Tax code 126. What is the personal income tax deduction code and how to use it? Tax refund changes
Standard tax deductions may apply to many employees. However, not every employee is aware of this. By the way, employees of the personnel department or accounting department are not required to inform applicants about this, since the provision of documents is the right of the employee, and not his duty. Deduction codes 126 and 127 are the most common, as they are related to the first and second child.
general information
A tax deduction is a kind of benefit for an employee. It is noteworthy that there are several types. The most popular are personal deductions for children.
The former include small amounts that are not taxed and to which participants in wars, as well as disabled people of the first and second groups, are entitled.
The second broad group includes those amounts that are not taxed at the rate of thirteen percent due to the fact that the employee has children. Here the classification is quite broad, since everything affects the deduction code, from the presence of a second parent to the number of children.
How can you calculate your tax?
If the employee himself wants to check his tax, then he must know how to calculate it correctly. In general, the whole amount of his wages is multiplied by thirteen percent, or by 0.13.
However, if an employee has the right to a tax deduction and he provided a complete package of documents, then he should not tax the entire amount of his salary, but only part of it.
The deduction code 126 and 127 assumes, for example, that an employee who has a first or second minor child has the right to a deduction in the amount of 1,400 rubles. If there are two children, then the amount doubles. However, it is necessary to bring all documents for children on time. Otherwise, you will have to return the lost amounts through the tax authorities and only for a certain period.
Practical example. Tax calculation
Employee Ivanova I.I. submitted documents for her children. The deduction codes 126 and 127 apply to her, that is, for the first and second child, respectively. If the total amount of earnings Ivanova I.I. for the month amounted to 10,000 rubles, then without benefits she had to pay the state 1,300 rubles.
But, since the employee has the right to standard tax deductions for codes 126, 127, then 1400 and 1400 rubles can be safely deducted from her salary when calculating the tax. In total, the amount of 7200 rubles is taxed. The amount of tax transferred to the budget will be 936 rubles. This means that the benefit of Ivanova I.I. saved her 364 rubles.

Code deduction 126: what is it?
Tax deduction with code 126 indicates a personal income tax exemption for the first child. It is noteworthy that not only those whose child has not reached eighteen years of age can use it. When providing a certificate from an educational institution confirming that the child is studying full-time, the benefit continues to be valid until the child reaches twenty-four years of age.
It is also worth noting that this deduction code has been used since the end of 2016. Previously, it was coded 114, which also referred to the first child under the age of majority or receiving education, but only in full-time education.
The amount of deduction code 126 is 1400 rubles. This means that it is this part of the employee's salary that is not taxed. That is, a monthly savings of 182 rubles is obtained.
Also, we must not forget that the deduction ceases to apply if the amount of wages for the calendar year has reached 350,000 rubles. In the month in which this amount was collected, deduction codes 126 and 127 will not be valid.
If a child is born: we carry documents
If an employee who works at the enterprise has a child, then he can immediately bring the entire package of documents to provide the standard deduction of codes 126 and 127, and any other. It all depends on what kind of child appeared in the family.
This requires only two documents: a personal statement and a copy of the birth certificate of the child. However, nuances are possible. If a parent is raising a child alone, he must also provide documents that confirm this.
These include a certificate for single mothers in form number 25, a death certificate of the second parent, a certificate stating that he was recognized as missing. It is also worth bringing a copy of the passport, which indicates that after the death of a spouse or the status of a single mother, the parent did not marry. This is necessary so that the accounting department knows which codes to apply. The personal income tax deduction code 126 and 127 applies only to those who are raising a child in a complete family. For a single parent, these amounts will be doubled.
It is also worth paying attention to the change of surname. This is especially true for women. If the maiden name is entered on the birth certificate, and now the employee has other data, then it is also worth bringing a document confirming this. In this case, it will be a marriage certificate.
In a personal statement, you should indicate your data, in which department the employee works, as well as the data of the child, starting with the last name, first name and patronymic and ending with the date of birth. You should also sign and date the application.
It is not worth delaying the provision of documents, since even if the baby appeared on the 29th, the deduction will be provided for the entire month worked. This should also be taken into account by accountants. A tax deduction for a child is provided from the month of his birth, subject to the timely provision of documents. 
New place of work. What do you need?
If an employee has come to a new place of work and wants to receive a tax deduction, then in addition to the documents listed above, he must also provide a certificate in the form 2-NDFL. This is necessary so that the accountant can enter information about the employee's salary from the beginning of the year. This allows you to prevent the use of the deduction upon reaching the threshold of 350,000 rubles.
Also, if an employee takes a new job in the same month in which he was fired from another organization, the accountant can check whether he has already accrued deductions for this month.
The deduction code 126 and 127 in the 2-personal income tax certificate can be seen directly under the column with the employee's income. By dividing the amount of each of them by 1400, you can find out for how many months the deduction was provided. If the employee has already received his benefit for the given month, then the employer establishes deductions only from the next month. If there was a break between jobs, then a refund for this period is not provided.
It is noteworthy that if an employee managed to change several jobs in a year, he will have to take certificates from each of them. Even if it was worked out there for several days. Income must be summed up and entered into the base in order to correctly calculate taxes.
Otherwise, for those who want to use the tax deduction code 126 and 127, you must bring a copy of the children's birth certificates, as well as a personal statement. It is also worth bringing certificates from places of study if the child is over eighteen years old.

Code 127. Features
The deduction code number 127 indicates a benefit for those who have a second child. Provide it to those who transfer the package of documents. The amount of the deduction in this case coincides with the amount of the benefit for the first child and amounts to 1,400 rubles.
This means that every month an employee who is entitled to a benefit saves 182 rubles. The limit for using this deduction is the same as for the first child, namely 350,000 rubles.
Until the end of 2016, this code corresponded to the designation with the number 115, it had all the same parameters. This code is also used by those parents whose second child has reached the age of majority, but has not yet reached twenty-four years of age and is studying full-time.

Documents for withdrawal. Code 127
Tax deduction codes 126 and 127 are similar, therefore they have a similar set of documents. However, for the latter it will be somewhat wider.
If an employee has two children under the age of eighteen or full-time students, he must provide the following documents:
- Personal statement. In one, you can enter both children at once.
- Birth certificate of both children, as well as their copies. It is worth noting that even if the child already has a passport, it is the certificate that is provided, since it is in this document that there is information about the parents.
- Help in the form 2-NDFL, if the employee gets a job.
It is also worth noting that if the first child no longer fits the category of persons for whom the deduction is provided, then a certificate for him still needs to be brought. This confirms the fact that the child for whom code 127 is used is the second.

What if the employee did not receive the benefit?
It happens that the employee did not know that he was entitled to any personal income tax benefit. Probably, he either was not informed about this, or did not provide documents in a timely manner. In this case, he can return the amount overpaid by him to the tax authorities.
To do this, you must submit a package of documents to the tax service. The deduction code 126 and 127 in the 3-NDFL declaration will also have to be indicated if it is under this value that suitable deductions are made.
It is also necessary to take a certificate from the place of work in the form 2-NDFL, as well as copies of the birth certificates of children, if necessary, and certificates from their place of study. It is worth remembering that you can return the amount only for the last three years. That is, in 2017 you can get money for 2014, 2015, 2016.

Deduction codes 126 and 127 in the declaration will sit down automatically if you specify them in a specific tab in the program provided by the Tax Service website. If the return is carried out for several years, then several declarations will have to be drawn up, separately for each year.
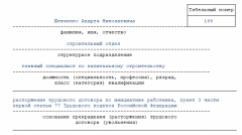
How the “Deductions” section looks like after filling out, see the figure: In order for the program to calculate the amount of standard deductions and generate the necessary sheets in 3-personal income tax, Stepanov filled out another section - “Income received in the Russian Federation” - as follows: As a result of filling in these sections in the declaration, the program generated sheet E1 with information on the total amount of standard tax deductions provided to Stepanov I.A. at his place of work. The program calculated the total amount of deductions taking into account the income limit established by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, within which standard "children's" deductions are provided. A fragment of the completed sheet E1 with information on the total amount of standard deductions and the number of months for their provision, see below: Explanation of information in Sheet E1:
- deductions for 1 child in the amount of 7,000 rubles. (1,400 rubles/month × 5 months);
- deductions provided for 5 months.
What if the employee did not receive the benefit? It happens that the employee did not know that he was entitled to any personal income tax benefit. Probably, he either was not informed about this, or did not provide documents in a timely manner. In this case, he can return the amount overpaid by him to the tax authorities.
To do this, you must submit a package of documents to the tax service. The deduction code 126 and 127 in the 3-NDFL declaration will also have to be indicated if it is under this value that suitable deductions are made. It is also necessary to take a certificate from the place of work in the form 2-NDFL, as well as copies of the birth certificates of children, if necessary, and certificates from their place of study.
It is worth remembering that you can return the amount only for the last three years. That is, in 2017 you can get money for 2014, 2015, 2016.
How to fill in tax deductions in the 3-NDFL declaration?
Because with the same sale of real estate, for example, it is not necessary to indicate such data in the declaration Reply with citation Up ▲
- 02/17/2018, 02:31 PM #7 Message from bukh1017 Your income for months 6 and 7 is not reflected, so the program does not find deductions. Generate an income code (any), indicate month 6, (7), income is zero. And the deduction will be formed in these months Ahaha)) Thank you, I would never have thought of this myself, I’ve already broken my head - where does the error come from when calculating the deduction .. The logic of the program developers is incomprehensible - why did they do it, last year everything worked without such strange frills) ) Reply with quote Up ▲
- 04/05/2018, 07:33 #8 Filling out deduction 126 in 3-NDFL Good afternoon! Please tell me how to display in the declaration the amount of the deduction for code 126 in the amount of 6750. Since May, she went on vacation, then on maternity leave. I can't figure out how to display this amount.
Deduction code 126 and 127 for personal income tax
However, for the latter it will be somewhat wider. If an employee has two children under the age of eighteen or full-time students, he must provide the following documents:
- Personal statement. In one, you can enter both children at once.
- Birth certificate of both children, as well as their copies. It is worth noting that even if the child already has a passport, it is the certificate that is provided, since it is in this document that there is information about the parents.
- Help in the form 2-NDFL, if the employee gets a job.
It is also worth noting that if the first child no longer fits the category of persons for whom the deduction is provided, then a certificate for him still needs to be brought.
This confirms the fact that the child for whom code 127 is used is the second.
Deduction code for children 126 and 144
Attention
First, be sure to uncheck the “provide standard deductions” tab on the standard deductions tab (In the event that you want to receive both the standard and property deductions, fill out both tabs) 1. If you purchased a home and want to receive a property tax deduction, go to the house tab, check the box — provide a property tax deduction More... If you did not receive a standard deduction for children from your employer, by writing an application to him and providing a package of documents, you can get it by filling out a declaration for the previous year.
So let's start filling out the declaration 3-NDFL.1. Go to the appropriate tab More... 1. When filling out the 3-NDFL declaration for the social tax deduction, go to the appropriate tab and select the appropriate item.
The deduction code for a child in 2018 in the 2-NDFL certificate
Khimki Dolgoprudny Skhodnya Lobnya We are on Vkontakte Important up-to-date information Plan to introduce new fines for violations in the field of CCP application The Ministry of Finance, the Ministry of Economic Development and the Federal Tax Service have prepared a draft with clarifications to the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. It concerns not only fines, but also the powers of inspectors, as well as exemption from liability. Let's consider what innovations will affect the majority of CCP users.
Tax amnesty 2018. Write-off of debts on taxes and insurance premiums. In accordance with the Order of the President of the Russian Federation, as well as Federal Law No. 436-FZ of December 28, 2017 “On Amendments to Parts One and Two of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and Certain Legislative Acts of the Russian Federation”, tax debts are written off for the following categories of taxpayers…
news
It is not worth delaying the provision of documents, since even if the baby appeared on the 29th, the deduction will be provided for the entire month worked. This should also be taken into account by accountants. A tax deduction for a child is provided from the month of his birth, subject to the timely provision of documents. New place of work. What do you need? If an employee has come to a new place of work and wants to receive a tax deduction, then in addition to the documents listed above, he must also provide a certificate in the form 2-NDFL.
This is necessary so that the accountant can enter information about the employee's salary from the beginning of the year. This allows you to prevent the use of the deduction upon reaching the threshold of 350,000 rubles. Also, if an employee takes a new job in the same month in which he was fired from another organization, the accountant can check whether he has already accrued deductions for this month.
Next, we will tell you how to fill out certain types of deductions in the 3-NDFL declaration. Find out important news about tax declarations from the messages posted on our portal: How to fill out standard deductions in 3-personal income tax Standard tax deductions are provided to certain categories of individuals (“Chernobyl victims”, people with disabilities from childhood, parents and caregivers, depending on the number of children, etc.). Learn more about standard deductions from the material "Standard tax deductions in 2015-2016 (personal income tax, etc.)".
Important
In 3-NDFL, information on standard deductions is given from the data of the 2-NDFL certificate and is necessary for the correct calculation of the amount of personal income tax (its refundable part or paid to the budget). Filling in information in 3-personal income tax on standard tax deductions will be considered using an example. Example 1 Stepanov Ivan Andreevich bought an apartment in 2016 and decided to return part of the personal income tax.
Deduction code 127 in the declaration 3 personal income tax 2018 how to fill out
- 01/17/2018, 12:20 #2 Irena-D, why do you fill out 3-personal income tax? Didn't they give you deductions at work? Reply with quote Up ▲
- 01/17/2018, 12:23 #3 Your income for months 6 and 7 is not reflected, so the program does not find deductions. Generate an income code (any), indicate month 6, (7), income is zero. And the deduction will be generated for these months Reply with quote Up ▲
- 01/17/2018, 02:23 PM #4 Thank you very much!!!Everything worked out Reply with quote Up ▲
- 01/17/2018, 02:24 PM #5 Message from Nad.K Irena-D, why do you fill out 3-personal income tax? Didn't they give you deductions at work? friends asked for help) Reply with quote Up ▲
- 01/17/2018, 02:35 PM #6 Well, I asked about it And about why this is necessary.
It is noteworthy that not only those whose child has not reached eighteen years of age can use it. When providing a certificate from an educational institution confirming that the child is studying full-time, the benefit continues to be valid until the child reaches twenty-four years of age. It is also worth noting that this deduction code has been used since the end of 2016. Previously, it was coded 114, which also referred to the first child under the age of majority or receiving education, but only in full-time education. The amount of deduction code 126 is 1400 rubles. This means that it is this part of the employee's salary that is not taxed. That is, a monthly savings of 182 rubles is obtained. Also, we must not forget that the deduction ceases to apply if the amount of wages for the calendar year has reached 350,000 rubles.
Info
In the month in which this amount was collected, deduction codes 126 and 127 will not be valid. If a child is born: we carry documents If an employee who works at the enterprise has a child, then he can immediately bring the entire package of documents to provide the standard deduction of codes 126 and 127, and any other. It all depends on what kind of child appeared in the family.
This requires only two documents: a personal statement and a copy of the birth certificate of the child. However, nuances are possible. If a parent is raising a child alone, he must also provide documents that confirm this. These include a certificate for single mothers in form number 25, a death certificate of the second parent, a certificate stating that he was recognized as missing.
The article “Sample of filling out a 3-NDFL tax return” will tell about the nuances of processing 3-NDFL. Reflection of social deductions in 3-personal income tax (in the amount with standard deductions) of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides for 5 types of social tax deductions (see diagram): to clarify the rules for filling out social deductions in 3-personal income tax. Example 2 Stepanov I.A. paid for his advanced training courses in 2016 in the amount of 45,000 rubles.
In the 3-NDFL declaration, he declared his right to a personal income tax refund in the amount of 5,850 rubles. (45,000 rubles × 13%). To reflect the social deduction in 3-personal income tax Stepanov I.A.
How and where to put deduction codes for a child in 2019 in the 2-NDFL certificate, because it has been completely changed. You will find out the answer to this question by reading our article. We will tell and show in samples how to fill in deduction codes for children line by line, especially deduction code 126, what is the procedure for issuing a 2-NDFL certificate now, what deduction codes are still valid in 2019.
Read with us
In 2019, a new form of certificate 2-NDFL comes into force, approved by order of the Federal Tax Service dated 02.10.2018 No. ММВ-7-11 / [email protected] This means that the procedure for reflecting deduction codes for a child in this document has also changed. In particular, deduction code 126, as well as others, will now be reflected in Section 3 of the new 2-NDFL. So let's look at everything in detail.
Deduction code for a child in 2019: what is it
As you know, income tax is taken from the income of employees. Those employees who have children can reduce this tax due to a certain amount deducted from the taxable base. This amount is called the deduction.
The amount of the deduction depends on the number of children in the family, whether they are relatives or guardianship is established over them, whether the children have a disability. Therefore, the amount by which you can reduce income will be different for each employee. And each of these deductions has its own code, which is affixed to the 2-NDFL certificate in 2019.
For example:
- Deduction code 126 in the 2-NDFL 2019 certificate is a deduction for the first child under 18 years old (full-time student, full-time graduate student up to 24 years old) in the amount of 1400 rubles to the parent;
- Deduction code 130 is a deduction for the first child under 18 years old (full-time student, full-time postgraduate student up to 24 years old) in the amount of 1,400 rubles for a guardian
Deduction code 126 in the 2-personal income tax certificate 2019: what is it
The deduction code 126 in the 2-NDFL certificate is set most often. It is deciphered as a deduction in the amount of 1,400 rubles for the first child under the age of 18, or for a child who is studying at any educational institution, even graduate school, but at the full-time department up to 24 years old to parents or adoptive parents.
Important! Deduction code 126 is put in 2-NDFL 2019 only if we are talking about reducing the tax base for parents or adoptive parents. There is a different code for trustees and guardians.
The confusion may be because until 2016 this code corresponded to 114. And now it just combined both parents and trustees. However, we recall that according to the order dated November 22, 2016 No. ММВ-7-11/ [email protected]"On making changes and additions to the annexes" to the order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated September 10, 2015 No. ММВ-7-11 / [email protected] deduction codes for children have been changed.
The result of these changes was not only a new numbering of deductions, but their semantic and quantitative content has changed. Here's what it looks like in practice.
Before the reform, the amount of deductions for different categories of employees was the same. It does not matter who the employee was to the child: parent, guardian, caregiver. The state considered that family ties mattered. Therefore, in 2019, when providing deductions, for example, for a disabled child:
- Foster parents, spouse (wife) of the foster parent, guardians, trustees make a deduction in the amount of 6,000 rubles (deduction code 133);
- Parents, adoptive parents, spouse of a parent or adoptive parent are already entitled to a deduction in the amount of 12,000 rubles (deduction code 129).
In order not to be mistaken about which code to put in the new 2-personal income tax certificate of 2019, look at the main difference between the tax deduction code 126 and 130.
*See the full table with new codes at the end of the article.
From 2019, all companies will have to submit a 2-NDFL certificate in a new format, which is approved by order of the Federal Tax Service dated 02.10.2018 No. ММВ-7-11 / [email protected] You can download the new certificate 2-NDFL 2019 above.
The new rules for filling out 2-NDFL 2019, which are established by the same order, require that deduction codes for the child be indicated without fail. Let's see how to do it right:
- Deduction codes are written only in Section 3, which is called “Standard, social and property tax deductions”
Be careful! The deduction code for a child is reflected only in Section 3, despite the presence of fields of the same name in the Appendix to the 2-NDFL certificate.

- If you repeat some code, then you can add up these amounts.
For example, you enter the deduction code 126, but you have three employees who have one child each, and for each you reduce the tax base by 1,400 rubles. Feel free to write opposite 126-4200 rubles (1400 * 3).
- However, when providing a physicist with several deductions with different codes during the tax period, then you need to draw up your own field for each.
This situation really arises when an employee has two children. You reduce his income for personal income tax by 1400 with code 126 and again by 1400, but with code 127 (for the second child).
Extremely important! If the amount of the deduction is the same, but the codes are different, separate the indicators, and never add them together. This is a very gross mistake.
Here's what these examples would look like in reality


If the accountant of the company is faced with a situation where the fields of the 2-NDFL 2019 reference are not enough to enter all the deduction codes used for children there. She can continue Section 3 on another sheet, but she must fill in the required lines.
So, when the need arose, add another Section 3 to 2-personal income tax, enter there:
- TIN / KPP of the company;
- Page #;
- Reference number and reporting year;
- Signs and number of adjustments;
- Code of the tax authority where the document is submitted;
- Code and amount of the deduction;
- Everything else can be crossed out.
Deduction codes per child in 2017: table
|
Deduction code 2019 |
The amount of the deduction |
Deciphering the codein what cases and to whom |
|---|---|---|
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
For the first child under the age of 18, or a full-time student of an educational institution under 24:
|
||
|
For a second child under the age of 18, or a full-time student of an educational institution under 24:
|
||
|
For a third child under the age of 18, or a full-time student of an educational institution under 24:
|
||
|
For a disabled child of I and II disability groups under the age of 18, or a full-time student of an educational institution up to 24 years of age:
|
||
|
Double deduction for the first child to the single parent, adoptive parent, spouse of the parent |
||
|
Double deduction for the first child to the sole guardian, guardian, foster parent. |
||
|
Double deduction for the second child to the single parent, adoptive parent, spouse of the parent: |
||
|
Double deduction for the second child to the sole guardian, guardian, foster parent. |
||
|
Double deduction for the third child to the single parent, adoptive parent, spouse of the parent: |
||
|
Double deduction for the third child to the sole guardian, guardian, foster parent. |
||
|
Double deduction for a disabled child with I and II disability groups to a single parent, adoptive parent, spouse of a parent: |
||
|
Double deduction for a disabled child with I and II disability groups to a single trustee, guardian, foster parent. |
||
|
Double deduction to the parent for the first child in case of refusal of the deduction of the second parent |
||
|
Double deduction to the adoptive parent for the first child if the deduction of the second parent is waived. |
||
|
Double deduction to the parent for the second child in case of refusal of the deduction of the second parent |
||
|
Double deduction to the adoptive parent for the second child in case of refusal of the deduction of the second parent. |
||
|
Double deduction to the parent for the third child in case of refusal of the deduction of the second parent |
||
|
Double deduction to the adoptive parent for the third child if the second parent refuses. |
||
|
Double deduction to the parent for a disabled child in case of refusal of the deduction of the second parent |
||
|
Double deduction for a foster parent for a disabled child in case of refusal of the deduction of the second parent. |
Two years ago, it was decided to change the form according to the 2-NDFL certificate. As a result, different codes began to be used in its different columns.
Sometimes putting the correct code is not a big problem, especially when it comes to, for example, the IFTS. Accountants know that this is a four-digit tax code in which the agent is registered and where, in fact, tax documentation must be submitted. Moreover, the first pair of digits is the number of the region, and another pair is the tax code, where all reports are submitted.
However, there are more complex codes that you need to know about and be able to apply in practice. These include the code of the document, which is responsible for the identity card. You can count 14 different codes corresponding to the documents. By the way, code 07 is a military ID, and 21 is, directly, a passport.
The form must indicate the citizenship of the FL, for which, in fact, a certificate will be issued. And this information is also encoded. And if we are talking about citizenship, but in practice - the country code, it is worth determining it according to OKSM. So, the code of Russia has the number 643.
However, the most interesting, of course, are the deduction and income codes. Most often, it is these codes that cause the greatest difficulties for accountants.
For different types of income
Let's talk about income codes first. The new codes used in the preparation of the document were developed and approved by the Federal Tax Service not so long ago - in 2015. This is evidenced by Order No. ММВ-7-11/387. These codes are placed in the third section opposite the FL income. The codes used below are especially commonly used.

So, the code number 2000 is used to indicate the remuneration that was paid to the employee for fulfilling his job duties. That is, in order to indicate in the salary, you should put down code 2000.
Moreover, this code is used for the RFP, which was paid in cash. The same code is used when you want to designate a premium.
But if the RFP is in its natural form, then it should be designated code 2530.
If we are talking about payments made under civil law contracts, then code number 2010. For this type of payment, a deduction can be applied in the amount of expenses that have documentary evidence. In this case, it will be placed code 403.
In the case of holiday pay will be used code 2012. We are talking about vacation, which is provided and paid to the employee daily, which is prescribed in article 114. If we are talking about vacation compensation, which is paid at the time of dismissal, then the code is affixed not 2012, but 2013 .
There is also a code for dividends. He has a number 1010 . In the event that we are talking about payment for goods and services, then the certificate puts code 2510. This may also include items such as rest, meals or utility bills.
When applying for a certificate, fill out the following fields:

Many accountants "puzzle" over what kind of code to put in the document. Deduction codes can be divided into several groups:
- 114 to 125- these are codes that belong to the standard;
- 311 to 312- these are property deductions;
- 320 to 324– social deductions;
- 403 to 405- professional deductions.
However, there are other codes for deductions that are not taxable within certain amounts. These are the codes from 501 to 508:
- 501 code- deduction from gifts made by an individual entrepreneur or organization;
- 503 code– withholding from financial assistance provided to retired employees;
- 505 code– deduction from prizes and winnings made as a result of a competition held as advertising;
- 508 code- a deduction from financial assistance that is provided at the birth of a child.
Standard children's
Standard child deductions include the following codes:
- 114 - deduction for the first child;
- 115 - for the second child;
- 116 - for the third, as well as subsequent children;
- 117 - for a child who has a disability of the first or second group;
- 118 – double withholding per child;
- 119 - double for two children;
- 120 - double for three and subsequent children;
- 121 - double for disabled children of the first or second group.

If one of the parents refused the double deduction, then the following codes apply:
- 122 - deduction for the first child;
- 123 - for the second child;
- 124 - for the third and subsequent children;
- 125 - for children with disabilities (only the first and second groups are taken into account).
Property
When it comes to property deductions, the following codes are used:
- 311 code- meaning deductions in relation to housing being acquired or under construction;
- 312 code- take into account the percentage of target loans that were taken for the purchase or construction of housing.
Social
Social type deductions:
- expenses incurred by the taxpayer in connection with his;
- the amounts that were spent by the taxpayer on the education of children;
- expenses incurred for medical services or medicines that were purchased for the taxpayer himself, his spouse or children.
Professional
There are several codes here:
- 403 - expenses that have arisen during the performance of work and have documentary grounds;
- 404 - deductions that have arisen due to the receipt of royalties and have a documentary basis;
- 405 - the amount that was spent on royalties.
On income without personal income tax within certain amounts
There are other codes for deductions that are not taxable within certain amounts. These are the codes from 501 to 508:
- 501 code- withholding from gifts made by an individual entrepreneur or organization;
- 503 code– deduction from financial assistance provided to retired employees;
- 505 code– deduction from prizes and winnings made following the results of competitions held as advertising;
- 508 code- withholding, which is carried out when paying parents at the birth of a child.
Changes for 2018
For 2018, several new deductions were introduced into the law.
So, the main changes were child deductions, which are used when filling out the 2-NDFL certificate. With a careful attitude to deductions and knowledge of the new rules, you can easily fill out a 2-NDFL certificate.
So, what new codes came into force in 2018?
- Code 104. 500 rub. per category taxpayer in accordance with paragraphs. 2 p. 1 art. 218 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- Code 105. 3000 rub. per category taxpayer in accordance with paragraphs. 1 p. 1 art. 218 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- Code 126. This code applies to a child under the age of 19, as well as to each cadet, student, intern, resident, graduate student enrolled in a full-time course, at the age of 24, to a parent, adoptive parent, and also to the spouse of the parent, on whose provision child.
- Code 127. Works under the same conditions as code 126, but already applies to the second child.
- Code 128. Extends to the same group of people, but in relation to the third and subsequent children.
- Code 129. The deduction applies to the same group of people, but in relation to a disabled child.
- Code 130. The code extends to the first child described in code 126, but now guardians, trustees or adoptive parents act instead of parents.
- Code 131. The deduction applies to the second child described in code 126, but instead of parents, foster parents, guardians or guardians are taken into account.
- Code 132. Extends to a third child who is described in code 126, but now to guardians, custodians or adoptive parents.
- Code 133. Applies to a disabled child studying under the same conditions as in code 126, but adoptive parents, guardians or guardians act as parents.
- Code 134. In double size for 1 child under 18, for each full-time student, graduate student, intern, intern, student, cadet under the age of 24 to a single parent, adoptive parent.
- Code 135. Double rate for 1 child under 18, for each full-time student, graduate student, intern, intern, student, cadet under the age of 24 to the sole guardian, trustee, foster parent.
- Code 136. In double the amount for the 2nd child under 18, for each full-time student, graduate student, intern, intern, student, cadet under the age of 24 to a single parent, adoptive parent.
- Code 137. Double the amount for the 2nd child under 18, for each full-time student, graduate student, intern, intern, student, cadet under the age of 24 to the sole guardian, trustee, foster parent.
- Code 138. Double the amount for the 3rd and each subsequent child under the age of 18, as well as for each full-time student, graduate student, intern, intern, student, cadet under the age of 24 to a single parent, adoptive parent.
- Code 139. Double the amount for the 3rd child under the age of 18, as well as for each full-time student, graduate student, intern, intern, student, cadet under the age of 24 to the sole guardian, trustee, foster parent.
- Code 140. In double the amount for a disabled child under the age of 18 or a full-time student, graduate student, intern, intern, student under the age of 24, who is a disabled person of group I or II to a single parent, adoptive parent.
- Code 141. In double the amount for a disabled child under the age of 18 or a full-time student, graduate student, intern, intern, student under the age of 24, who is a disabled person of group I or II to the sole guardian, trustee, foster parent.
- Code 142. Double the amount for 1 child under the age of 18, as well as for each full-time student, graduate student, intern, intern, student, cadet under the age of 24 to one of the parents of their choice based on the refusal of one of the parents from receiving a tax deduction.
- Code 143. Double the amount for 1 child under the age of 18, as well as for each full-time student, graduate student, intern, intern, student, cadet under the age of 24 to one of the adoptive parents of their choice based on a statement of refusal of one of adoptive parents from receiving a tax deduction.
- Code 144. In double the amount for the 2nd child under the age of 18, as well as for each full-time student, graduate student, intern, intern, student, cadet under the age of 24 to one of the parents of their choice on the basis of a statement of refusal of one of parents from receiving a tax deduction.
The Federal Tax Service of Russia has made changes to the codes of deductions for personal income tax. The coding for standard deductions for children has completely changed. In particular, the new child deduction code 126 is now in use.
Codes for children:
- for the first child 126 »;
- for the second child 127 »;
- 128 ».
For parents of disabled children, a separate personal income tax deduction code is also established - “ 129 ».
According to the law of the Russian Federation, one of the parents can refuse to receive a standard deduction for a child in favor of the other parent. For this case, their own deduction codes for reference 2-NDFL are also set:
- for the first child if the second parent refuses the right to a standard deduction - “ 142 »;
- for the second child 144 »:
- for the third and subsequent children - " 146 ».
The changes were made by order No. ММВ-7-11/ dated November 22, 2016 [email protected] Deductions must be applied when filling out 2-NDFL certificates for 2016, as well as for the periods of 2017.
The full list of changes is in the article " Withdrawal codes in 2017".
Table. New deduction codes for children in 2017
To whom the deduction and for which child |
First child (1400 rubles) |
Second child (1400 rubles) |
Third and subsequent (3000 rubles) |
Disabled person (12,000 or 6,000 rubles) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Parent, spouse, adoptive parent |
||||
|
Double size: |
||||
|
- single parents |
||||
|
- if the other parent refused the deduction |
||||
|
Adoptive parent, guardian and guardian |
||||
|
Single size (regular deduction) |
||||
|
Double size: |
||||
|
- single foster parent, guardian, caregiver |
||||
|
- if the second adoptive parent refused the deduction |
||||
Since 2016, the size of the standard deduction for a disabled child varies depending on who is granted it. If the parent, his spouse, wife, adoptive parent, then the deduction is 12,000 rubles. The adoptive parent, his spouse, guardian, trustee receive 6,000 rubles each. Separate codes were required to distinguish between deductions.