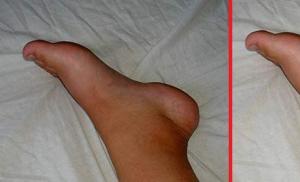
White tigers are albino. Bengal tiger
I'm sure you've all heard of the existence white tiger. But most likely, few people wondered what kind of wild cats and are white tigers found in wild nature Or is it a human creation? Let's try to figure it out.
The existence of the white tiger has been known for a very, very long time. AT ancient india believed that a meeting with a white tiger could bring enlightenment, and killing unusual beast- a series of troubles and death.
In the wild, white tigers are extremely rare. Over the past 60 years, neither scientists nor hunters have seen a white tiger in nature. Last time a white tiger was seen back in 1958. Unfortunately, he was not only seen, but also shot.
Before today Science knows only white Bengal tigers ( Panthera tigris tigris) lived and probably still lives in the wild.

It is believed that a white tiger cub is born with a probability of 1 in 10,000. This is a congenital mutation, but white tigers are not albinos, as indicated by the fact that their fur has dark stripes. In the wild, white tigers were probably perfectly healthy animals, not much different from their ordinary red counterparts. But in captivity, the situation is completely different ...
Today, from 150 to 200 individuals of the white Bengal tiger live in captivity and all thanks to one person and one tiger, respectively:
It all started back in 1951, when during a tiger hunt with the participation of Maharaja Reva Shri Martand Singh, a tiger den was discovered, in which there were four cubs - three red and one white. The red cubs, alas, were put on the skins, and the white one was settled in the Maharaja's palace and gave him the name Mohan. The tiger quickly became a favorite and the main pride of the ruler.

Maharaja hoped that sooner or later a white tiger cub would be born to this white tiger, but for several years all the kittens were born the most common - red. A few years later, the tiger was brought together with his own daughter. As a result of inbreeding (connection between related individuals), the tigress gave birth to several kittens, one of which was white. It is said that no one had ever seen the Maharaja so happy before that moment. A few more years passed and so many white tigers already lived in the palace that they decided to sell some of them. In the early 1960s, several white tiger cubs ended up outside of India, in particular in the USA and Great Britain. Today, white tigers are found in many zoos around the world, as well as a large number of lives in private nurseries, primarily in the United States.

Thus, absolutely all white tigers are descendants of the Mohan tiger, who lived in the Maharaja's palace. For the birth of a white tiger, you need a white tiger and a tiger that is the child of a white tiger. Also, a white tiger cub can be born to two red tigers, provided that both of them or at least one of them is the child of a white tiger. From all this it follows that all white tigers are the result of incest, which, of course, cannot but affect the offspring. White tiger cubs are smaller than their red brothers and sisters. They often have slanting eyes, twisted legs, and a weak spine.

At the same time, according to observations, white tiger cubs grow faster and grow larger than ordinary Bengal tigers.
As I said, only representatives of the Bengal subspecies are white, but whites (with black stripes) are often found in zoos Amur tigers. But in the wild whites Amur tigers no. More precisely, there was not a single documented case of a meeting with a white Amur tiger. As for the white Amur tigers living in captivity, this is not a purebred Amur tiger, but a mixture of Amur and Bengal tigers with a congenital white mutation.
The white tiger is a subspecies of the Bengal tiger with a special coat color. White tigers have white or cream fur with brownish-black stripes and beautiful blue eyes. These tigers are not classified as a separate subspecies - they are also considered Bengal tigers, but with a genetic mutation. These are quite large animals weighing up to 230 kg and with a body length of up to 3 meters.
Distribution and habitats
See the white tiger vivo very difficult, ten thousand individuals come across only one tiger with such a rare color. In nature, these tigers were found only in a few regions of India. However, they are kept in zoos quite often.
The first white tiger was caught by man in the middle of the last century. Subsequently, other individuals with a white color were obtained from him. Now many zoos in the world contain white tigers, all of them are descendants of the tiger that was caught in the last century.

Nutrition
The white tiger, like all other tigers, is a predator. He is able to hunt large prey - wild boars, deer and other animals. In zoos, tigers are fed fresh raw meat.
Lifestyle
Usually the white tiger is active in the morning and evening, and the rest of the time he prefers to sleep or lie down in some comfortable secluded place. Usually the tiger moves slowly on the ground and does not climb trees. Only small tiger cubs can play climbing trees. The white tiger can swim and loves to swim in hot weather. He is not afraid of winter and easily tolerates low temperatures.

In captivity, tigers breed quite well. Many zoos manage to get healthy offspring of white tigers, but they do not always give birth to the same white tiger cubs. Even if both the female and the male are white, they can have red babies.

- The contours of the stripes of each tiger are individual and never repeat, like human fingerprints.
- The white tiger is not an albino, as it has dark stripes on its coat, and its eyes are not red.
- Many white tigers suffer from kidney disease, poor eyesight, strabismus, clubfoot and curvature of the spine. All these diseases appear in tigers due to genetic mutations arising from inbreeding.
- Tigers rarely roar, but if they do, they can be heard from three kilometers away.
- There are approximately 100 white tigers in Indian zoos.
White tiger brief information.
White tigers are individuals of a predominantly Bengal tiger that have a congenital mutation, and therefore are not currently considered a separate subspecies. A peculiar gene mutation causes an animal to be completely white in color, and individuals are characterized by blue or green eyes and black-brown stripes on a background of white fur.
Description of the white tiger
White-colored specimens that exist today are very rare among any representatives of wild animals. On average, the frequency of occurrence in nature of white tigers is only one individual for every ten thousand representatives of the species that have a normal, so-called traditional red color. White tigers have been reported for many decades from different corners lands, from Assam and Bengal, as well as from Bihar and from the territories of the former principality of Rewa.
Appearance
The predatory animal has tight-fitting white fur with stripes. Such a pronounced and unusual color is inherited by the animal as a result of a congenital color mutation. The eyes of a white tiger are predominantly blue in color, but there are individuals endowed with naturally greenish eyes. Very flexible, graceful, with well-developed muscles, the wild animal is distinguished by a dense physique, but its dimensions, as a rule, are noticeably smaller than those with a traditional red color.
The head of a white tiger has a pronounced rounded shape, it is distinguished by a protruding facial part and the presence of a rather convex frontal zone. The skull of a predatory animal is quite massive and large, with very widely and characteristically spaced cheekbones. Tiger whiskers are up to 15.0-16.5 cm long with an average thickness of up to one and a half millimeters. They are white in color and arranged in four or five rows. An adult has three dozen strong teeth, of which a pair of fangs looks especially developed, reaching middle length in 75-80 mm.
Representatives of the species with a congenital mutation have not too large ears with a typical rounded shape, and the presence of peculiar bulges on the tongue allows the predator to easily and quickly separate the meat of its prey from the bones, and also helps to wash. On the hind legs a predatory animal has four fingers, and on the front - five fingers with retractable claws. Average weight an adult white tiger is about 450-500 kilograms with a total body length of an adult within three meters.
It is interesting! White tigers are naturally not in very good health - such individuals often suffer from various kidney diseases and excretory system, strabismus and poor vision, too arched neck and spine, as well as allergic reactions.
Among the wild white tigers that exist now, there are also the most common albinos with plain fur without the presence of traditional dark stripes. In the body of such individuals, the coloring pigment is almost completely absent, therefore the eyes of a predatory animal are distinguished by a clear reddish color, explained by very clearly visible blood vessels.
Character and lifestyle
Under natural conditions, tigers are solitary predatory animals that are very jealous of their territory and actively mark it, most often using all kinds of vertical surfaces for this purpose.
Females often deviate from this rule, therefore they are able to share their site with other relatives. White tigers are excellent swimmers and, if necessary, can climb trees, but too eye-catching color makes such individuals very vulnerable to hunters, so most often representatives with an unusual fur color become inhabitants of zoological parks.
The size of the territory occupied by the white tiger directly depends on several factors at once, including the characteristics of the habitat, the density of the areas populated by other individuals, as well as the presence of females and the number of prey. On average, one adult tigress occupies a territory equal to twenty square meters, and the territory of a male is about three to five times larger. Most often, during the day, an adult individual travels from 7 to 40 kilometers, periodically updating marks on the borders of its territory.
It is interesting! It should be remembered that white tigers are animals that are not albino, and the peculiar coloration of the coat is due exclusively to recessive genes.
An interesting fact is that Bengal tigers are not the only representatives of wildlife, among which there are unusual gene mutations. Cases are well known when white Amur tigers with black stripes were born, but such situations in last years occur quite rarely. Thus, today's population of beautiful predatory animals, distinguished by white fur, is represented by both Bengal and ordinary hybrid Bengal-Amur individuals.
How long do white tigers live
AT natural environment white individuals rarely survive and have a very short overall lifespan, since due to the light color of the fur, it is difficult for such predatory animals to hunt and feed themselves. Throughout her life, the female bears and gives birth to only ten to twenty cubs, but about half of them die in young age. Average duration The life of a white tiger is a quarter of a century.

sexual dimorphism
The female Bengal tiger reaches puberty at three or four years of age, and the male becomes sexually mature at four or five years of age. At the same time, sexual dimorphism in the color of the fur of the predator is not expressed. Only the location of the stripes on the fur of each individual is unique, which is often used for identification.
Range, habitats
Bengal white tigers are representatives of the fauna in the territory of Northern and Central India, Burma, Bangladesh and Nepal. Long time there was an erroneous opinion that white tigers are predators from the Siberian expanses, and their unusual color is just a very successful disguise of an animal in snowy winters.
The diet of white tigers
Along with most other predators living in natural environment, all white tigers prefer to eat meat. AT summer period adult tigers may well eat hazelnuts and edible herbs to satiate themselves. As observations show, males are strikingly different from females in their taste preferences. They most often do not accept fish, and females, on the contrary, often eat such aquatic representatives.
White tigers approach their prey with small steps or on half-bent legs, trying to move very imperceptibly. A predator can go hunting both in the daytime and at nightfall. In the process of hunting, tigers are able to jump about five meters in height, and also overcome a distance of up to ten meters in length.
In their natural environment, tigers prefer to hunt ungulates, including the Indian sambar. Sometimes a predator eats atypical food in the form, and. To secure yourself a complete diet food during the year, the tiger eats about five to seven dozen wild ungulates.
It is interesting! In order for an adult tiger to feel full, it needs to consume about thirty kilograms of meat at a time.
In captivity, predatory animals feed six times a week. The main diet of such a predator with an unusual appearance includes fresh meat and various organ meats. Sometimes the tiger is given "living creatures" in the form of rabbits or chickens. Every week, the animals are given a traditional "fasting day", which makes it easy to support the tiger " sportswear". Due to the presence of a well-developed subcutaneous fat layer, tigers can starve for some time.
The white tiger is a recessive mutant of the Bengal tiger that is occasionally found naturally in Assam, Bengal, Bihar and especially in the former Rewa state. Compared to normal-colored tigers without the white gene, white tigers are generally larger than normal, both at birth and at maturity. We bring to your attention a selection of photographs of beautiful white tigers.


1. Kailash Sankhala, director of the New Delhi Zoo in the 1960s, said that "perhaps one of the functions of the white gene is to maintain the size gene in the population, if that is ever needed, of course." (Tambako The Jaguar)

2. In the subspecies of the Bengal tiger, there were also individuals with black stripes. The same phenomenon can be found among individuals of the Amur tiger, and there have been cases in history when such individuals appeared in other species. (Tambako The Jaguar)

3. Now there are several hundred white tigers in zoos around the world, about a hundred of them in India. (Tambako The Jaguar)

4. However, their numbers are increasing. (Tambako The Jaguar)

5. The current population of white tigers includes pure Bengal and hybrid Bengal-Amur, but it is not clear whether the recessive white gene came only from Bengal tigers, or if the ancestors of the Amur tigers also took part in this. (Tambako The Jaguar)

6. The white tiger is born as a result of the homozygous occurrence of a recessive allelomorph in the genome. (Tambako The Jaguar)

7. It is estimated that one in 15,000 Bengal tigers in the wild is born white. (Tambako The Jaguar)

8. The existence of white Amur tigers has not been scientifically documented, despite occasional anecdotal evidence that they have been sighted in regions where Amur tigers live. (Nancy Chan)

9. It is possible that the white mutation does not exist in the nature of Amur tiger populations: not a single white Amur tiger has yet been born in captivity, despite the fact that these subspecies are actively used for reproduction (with a large percentage of outbreeding between different hereditary lines of Amur tigers in order to preserve genetics). (Nancy Chan)

10. The recessive allelomorph periodically becomes homozygous during such a crossing, and in this case, a white cub may be born to "ordinary" parents, but so far there is no evidence for this. (Nancy Chan)

11. Known white Amur tigers in captivity are not actually purebreds. (Nancy Chan)

12. This is the result of crossing Amur tigers with Bengal tigers. (Karl Drilling)

13. The gene for white coat color is quite common among Bengal tigers, but the natural birth of a white Bengal tiger in captivity is still a rare case. (Dpfunsun)

14. The white tiger is not considered a subspecies of the tiger, rather it is a mutational variant of the existing subspecies of the tiger. (Mandy)

15. If a purebred Amur white tiger is ever born, it will not be selectively crossed as part of conservation programs. (Andrea Mitchell)

16. Although, most likely, it will still be selectively crossed so that more white Amur tigers are born. (Frost Photography)

17. Due to their popularity, white tigers are always the stars of zoos. (In Cherl Kim)

In nature, the animal is divided into nine subspecies. Currently, only six exist, the rest were exterminated or extinct.
Tiger subspecies:
- Amur - the main habitat - Primorsky and Khabarovsk region Russia, also a small amount is located in the northeast of China and in the north of Korea;
- Bengali - habitat India, Nepal, Bangladesh, Bhutan;
- Indochinese - habitat south of China, Thailand, Laos, Cambodia, Vietnam, Malaysia;
- Malay - south of the Malay Peninsula;
- Sumatran - the habitat of the island of Sumatra (Indonesia);
- Chinese - at present, individuals of this subspecies have practically disappeared, a small number are found in Chinese reserves;
And extinct subspecies:
- Bali tiger- lived only on the territory of the island of Bali, the last individual was killed by hunters in 1937;
- javan tiger- lived on the island of Java, the last representative of the subspecies was killed in 1979;
- Transcaucasian tiger- lived in Iran, Armenia, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Uzbekistan, Iraq, Kazakhstan, Turkey and Turkmenistan. The last time a tiger of this subspecies was seen was in 1970.
Currently, the most numerous is the Bengal tiger, which makes up approximately 40% of the total number of animals of this species.
The Bengal tiger is usually red in color with black stripes. But there are also individuals with white hair, which also has dark spots. In the natural environment, such individuals rarely survive, since it is difficult for them to hunt because of their light color. In captivity, white tigers easily adapt and breed well.
There is an opinion among people that a white-haired tiger belongs to albinos, but in fact this is not so. White tigers are a variety of the Bengal tiger that first appeared in India.

History of the origin of the white tiger
All white tigers currently in captivity have one common ancestor- a male Bengal tiger, nicknamed Mohan. It all started in May 1951, when during a tiger hunt with the participation of Maharaja Reva, a tiger den was discovered, in which there were four teenage tiger cubs. Three red tiger cubs were killed, and the fourth, distinguished by its unusual white color and attracted the attention of the ruler, was left and moved to the Maharaja's palace. The tiger lived here for 12 years.
Maharaja Reva was very proud that only he had such a unique beast. And he wanted to have more of them. To do this, Mohana was brought in an ordinary, red tigress. However, no matter how many offspring there were after that, not a single tiger cub was white. Until one day a tigress from previous copulations was brought to the white tiger as a bride. As a result of inbreeding (connection between related individuals), a tigress in 1958 gave birth to offspring of four kittens, one of which was white.
Since then, the number of white tigers has increased dramatically. Now there is not enough space in the palace for all these individuals, and the ruler of Reva decided to sell unique animals. White tigers at that time were considered natural heritage country, but still a few copies were taken out of the country.
So, in 1960, one of the descendants of the white tiger Mohan came to the United States, in national park in Washington. A little later, they appeared in the Bristol Zoo in the UK. And then they began to spread throughout the globe.
Currently, the number of white tigers is not known, as they are kept not only in zoos and circuses, but also in private menageries, where it is difficult to track their numbers. Nai large quantity white tigers come from their country of origin, India.
Despite the fact that white tigers are born only between relatives, and this, as a rule, leads to a weakening of the viability of offspring, this has not yet been observed among white tigers. The birth rate of white tigers is approximately one in 10,000 red-colored tigers.
white tiger
Physiology of the white tiger
The white tiger differs from the red one in its smaller size. Individuals of this species have brown-red, pink or Blue eyes. Most often there are animals with blue eyes.
The tiger has a massive body, elongated in length, with well-developed muscles and a fairly high flexibility inherent in all animals of the cat family. The anterior part of the body is more developed than the posterior, and the animal is higher at the shoulders than at the sacrum. A tiger has four toes on its hind paws and five on its front paws. They all have retractable claws.
The rounded head of a tiger is distinguished by a protruding front part and a rather convex forehead. The skull of the animal is quite massive, large, with widely spaced cheekbones. Small ears are rounded. Vibrissae up to 16.5 cm long and up to 1.5 mm thick are arranged in 4-5 rows and have White color, turning brown at the base.
An adult tiger should have 30 teeth, of which 2 canines, reaching a length of up to 8 cm. Such powerful teeth help the predator kill prey. In addition, on the sides of the tongue of the animal there are special tubercles covered with keratinized epithelium, with the help of which the tiger separates the meat from the bones of prey. Also, these tubercles help the animal when washing.
The white tiger has a short, rather dense and low hairline. And if an ordinary tiger has various shades of red, then white has shades from cream to white. The entire surface of the body is covered with dark stripes, which can range from light gray (in some individuals) to completely black. On the body and neck, the stripes are arranged transversely vertical position. The edges of the strip are pointed, or they bifurcate, and then reconnect. In the back, the tiger has more stripes.

Territorial behavior
Tigers are territorial animals, that is, adults lead a solitary lifestyle in their own territory. Intrusion into it is subjected to fierce resistance from the owner-tiger. Animals mark their territory, as a rule, marks are left on vertical objects.
The size of the territory occupied by a tiger depends on several factors, in particular, on the habitat, the density of population of other individuals, the presence of females and prey. On average, 20 square meters is enough for a tigress. km, and for males - 60-100 sq. km. At the same time, in the habitat of the male, there may be separate areas for the habitat of females.
During the day, tigers constantly move around their territory, periodically updating marks along its borders. On average, a tiger can walk from 9.6 to 41 km per day, and females walk from 7 to 22 km per day.
Although tigresses, like males, have a personal territory, but when they invade or cross borders with other females, they are perceived as normal, tigresses are able to peacefully coexist with each other. While males not only do not tolerate the residence of other males on their territory, but also aggressively treat individuals that accidentally cross the border of someone else's site. However, male tigers can peacefully coexist with females, and in some situations even share prey with them.
Food and hunting
In the natural environment, the main food of tigers are ungulates. For a white tiger, it could be deer, wild boars, Indian sambar, etc. Sometimes it happens that a tiger can eat food that is unusual for him in the form of monkeys, hares, pheasants, in some cases it can even be fish. On average, for good nutrition, a tiger needs about 50-70 ungulates per year.
At one time, the tiger eats 30-40 kg of meat. At the same time, the animal can go without food for a considerable time. This is due to the presence of subcutaneous adipose tissue, which can reach 5 cm in some individuals.
The tiger hunts animals alone. At the same time, he uses one of two hunting methods inherent in him - he sneaks up on prey or waits for it in ambush. The first method is most often used by a predator in winter time, the second is more typical in summer. Having tracked down the prey, the tiger approaches it from the leeward side, so that the wind does not carry the smell of the tiger to the animal. The predator moves with cautious short steps, while often falling to the ground. At the closest approach to the prey, the tiger makes several large jumps, thereby reaching the target animal.
In the second method - waiting - the tiger hides from prey, while lying under the wind, and when it approaches, it makes a sharp jerk for a short distance.
If the animal on which the hunt is on, manages to get away from the tiger for 100-150 meters, then the predator stops hunting. When chasing, a tiger can develop a high speed for such a large animal - up to 60 km / h.
When hunting, a tiger can make a jump up to 5 meters high and up to 10 meters long. The tiger can carry the caught and killed prey by holding it with its teeth, or by throwing it on its back. At the same time, it can carry an animal weighing up to 100 kg. Holding a dead animal with a weight of 50 kg in its teeth, a predator can overcome an obstacle that has a height of up to 2 meters. The tiger moves very large prey by pulling it along the ground. At the same time, he can prey can have a weight exceeding the weight of a tiger by 6-7 times.

reproduction
Mating tigers most often occur in December-January. At the same time, only one male follows the female. If a rival appears, then a fight takes place between the males for the right to mate with the female.
The female tiger is capable of fertilization for only a few days a year. If at this time the female is not fertilized, then estrus is repeated after a short time.
Most often, a tigress brings her first offspring at the age of 3-4 years, and a female can give birth every 2-3 years. Bearing of cubs proceeds approximately 97-112 days.
Tiger cubs are born in March-April. In one brood, there are most often 2-4 tiger cubs, offspring with one tiger cub is less common, and even less often - 5-6 cubs. The weight of born tiger cubs is 1.3-1.5 kg. The cubs are born blind, but after 6-8 days they begin to see clearly.
During the first six weeks, the cubs feed only on the milk of the tigress. Tiger cubs grow only near their mother, male tigresses are not allowed to come to the offspring, since the male can kill the born cubs.
After 8 weeks, the cubs become able to follow their mother and leave the den. To independent living the new generation becomes capable only at the age of about 18 months, but, as a rule, they remain further with their mother until they reach 2-3 years, in some cases up to 5 years.
After the young tigers begin to live on their own, the females remain in close proximity to matter. Males, unlike them, go to longer distances, in search of their own unoccupied territory.
Throughout their lives, females bear about 10-20 cubs, and half of them die at a much younger age. On average, the life expectancy of a tiger is 26 years.
However, it is worth considering that white tigers are very rare in natural conditions.
They are more prevalent in captivity, where mating occurs between certain members of the species. At the same time, if earlier for the birth of a white tiger it was required to cross tigers with kinship, then at present white tigers have become quite common, thanks to which it is possible to obtain offspring with a white color from two white tigers.
White tigers are very popular in zoos. However, opinions of zoologists about white tigers differ. Some believe that any color variation is worthy of attention, while others argue that white tigers are genetic freaks. For the first time, the director of the Zoological Association, William Conway, spoke out against this species of animals, calling white tigers freaks and calling for them to be excluded from all zoos.
Nevertheless, the popularity of the white tiger continues unabated, and its further distribution continues among various zoos around the world.