diagnostics. The study of the biomaterial is carried out in order to detect these molecules. The disadvantage of the method is that it detects only the presence of an infection, and it is impossible to obtain information regarding the degree of activity with its help.
As a rule, doctors prescribe several types of studies at once. This is because the disease can have various forms, and one method is not enough to make an accurate diagnosis.

Conservative therapy
Information on how to treat CMV infection should only be provided by a physician based on diagnostic results.
Currently, there are no drugs whose action can completely rid the body of the pathogen. According to the guidelines, uncomplicated CMV infection does not require treatment. In other cases, it is aimed at getting rid of unpleasant symptoms. To eliminate intoxication, it is necessary to consume at least 2.5 liters of pure non-carbonated water per day.
In most cases, the treatment of CMV infection in adults is carried out with the drug "Ganciclovir". This is an antiviral agent that is prescribed only when the immune system is weakened. It is available in the form of tablets and solution. Injections are indicated for patients with severe forms of the disease.
In the treatment of pathology in people with immunodeficiency, the drug "Foscarnet" showed the greatest effectiveness. But it can also cause serious complications, and therefore it must be taken with caution and according to a strict regimen drawn up by a doctor.
During treatment, it is not required to adhere to any diet or a specific daily routine.

Cytomegalovirus infection during pregnancy
During the period of bearing a child, the disease poses a danger to the fetus. In some cases, it serves as an indication for artificial termination of pregnancy. The most serious consequences are observed during primary infection. This is due to the fact that in the mother's body there are no antibodies to the pathogen. It is necessary to know that CMV infection in women is an ailment that is transmitted at the time of conception, through the placenta and during delivery. In addition, the pathogen enters the body of the child along with breast milk.
CMV infection during pregnancy can provoke intrauterine death of the child, especially in the first trimester. If the gestational period is completed successfully, they speak of a congenital form of the disease. In this case, the symptoms in the infant appear immediately or after 2-5 years.
However, one should not think that CMV infection in women is such a pathology that is a sentence. Currently, pregnant women at risk are given special attention. With the timely provision of medical care, the likelihood that the child will be born healthy is significantly increased.
In order to prevent infection, a pregnant woman is advised to avoid mass gatherings of people. If it does, the following symptoms occur:
- general weakness;
- slight increase in body temperature;
- aching sensation in muscles and joints.
In many cases, the course of the disease is not accompanied by the appearance of any alarming signs. As a rule, pathology is detected in the process of standard diagnostics.
Treatment of CMV infection in pregnant women involves taking antiviral and immunomodulating agents. If a woman is a carrier of a pathogen that is in an inactive phase, therapy is not required. But in this case, she needs to monitor her health and avoid situations that weaken the body's defenses.

Cytomegalovirus infection in children
In most cases, infection occurs in utero. In this case, only about 17% of the pathogen manifests itself with various signs.
Symptoms of CMV infection in children are:
- jaundice;
- enlargement of the liver and spleen in size;
- low hemoglobin level;
- changes in the composition of the blood;
- disturbances in the work of the central nervous system;
- damage to the visual system and hearing aid;
- rashes on the skin;
- the presence in the stool of an admixture of liquid connective tissue.
In severe cases, the vital activity of pathogenic microorganisms negatively affects the brain. At the same time, the child has convulsions, and hands often tremble.
Shortly after birth, the baby's blood is taken for analysis. The presence of antibodies in it does not mean that the child may develop an acute form of the disease. Children with an identified infection should be regularly examined by a doctor to prevent the occurrence of various complications.
In the acquired form of the disease (for example, if the infection occurred in a kindergarten through saliva on toys), the following symptoms appear:
- increased body temperature;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- chills;
- runny nose;
- drowsiness.
In addition, the endocrine and respiratory systems are often affected.
Treatment of CMV infection in children involves taking antiviral and immunomodulating agents.

Possible Complications
The negative consequences of the disease are very diverse. The following disorders are most often diagnosed in patients:
- hepatitis;
- stomach and duodenal ulcer;
- esophagitis;
- pancreatitis;
- diabetes;
- significant deterioration of vision up to its complete loss;
- low blood pressure;
- anorexia;
- hyperpigmentation of the skin;
- mental and neurological disorders;
- deafness;
- pathology of the cardiovascular system.
The above disorders are only a part of the possible complications. It is impossible to predict which organ will be affected. In this regard, if CMV infection is detected, the recommendations of the attending physician should be followed regularly. In addition, it is necessary to periodically donate blood to timely detect the transition of the pathogen into the active phase.
Prevention
Currently, there is no vaccine that would reliably protect a person from infection. In addition, standard measures (for example, good personal hygiene) also do not reduce the likelihood of infection.
The issue of prevention in relation to persons at risk is extremely acute. To reduce the likelihood of infection, they are prescribed immunomodulators and antiviral drugs. In addition, women planning a pregnancy need to undergo a thorough examination.
Finally
Cytomegalovirus infection is a chronic disease. Its causative agent belongs to the herpes family and, when it enters the human body, remains in it forever. With strong immunity, the pathogen does not affect the functioning of internal organs and systems. Activation of the infection occurs with a significant weakening of the body's defenses.
Currently, there is no treatment that can completely get rid of CMV infection. The aim of therapy is to eliminate symptoms and prevent the development of complications. Treatment is with antiviral and immunomodulatory drugs. Compliance with standard preventive measures also does not reduce the risk of infection.
Cytomegalovirus infection (CMVI)
In this article, we will look at what a cytomegalovirus infection is, how it manifests itself, how to treat, and much more regarding this infection.
Introduction
Cytomegalovirus infection (CMVI) is a viral infection that can affect one part of the body, such as the eyes, or spread throughout the body.
Before the advent of effective therapy for human immunodeficiency virus (commonly referred to as highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART)) people with co-morbidity were more likely to develop CMVI.
Today, thanks to HAART, cases of cytomegalovirus infection in people with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) are relatively rare. People with HIV whose CD4 cell count is below 50 cells/mm 3 are most at risk of developing the disease. Fortunately, the treatment of cytomegalovirus infection has improved significantly in recent years.
What is a cytomegalovirus infection?
Cytomegalovirus infection or abbr. CMVI is a serious infection caused by a virus called cytomegalovirus, or abbr. CMV (lat. Cytomegalovirus, CMV). This virus is related to the herpes viruses that cause chickenpox and infectious mononucleosis (benign lymphoblastosis).
CMV is one of the many infections that develop in people living with HIV, referred to as opportunistic infections.
Opportunistic infections only occur when a person's immune system is severely weakened and the body becomes vulnerable to infections that would not otherwise affect the person's body.
Most healthy adults carry CMV but don't know it because the virus doesn't cause them any symptoms, and generally doesn't show up at all. However, in people with severely weakened immune systems, CMV can cause infectious mononucleosis.
Cytomegalovirus infection can also cause serious illness in various parts of the body, most commonly in the eye area (see symptoms section below).
Who is in danger CMV ?
People with weakened immune systems due to the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), cancer, long-term use of drugs that weaken the immune system, or people with organ and tissue transplants are most at risk of developing cytomegalovirus infection.
People living with HIV are most at risk of developing CMV and typically have the following:
- the number of CD4 lymphocytes below 50 cells/mm 3 ;
- are not taking or responding to highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART);
- previously had CMV or other life-threatening infections.
Symptoms and signs of CMVI
The most common complication and manifestation of cytomegalovirus infection is:
- retinitis- this includes inflammation of the light-sensitive part of the eye, the retina. CMV infects these cells, causing inflammation and death of these cells. Usually, people with CMV retinitis may initially have no or gradually worsening symptoms that affect vision. Others experience more severe symptoms. Retinitis can cause blurred vision, blind spots, flashes of light, and dark spots in the eyes that seem to float in your field of vision, sometimes referred to as "floating eyes".
Two-thirds of people initially diagnosed with retinitis have the disease in only one eye; however, without highly active antiretroviral therapy or anti-CMV therapy, most people develop retinitis in both eyes within 10 to 21 days of the onset of symptoms.
Left untreated, retinitis leads to permanent blindness within three to six months. If you have vision problems, contact your doctor immediately.
Other diseases and symptoms of CMV may include (but are not limited to):
- esophagitis- when a cytomegalovirus infection affects the esophagus (the passage that connects the mouth to the stomach). Symptoms of this complication may include fever, nausea, painful swallowing, and swollen lymph nodes.
- colitis- when CMV affects the colon (the longest part of the colon). Symptoms include fever, weight loss, abdominal pain, and a general feeling of being unwell.
- diseases of the central nervous system (CNS)- when the infection affects the brain and spinal cord. Symptoms include confusion, fatigue, fever, cramps, weakness and numbness in the legs, and loss of bowel and bladder control.
- - if CMV affects the lungs (rare in HIV-positive people).
A cytomegalovirus infection that has spread throughout the body can make a person feel like they have mononucleosis. When the infection has spread throughout the body, it is called dissemination.
Symptoms of disseminated CMVI may include sudden fatigue, joint stiffness, muscle pain, fever, swollen lymph nodes, sore throat, and loss of appetite.

Because CMVI can be life-threatening if not treated early, it is important that you call your doctor as soon as possible if you have HIV and experience any symptoms of CMV, regardless of your CD4 count.
Diagnosis of CMVI
Blood and urine tests are often used to detect and measure CMVI. A biopsy (a procedure in which a doctor removes a small piece of tissue that is then examined under a microscope in a laboratory) may be needed to confirm the diagnosis of cytomegalovirus infection, unless the disease affects the eyes or the central nervous system.
If your doctor suspects cytomegalovirus retinitis, he will refer you to an optometrist (ophthalmologist). A vision specialist will check your eyes for CMV retinitis.
If you are pregnant and have CMV, your doctor may recommend a test called an amniocentesis to determine if your baby has CMV. To perform an amniocentesis, the doctor inserts a long, thin needle through the abdomen and into the uterus to collect a small amount of fluid from the amniotic sac surrounding the baby.
Data Feb 15 ● Comments 0 ● ViewsCMV infection can harm the developing fetus. If the test shows that the fetus does indeed have infections, the doctor will examine your baby after birth to check for birth defects or health problems so they can be treated if possible.
Doctor Maria Nikolaeva
Cytomegalovirus infection (CMVI) belongs to the group of herperoviruses, which, due to the presence of DNA cells, invade the cells of the nervous system. Due to this, after infection with CMV, a permanent carriage is formed. Cytomegalovirus (in the international classification referred to as CMV) proceeds secretly and poses a threat under the condition of severe immunodeficiency. The most dangerous cytomegaly in adults, which during pregnancy provokes miscarriages.
Cytomegalovirus is a viral infection that belongs to one of the varieties of herpes and is not amenable to medication or other treatment. CMV is large in size. Each cytomegalovirus particle contains:
- Genome. These DNA cells contain the genetic information of the virus.
- Nucleocapsid. The protein coat that encloses the core of a virus particle.
- protein matrix. It contains proteins that are activated after human infection and start the processes of CMVI cell division.
- Supercapsid. The outer shell of a virus particle. The composition of the supercapsid includes complex protein compounds, through which the cytomegalovirus "analyzes" the external environment.
A diagnosis of cytomegalovirus infection means that the person is a carrier of the virus. However, the presence of particles in the patient's body does not pose a danger to others. This is explained by the following features of cytomegalovirus:
- Low virulence. Up to 95% of the world's population are carriers of cytomegalovirus infection. In most patients, the virus does not manifest itself during life or causes mild symptoms.
- Latency. Symptoms of cytomegalovirus appear after a sharp weakening of the immune system. This is explained by the fact that CVMI multiplies at the expense of host cells that die after contact with the virus. Therefore, in the absence of exposure to provoking factors, the course of cytomegalovirus infection is hampered by the immunity of the patient, which suppresses the reproduction of the pathogenic agent.
- Low resistance to environmental influences. Cytomegalovirus infection dies at temperatures above 40 and below 0 degrees.
Another important feature of CMV is that infection is possible through constant contact with the carrier. This is also due to the ability of the immune system to suppress this type of pathogen.
Cytomegalovirus detected - what to do?
Classification
In children, the congenital form of the disease is more often diagnosed. At the same time, in 95% of cases, intrauterine infection provokes an asymptomatic course of cytomegaly. In the congenital form, development is observed:
- petenchial rash (small hemorrhages on the skin);
- jaundice;
- acute inflammatory process in the retina (chorioretinitis).
Due to intrauterine infection, up to 30% of children die. In other cases, prematurity is often diagnosed. The latter also contributes to the infection of the child at the time of birth. The acquired form of the disease in children in the first days of life threatens with the development of severe complications.
In older patients, CMVI after an exacerbation causes a mononucleosis-like syndrome, which proceeds according to the type of infectious mononucleosis (occurs due to the activation of the Epstein-Barr virus).
A number of studies highlight the cytomegalovirus that affects people with immunodeficiency in a separate form. CMV infection of persons with HIV leads to the development of severe complications, up to cancerous tumors and death. In case of infection after transplantation of internal organs, cytomegalovirus causes rejection of foreign tissues.
Is there a cure for cytomegalovirus? Treatment of exacerbation of cytomegalovirus. Antibiotics for cytomegalovirus
In addition to the above classifications, there is another CMVI gradation according to the characteristics of the course of the disease. Accordingly, it is divided into acute and latent. In addition, people with severe immunodeficiency develop a generalized form of cytomegalovirus.
Causes
The pathogenesis (development mechanism) of cytomegalovirus does not depend on external factors. In response to CMV infection, the body produces specific antibodies (immunoglobulins of classes M and G), which suppress the activity of the pathogen. But under the influence of factors that weaken the immune system, cytomegalovirus develops rapidly, spreading and causing the death of healthy cells. The latter after infection increase in size, which is clearly visible when viewed under a microscope.
The disease of this etiology persists for life. This means that there is still a chance that the carrier will infect its own environment.
How the virus enters the body
Cytomegalovirus infection enters the body in the following ways:
- Contact household. This method of distribution of CMVI is typical for families and other closed groups. Infection occurs through the transmission of infected biological fluid (blood, saliva) or through household items.
- Airborne. CVM is spread through saliva when sneezing or coughing.
- Sexual. The infection enters the body through the biological fluids secreted by the organs of the reproductive system.
- Transplacental. Cytomegalovirus infection enters the baby's body through the placenta during fetal development.
- Iatrogenic. Infection occurs through the transfusion of infected blood.
- Transplant. Due to the fact that CMV is stored in the cells of internal organs, when transplanting the latter, a possible transmission of the infection to a healthy person.
The first three ways are considered the most common. At the same time, the probability of infection directly depends on the state of immunity of a healthy person: the stronger the body, the lower the risk of infection. Also, for the spread of CMVI, the presence of lesions on the skin or contact with the mucous membrane is necessary.
Causes of infection
With primary infection with cytomegalovirus, a temporary deterioration in the general condition of the body is possible. Over time, the immune system will suppress the activity of the pathogen, as a result of which CMVI will go into the latent stage of the course.
The relapse of cytomegalovirus occurs against the background of a sharp weakening of the immune system. It happens:
- during pregnancy;
- against the background of a protracted or severe course of diseases of internal organs;
- after chemotherapy;
- with autoimmune diseases;
- after organ transplant.
The risk group for exacerbation of CMVI includes older people. In addition, the infection recurs against the background of systemic diseases.
Diagnostics
A specialized examination of the patient in order to detect cytomegalovirus infection in the body is carried out mainly in pregnant women and people with immunodeficiency. This is explained by the fact that with this combination, CMV can give serious complications. The virus is diagnosed by:
- pathogen cultivation;
- polymerase chain reaction (PCR);
- enzyme immunoassay (ELISA);
- cytological method.
With such research methods, it is possible to detect CVMI in the human body with high accuracy. Moreover, the first method gives the best results. Through PCR, it is possible to identify the DNA of the virus, thereby differentiating cytomegalovirus from other forms of herpes.
Cytomegalovirus Igg and Igm. ELISA and PCR for cytomegalovirus. Avidity for cytomegalovirus
Enzyme immunoassay is indicated in cases where signs of an exacerbation of CMV are diagnosed, since this method allows it to be used to detect specific antibodies. Diagnosis using the above methods is carried out using biological fluids. For cytological examination, a small piece of the affected tissue will be taken.
Symptoms
Signs of cytomegalovirus are as follows:
- generalized lymphadenopathy, in which lymph nodes located in various parts of the body increase;
- high body temperature;
- chills;
- increased fatigue;
- an increase in the size of the liver (not always);
- skin rash;
- muscle pain.
The nature of symptoms in CMV depends on the gender of the patient. In men, the virus is often localized in the organs of the reproductive system, which manifests itself in the form of pain during urination. Also, swelling of the nasal mucosa is not excluded. In women, there are signs of damage to the liver, lungs, gastrointestinal tract and pancreas.
In children with congenital CMVI in the acute stage of the course, signs of rubella and jaundice are diagnosed simultaneously. In case of brain damage, cramps in the limbs are disturbing. The congenital form is dangerous because it causes serious malformations of internal organs.
In older children the disease proceeds in a milder form, causing cyanosis and shortness of breath. Otherwise, the clinical picture does not differ from the manifestation of CMVI in adults.
Cytomegalovirus infection differs in that these symptoms occur suddenly. Body temperature after the end of the incubation period (if we are talking about primary infection) increases dramatically. The nature of the clinical picture changes over time depending on which organ is affected by the virus.
Symptoms of cytomegalovirus
Treatment
CMV therapy is carried out only during an exacerbation of the infection. To restore the patient's condition, drugs are prescribed that stimulate the activity of the immune system. Basically, interferon preparations are used for these purposes:
- "Viferon";
- "Laferon";
- "Kipferon";
- "Realdiron".
Together with these drugs, it is recommended to take directed antiviral drugs: Ganciclovir, Foscarnet. Additionally, immunoglobulins and drugs are prescribed that stimulate the regeneration of damaged tissues. In addition, the composition of complex therapy includes medications that suppress concomitant symptoms: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, analgesics, and others.
The type of drug for exacerbation of CMVI is selected taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient, the presence of concomitant diseases or complications.
Treatment of cytomegalovirus
Possible Complications
There are a lot of complications that CMVI causes. Cytomegalovirus is able to penetrate into various parts of the body, causing lymphadenitis, inflammation of the tonsils and adenoids, liver and kidney diseases, intestinal obstruction. In women, the pathogen contributes to the occurrence of cervical erosion and other abnormalities, due to which infertility develops.
With a congenital form of CMV, there is a high probability of fetal death. Severe malformations affecting vital organs are also not excluded. Often in children and adults against the background of an exacerbated infection, pneumonia, jaundice, hemorrhagic syndrome, inflammation of the eyes, and myocarditis occur. If a child is infected in the first years, a lag in psychomotor development and a violation of the blood composition are possible. Rarely, there are cases of systemic diseases.
Also read with this