The wealth of the water artery of our country: the names of the rivers of Russia. Russian seven
There are many rivers and reservoirs in Russia. Our country is one of the richest in the world in terms of water supply. Water spaces occupy 12.4% of Russia's territory. Of these, the vast majority - 84% of surface water - is located east of the Urals. But in many densely populated areas of the European part of Russia there is a shortage of water resources.
The rivers of Russia belong to five main basins:
Black Sea basin
The basin of the Black and Azov Seas includes the Dnieper (in Russia only the upper reaches), Don, Kuban.
Caspian basin
The Volga is the largest river in this basin. At the same time, the Volga is also the largest river in Europe.
Arctic Basin
More than half of Russia's territory is irrigated by rivers flowing north into the marginal seas of the North Arctic Ocean: Barents, White, Kara, Laptev, East Siberian and Chukotka. That is, the Arctic basin is the most extensive of the Russian river basins. It is also called the Arctic Ocean basin.
It is located mostly in Siberia, but also includes the northern part of European Russia.
This pool includes greatest rivers Russia - (length 3650 km) and Irtysh (5410 km), (4090 km) and (4400 km). These rivers flow mainly from south to north, and despite the seasonality of navigation, they provide transport links between the interior of the country and the coast of the Arctic Ocean.
In the European part of Russia, the Arctic basin includes Northern Dvina(with Vychegda and Sukhona) and Pechora. The most famous, but not the most powerful rivers of this basin in the Asian part - Taz, Indigirka and Kolyma.
A feature of rivers in Siberia is their low gradient. For example, the Ob will decrease its current by only 200 m over a length of more than 2010 km. Due to their large length, these rivers are located in areas with different climatic regimes. Therefore, rivers often open up in the upper reaches earlier than in the lower ones, which leads to the appearance of ice jams. This causes floods, when water floods vast areas where temporary or permanent swamps form. One of the largest, the Vasyugan swamp at the confluence of the Ob River, covers an area of 49 thousand km².
Baltic Basin
A relatively small area in the north-west of European Russia drains into the Baltic Sea. The most significant river in this basin is the Neva.
Pacific Basin
The Pacific basin includes the rivers of the eastern part of the country, flowing from the eastern slopes of the Yablonovy and Stanovoy ridges, the Dzhugdzhur and Kolyma ridges and belonging to the basins of the marginal seas Pacific Ocean: Bering, Okhotsk and Japanese.
The main river of this basin is (2820 km long). The Amur basin covers most of the south and for a significant part of its length forms the state border between China and Russia.
Another famous river in Primorye, which in turn flows into the Amur, also forms part of the border with in Primorye. To the north of the mouth of the Amur, the watershed comes close to the seashore, which is why the rivers here have a short length, but are distinguished by a significant slope and rapid current.
Watersheds
We can talk about watersheds for a very long time. A watershed is a hill that separates different basins, directing the flow of water in two opposite directions.
The watershed between the Arctic and Pacific basins runs along the Chukotka Range, the Anadyr Plateau, and the Kolyma, Dzhugdzhur, Stanovoy and Yablonovy mountain ranges.
The watershed between the Black Sea and Caspian basins runs along the Valdai, Central Russian, Volga and Stavropol uplands, along the Main Caucasus Range.
On the territory of Russia, rivers are distributed unevenly. In the desert spaces of the Caspian region, in some places there are no rivers at all, and in the Caucasus mountains, mountain systems Altai and Eastern Siberia there are a lot of them.
The largest rivers in Russia
Eight of the world's fifty largest river basins are located partially or completely on Russian territory. These rivers of Russia are: Don, Volga, Dnieper, Ural.
The most big square basin y - 2990 thousand km2. The length of the Ob River is 3650 km. At the confluence with the Ob Bay Kara Sea The Ob River forms a delta of a huge area.
Mostly located on Russian territory. This is one of the largest rivers in the Far Eastern region (length 2824 km, basin area 1855 km2). The source is in Western (China). The Chinese are intensively developing the right bank of the river, due to ecological situation on the Amur has deteriorated sharply in the last decade. The Chinese are even changing the river's fairway as a result of uncontrolled excavation work, accidentally polluting it with harmful substances.
River Volga. It has the largest drainage basin in Europe - 1360 thousand km2, that is, 62.2% of the European part of Russia, 8% of the area of Russia, almost 13% of the territory of Europe. The source is located on the Valdai Hills in the Tver region. The length of the Volga is 3530 km. Flows into the Caspian Sea.
Four of the largest cities in Russia by population are located on the banks of the Volga:
- Nizhny Novgorod,
- Samara,
- Volgograd.
The main tributary of the Volga is the river Kama. The banks of the Kama are densely populated. The Volga river system carries out 2/3 of Russia's inland water transport.
2,600 rivers flow directly into the Volga, and in total there are more than 150 thousand watercourses more than 10 km long in its basin. Its largest tributaries are the Oka and Kama rivers.
There are about 2.5 million rivers on the map of Russia. The lion's share of them are relatively small, no more than 100 kilometers long. But there are also rivers that amaze. They reach truly shocking sizes.
The largest river in Russia is the Ob River. It flows through the territory Western Siberia, ranks first in terms of length in the country and second in Asia.
Every tribe that ever lived on the banks of the Ob gave the river its name. For example, the Nenets called it “Sala-yam”, which means “Cape River”. But in the Khanty and Mansi language the Ob sounded like “As” or “big river”. The Selkups called the river “Eme”, “Kvay”, “Kuay”, which means “large river”. But the residents of Russia saw for the first time during their hikes beyond the Ural Mountains. Before Ermak came to Siberia, the area near the Ob was called Obdorskaya.
There are several versions of the origin modern name rivers. According to one of them, in the Komi language Ob means “snowdrift” or “snow”. According to another version, the river got its name from the Iranian word “about” or “water”. There is an opinion that Ob comes from the Russian word “both”. This version also has the right to exist, since the Ob was formed at the confluence of the two rivers Katun and Biya.
So, the Ob is formed in Altai, where the Katun and Biya rivers connect. The river has a length of 3,650 kilometers from this point. Its length is 5410 kilometers from the source of the Irtysh. The area of the Ob water basin is 2,990,000 km². The river flows into the Kara Sea, and at the same time forms the 800-kilometer Gulf of Ob.
The rivers that form the Ob have different colors water. Katun has a greenish tint, but Biya is white or dirty gray. In one stream, both rivers have a striped stream of water for some time. But this phenomenon can only be observed in summer and autumn.
The Ob basin is located in different physiographic conditions, ranging from semi-deserts in the south to tundra in northern Russia. The nature of the flow divides the river into lower, middle and upper.
Bridge over the Ob
There is a dam on the river near Novosibirsk, where the Ob Sea was formed. In the upper reaches of the Ob, the depth is from 2 to 6 meters, and in places of rapids it is only 0.6 meters. The middle section starts from the mouth of the Tom and goes to the confluence of the Irtysh. Here the Ob is a full-flowing river. The width of the valleys is 30-50 kilometers, and the floodplains are 20-30 kilometers. The depth is already up to 8 meters.
But at the mouth of the Irtysh, the largest river in Russia becomes truly great. Its width is from 3 to 7 kilometers, and its depth is up to 20 meters. However, the river valley has a rather asymmetrical shape. If the right bank is steep and steep, then the left bank is flat. The floodplain is very saturated with canopies, which is similar to the circulatory system. From the mouth of the Irtysh to the village of Peregrebnoye, the Ob has one wide channel. Below, the river divides into the Bolshaya and Malaya Ob. They are separated by an island 30-40 kilometers wide and about 450 kilometers long. South of Salekhard, the Big and Small Ob Rivers unite again. The delta occupies more than 4 thousand square kilometers, and here the river is again divided into two branches - Nadymsky and Khamanelsky.

The water in the river can warm up to 23 degrees in the lower reaches and up to 28 degrees in the Barnaul area. The river is fed by meltwater and is characterized by spring floods.
The Ob, of course, is of key importance for the industrial and economic development of the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug. Now oil and gas are extracted here. Half of all peat reserves in the CIS countries are mined in the same region. It is worth noting that the Ob is a navigable river. Both freight and passenger transportation are developed. The Ob basin ranks first in the country in terms of the number of fish caught. Moreover, every year the catch is getting lower. This applies, first of all, to valuable fish species. Compared to the 80s, the catch of sturgeon has decreased by 10 times, peled by 6 times, and vendace by 3 times. This change is associated with industrial development of land, as a result of which spawning grounds are destroyed. In the lower reaches the river is rich in whitefish species. Every year, fishermen catch about 11 tons of whitefish, omul, tugun, peled, muksun, and nelma. This is half of the Russian catch and a third of the world's catch.
In general, in the Ob and Ob Bay there are about 50 different breeds fish, half of which are caught for industrial purposes. In addition to whitefish, there are ide, pike perch, roach, perch, crucian carp, burbot, and pike.
Storm on the Ob
Ob is not only one of the most beautiful rivers Russia and the world, she plays important function water main. The population of three countries is concentrated on its shores, namely Russia, China and Kazakhstan. Number of about 30 million people. For arid Kazakhstan and China, the Ob River is very important. The Ob first appeared on the map of Russia in 1542; the map was compiled by the German Anthony Wied and published two years later. There were no names at the top of the river. In 1546, already on the map of Sigismund Kerberstein, a large lake was drawn at the top of the Ob, and it was given the name Chinese. The author of the map indicated that the width of the river is 80 versts. Therefore, he believed that it must flow out of a large lake. For the next two centuries, a lake was painted near the top of the Ob.
The first Russian drawings of that area, which appeared in the 17th century, also depicted the lake, only they called it Telesskoye. At that time there lived a tribe with that name. Well, in 1688, on a newly published map, the lake was named Teletskoye. Chinese, also known as golden, Telesskoye and Teletskoye, one way or another, the lake is the source of the Biya, the river that merges with the Katun.

It is worth noting that the next largest Russian rivers– this is Yenisei and Lena. They are also located in Siberia. The Yenisei flows into the Kara Sea, its length is 4287 kilometers from the sources of the Small Yenisei. The river is located on the territory of two countries: Mongolia and Russia. Its area is 2 million 580 thousand square kilometers. This is what allows the Yenisei to take second place in the list of the largest rivers in Russia. Well, the Lena River begins in the mountains of Siberia and ends in the Laptev Sea. This is one of the largest rivers in the country, its length is 4,480 kilometers and its area is 2 million 490 thousand square kilometers. It is believed that the Russians first learned about the existence of this river in the 17th century, when they sent a detachment of Cossacks to search for it.
Subscribe to our channel in Yandex.Zen
Russia occupies a vast geographical area, and it is not surprising that numerous rivers stretch across its expanses, which played an important historical role in the settlement and development of new lands. Almost all the largest cities in the country are located on rivers.
In total, there are about 3 million rivers on the territory of the Russian Federation, and all of them are an important component of the life of many people, animals and plants. Rivers provide us with food, water, electricity, places for recreation, and also serve as transport routes connecting different settlements. It is an indispensable source of water for Agriculture and industry.
In this article you can get acquainted with the largest rivers of Russia, get them brief description and to look geographical location on the map of the country.
Rivers of the Russian Federation
Map of the largest rivers in Russia
The country's territory is divided into European and Asian parts. The dividing line is usually considered to be the Ural Mountains and the Caspian Sea. The rivers of the European part flow into the Arctic Ocean, the Baltic Sea, the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea. The rivers of the Asian part flow into the Arctic and Pacific oceans.
The largest rivers in European Russia are the Volga, Don, Kama, Oka and Northern Dvina, while some rivers originate in Russia but flow into other countries, such as the Dnieper and Western Dvina. The following large rivers flow through the Asian expanses of the country: Ob, Irtysh, Yenisei, Angara, Lena, Yana, Indigirka and Kolyma.
Of the five main drainage basins: Arctic, Pacific, Baltic, Black Sea and Caspian, the first, located in Siberia and including the northern part of the Russian Plain, is the most extensive. To a large extent, this basin is filled by the three largest rivers in Russia: the Ob (3650 km), which, together with its main tributary, the Irtysh River, forms a river system 5410 km long, the Yenisei (3487 km), and the Lena (4400 km). The sum of their drainage areas exceeds 8 million km², and the total water flow is about 50,000 m³/s.
Large rivers of Siberia provide transport arteries with inside to the Arctic Sea Route, although they are blocked by ice for long periods each year. The slight slope of the Ob River causes it to slowly meander through a huge floodplain. Due to the flow to the north, from the upper reaches to the lower boundaries of the thaw, extensive flooding occurs quite often, which leads to the development of huge swamps. The Vasyugan swamps on the Ob-Irtysh interfluve cover an area of more than 50,000 km².
The rivers of the rest of Siberia (about 4.7 million km²) flow into the Pacific Ocean. In the north, where the watershed is close to the coast, numerous small, fast-flowing streams flow from the mountains, but most of southeastern Siberia is drained by the Amur River. For most of its length, the Amur forms the border separating Russia and China. The Ussuri, one of the tributaries of the Amur, forms another significant border line between the countries.
Three large drainage basins located in the European part of Russia south of the Arctic basin. The Dnieper, only the upper reaches of which are in Russia, as well as the Don and Volga are the longest European river, originating in the north-west of the Valdai Hills and flowing into the Caspian Sea. Second only to the Siberian rivers, the Volga basin covers an area of 1,380,000 km². The rivers of the East European Plain have long served as important transport arteries; in fact, the Volga river system provides two-thirds of the entire Russian inland waterway traffic.
10 largest and longest rivers in Russia
Many mighty rivers flow through the territory of the Russian Federation, but the size of some of them is truly impressive. Below is a list and maps of the country's largest rivers, both by length and by drainage basin area.
Lena

 The Lena River is one of the most long rivers planets. It originates near Lake Baikal in southern Russia and flows west, and then above Yakutsk it smoothly turns north, where it flows into the Laptev Sea (a basin of the Arctic Ocean). Near its mouth, the river forms a huge delta with an area of 32,000 km, which is the largest in the Arctic and the largest protected wilderness area in Russia.
The Lena River is one of the most long rivers planets. It originates near Lake Baikal in southern Russia and flows west, and then above Yakutsk it smoothly turns north, where it flows into the Laptev Sea (a basin of the Arctic Ocean). Near its mouth, the river forms a huge delta with an area of 32,000 km, which is the largest in the Arctic and the largest protected wilderness area in Russia.
The Lena Delta, which floods every spring, serves as an important area for nesting and migration of birds, and also supports rich fish populations. The river is home to 92 planktonic species, 57 benthos species and 38 fish species. Sturgeon, burbot, chum salmon, whitefish, nelma and albula are the most commercially important fish species.
Swans, dippers, geese, ducks, plovers, waders, snipe, phalaropes, terns, skuas, predator birds, sparrows and gulls are just some of the migratory birds that nest in the Lena's productive wetlands.
Ob

 The Ob is the seventh longest river in the world, stretching over a distance of 3,650 kilometers in the Western Siberian region of the Russian Federation. This river playing big economic importance for Russia, it occurs at the confluence of the Biya and Katun rivers in Altai. It mainly passes through the country, although many of its tributaries originate in China, Mongolia and Kazakhstan. The Ob is connected to its largest tributary by the Irtysh River, about 69° east longitude. It flows into the Kara Sea of the Arctic Ocean, forming the Ob Bay. The river has a huge drainage area, which is about 2.99 million km².
The Ob is the seventh longest river in the world, stretching over a distance of 3,650 kilometers in the Western Siberian region of the Russian Federation. This river playing big economic importance for Russia, it occurs at the confluence of the Biya and Katun rivers in Altai. It mainly passes through the country, although many of its tributaries originate in China, Mongolia and Kazakhstan. The Ob is connected to its largest tributary by the Irtysh River, about 69° east longitude. It flows into the Kara Sea of the Arctic Ocean, forming the Ob Bay. The river has a huge drainage area, which is about 2.99 million km².
The habitat surrounding the Ob consists of vast expanses of steppe and taiga flora in the upper and middle reaches of the river. Birches, pines, firs and cedars are some of the famous trees growing in these areas. Thickets of willow, rose hips and bird cherry also grow along the watercourse. The river basin is replete with aquatic flora and fauna, including more than 50 species of fish (sturgeon, carp, perch, nelma and peled, etc.) and about 150 species of birds. Minks, wolves, Siberian moles, otters, beavers, stoats and other local mammal species. In the lower reaches of the Ob, the Arctic tundra is characterized by snow-covered landscapes for most of the year. Polar bears, arctic foxes, polar owls and arctic hares represent this region.
Volga

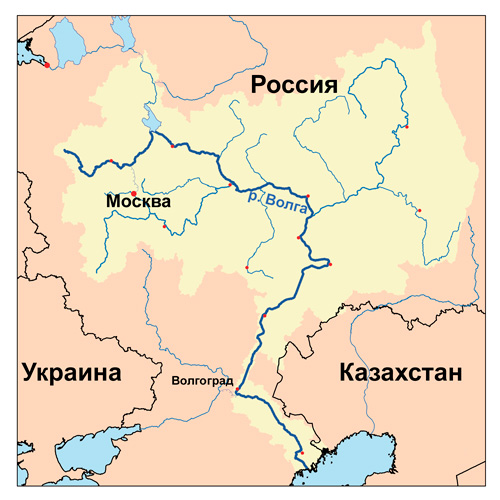 The longest river in Europe, the Volga, which is often considered the national river of Russia, has large swimming pool, covering almost two-thirds of the European part of Russia. The Volga originates in the north-west of the Valdai Hills, and flows south over 3530 km, where it flows into the Caspian Sea. About 200 tributaries join the river along the entire route. Eleven of the country's major cities, including Moscow, are located along the Volga basin, which covers an area of 1.36 million km².
The longest river in Europe, the Volga, which is often considered the national river of Russia, has large swimming pool, covering almost two-thirds of the European part of Russia. The Volga originates in the north-west of the Valdai Hills, and flows south over 3530 km, where it flows into the Caspian Sea. About 200 tributaries join the river along the entire route. Eleven of the country's major cities, including Moscow, are located along the Volga basin, which covers an area of 1.36 million km².
The climate in the river basin varies along its course from north to south. In the northern regions it predominates temperate climate with cold snowy winters and warm humid summers. The southern regions are characterized by cool winters and hot, dry summers. The Volga Delta is one of the richest habitats, which is home to 430 plant species, 127 fish species, 260 bird species and 850 aquatic species.
Yenisei

 The mouth of the Yenisei River is located near the city of Kazyl, where it merges with the Little Yenisei River, which originates in Mongolia and flows north, where it drains a vast area of Siberia before emptying into the Kara Sea (Arctic Ocean), a journey of 3,487 km. The Angara River, which flows from Lake Baikal, is one of the main tributaries of the upper Yenisei.
The mouth of the Yenisei River is located near the city of Kazyl, where it merges with the Little Yenisei River, which originates in Mongolia and flows north, where it drains a vast area of Siberia before emptying into the Kara Sea (Arctic Ocean), a journey of 3,487 km. The Angara River, which flows from Lake Baikal, is one of the main tributaries of the upper Yenisei.
The waters of the Yenisei are home to about 55 species of local fish, including Siberian sturgeon, flounder, roach, northern pike, Siberian gudgeon, tench and sterlet. Most of the river basin surrounds, mainly consisting of the following rocks coniferous trees: fir, cedar, pine and larch. In some areas of the upper Yenisei there are also steppe pastures. In the north, boreal forests give way to arctic forests. Musk deer, elk, roe deer and Japanese mouse are some of the mammal species found in the taiga forests along the river. Also found are birds such as the Siberian blue robin, Siberian lentil, capercaillie and wood snipe. Ducks, geese and swans are found in the lower reaches of summer time of the year.
Lower Tunguska

 Lower Tunguska is a right tributary of the Yenisei flowing through Irkutsk region And Krasnoyarsk region Russia. Its length is 2989 km, and the basin area is 473 thousand km². The river extends near the watershed between the Yenisei and Lena river basins and flows north and then west across the Central Siberian Plateau.
Lower Tunguska is a right tributary of the Yenisei flowing through Irkutsk region And Krasnoyarsk region Russia. Its length is 2989 km, and the basin area is 473 thousand km². The river extends near the watershed between the Yenisei and Lena river basins and flows north and then west across the Central Siberian Plateau.
In the upper reaches the river forms a wide valley with numerous shallows, but after turning to the west the valley narrows and numerous gorges and rapids appear. In the river basin lies the vast Tunguska coal basin.
Amur

 The Amur is the tenth longest river in the world, located in East Asia and forms the border between Far Eastern District Russian Federation and Northeast China. The river originates at the confluence of the Shilka and Argun rivers. The Amur flows for 2825 km to the northwestern part of the Pacific Ocean and flows into the Sea of Okhotsk.
The Amur is the tenth longest river in the world, located in East Asia and forms the border between Far Eastern District Russian Federation and Northeast China. The river originates at the confluence of the Shilka and Argun rivers. The Amur flows for 2825 km to the northwestern part of the Pacific Ocean and flows into the Sea of Okhotsk.
The river has many vegetation zones in various parts of its basin, including taiga forests and swamps, Manchurian mixed forests, Amur meadow steppes, forest-steppes, steppes and tundra. The wetlands along the Amur basin are some of the most valuable ecosystems, home to a huge variety of flora and fauna. These are important refuges for millions of migratory birds, including white storks and red-crowned cranes. The river basin is home to more than 5,000 species of vascular plants, 70 species of mammals and 400 species of birds. Rare and endangered species are found here, such as Amur tiger And amur leopard- the most iconic mammal species in the region. The waters of the Amur are home to a wide variety of fish species: about 100 species in the lower reaches and 60 in the upper reaches. Chum salmon, burbot and whitefish are among the most commercially important northern fish species.
Vilyui

 The Vilyui is a river in Central and Eastern Siberia, flowing primarily through the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) in eastern Russia. This is the largest tributary of the Lena, with a length of 2650 km and a basin area of about 454 thousand km².
The Vilyui is a river in Central and Eastern Siberia, flowing primarily through the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) in eastern Russia. This is the largest tributary of the Lena, with a length of 2650 km and a basin area of about 454 thousand km².
The Vilyui originates on the Central Siberian Plateau and first flows east, then south and southeast, and again east to its confluence with the Lena (about 300 km northwest of the city of Yakutsk). The river and adjacent reservoirs are rich in commercial fish species.
Kolyma

 With a length of more than 2,100 kilometers and a basin area of 643 thousand km², Kolyma is the most big river Eastern Siberia, flowing into the Arctic Ocean. The upper reaches of this river system began to develop back in the Cretaceous period, when the main watershed between the Sea of Okhotsk and the Arctic Ocean was formed.
With a length of more than 2,100 kilometers and a basin area of 643 thousand km², Kolyma is the most big river Eastern Siberia, flowing into the Arctic Ocean. The upper reaches of this river system began to develop back in the Cretaceous period, when the main watershed between the Sea of Okhotsk and the Arctic Ocean was formed.
At the beginning of its journey, Kolyma makes its way through narrow gorges with numerous rapids. Gradually, its valley expands, and below the confluence with the Zyryanka River, it flows through the wide swampy Kolyma Lowland, and then flows into the East Siberian Sea.
Ural

 The Ural is a large river flowing in Russia and Kazakhstan, 2428 km long (1550 km in the Russian Federation), and a basin area of about 231 thousand km². The river originates in the Ural Mountains on the slopes of the Round Hill and flows into south direction. In the city of Orsk, it turns sharply west through the southern outskirts of the Urals, past Orenburg, and turns south again, heading towards the Caspian Sea. Its flow has a large spring maximum, and freeze-up lasts from late November to April. Navigation on the river is carried out to the city of Oral in Kazakhstan. The dam and hydroelectric power station were built on the Iriklinskoye reservoir, south of the city of Magnitogorsk.
The Ural is a large river flowing in Russia and Kazakhstan, 2428 km long (1550 km in the Russian Federation), and a basin area of about 231 thousand km². The river originates in the Ural Mountains on the slopes of the Round Hill and flows into south direction. In the city of Orsk, it turns sharply west through the southern outskirts of the Urals, past Orenburg, and turns south again, heading towards the Caspian Sea. Its flow has a large spring maximum, and freeze-up lasts from late November to April. Navigation on the river is carried out to the city of Oral in Kazakhstan. The dam and hydroelectric power station were built on the Iriklinskoye reservoir, south of the city of Magnitogorsk.
The Ural Delta wetlands are particularly important for migratory birds as a primary refuge along the Asian Flyway. The river is also important for many fish species of the Caspian Sea, which visit its deltas and migrate upstream to spawn. In the lower reaches of the river there are 47 species from 13 families. The carp family accounts for 40% species diversity fish, sturgeon and herring - 11%, perch - 9% and salmon - 4.4%. The main commercial species are sturgeon, roach, bream, pike perch, carp, asp and catfish. TO rare species include Caspian salmon, sterlet, nelma and kutum. The Ural delta and surrounding areas are home to about 48 species of animals, of which 21 species belong to the order of rodents.
Don

 The Don is one of the largest rivers in the Russian Federation and the 5th longest river in Europe. Its basin is located between the Dnieper-Donets depression in the west, the Volga basin in the east, and the Oka River basin (a tributary of the Volga) in the north.
The Don is one of the largest rivers in the Russian Federation and the 5th longest river in Europe. Its basin is located between the Dnieper-Donets depression in the west, the Volga basin in the east, and the Oka River basin (a tributary of the Volga) in the north.
The Don originates in the city of Novomoskovsk 60 km southeast of Tula (120 km south of Moscow), and flows for a distance of about 1870 km to the Sea of Azov. From its source, the river heads southeast to Voronezh and then southwest to its mouth. The main tributary of the Don is Seversky Donets.
Table of the largest rivers of the Russian Federation
| River name | Length in Russia, km | Total length, km | Basin, km² | Water consumption, m³/s | Place of confluence (Mouth) |
| R. Lena | 4400 | 4400 | 2.49 million | 16350 | Laptev sea |
| R. Ob | 3650 | 3650 | 2.99 million | 12492 | Kara Sea |
| R. Volga | 3530 | 3530 | 1.36 million | 8060 | Caspian Sea |
| R. Yenisei | 3487 | 3487 | 2.58 million | 19800 | Kara Sea |
| R. Lower Tunguska | 2989 | 2989 | 473 thousand | 3680 | R. Yenisei |
| R. Amur | 2824 | 2824 | 1.86 million | 12800 | Sea of Okhotsk |
| R. Vilyui | 2650 | 2650 | 454 thousand | 1468 | R. Lena |
| R. Kolyma | 2129 | 2129 | 643 thousand | 3800 | East-Siberian Sea |
| R. Ural | 1550 | 2428 | 231 thousand | 400 | Caspian Sea |
| R. Don | 1870 | 1870 | 422 thousand | 900 | Sea of Azov |
If you find an error, please highlight a piece of text and click Ctrl+Enter.
Natural sources, such as rivers, are not only a tourist attraction in Russia. This is a real treasure of our rich Natural resources, countries.
The world leadership in terms of river flow per year was recently revised, and Russia currently ranks second in this indicator.
The largest rivers in Russia
How many rivers are there in Russia? Famous among them, with a length of more than one and a half thousand kilometers, are the Amur, Yenisei, Lena and Ob.
In total, there are over two million such “arteries” of land in Russia. They are easy to find on the map of Russian rivers.

Map of Russian rivers (click to enlarge)
The table shows a list of rivers in descending order of length. The text gives a description in alphabetical order.
Amur
The great Russian river runs along the southeastern Russian border with the country “where the sun rises” (China). The “black dragon” (Heilongjiang in Chinese) settled down at ease.

It originates where the flow of the Arguni and Shilka ends. Having covered two and a half thousand kilometers, the Amur flows into the Sea of Japan (Okhotsk). All along the route, from Pokrovka to the Amur Estuary, cargo and passengers are supplied.

Fish White Cupid
Amur is the Russian leader in the diversity of ichthyofauna: up to 139 species and subspecies of fish live in its waters, including unique breeds of sturgeon and salmon.

The tributary of the Amur - Zeya - is fuller. There is a similar situation between the Volga and Kama. Thus, width and depth of water are not always taken into account when determining tributary rivers.
Volga
A source of inspiration for poets. The subject of the artist's beautiful paintings. Character from folk tales and myths. A famous river in the western part of Russia, the beauty of which cannot be compared with others.

The Volga occupies a special place in the soul of Russian people. She was endowed with will and intelligence, making her a symbol of an unenslaved people. In Rus' it had a special name “Mother Volga”.
The uniqueness is that the main water branch does not flow into the world's oceans, having an internal flow. On its banks stand big cities(for example, Samara).

The main navigable river in Russia. Its bed is so deep and rich in tributaries that it is rightfully considered the central water artery, which is divided into three parts:
- lower;
- average;
- top.
This made navigation easier.
From the point of view of science (hydrology and history), the lower part of the Volga is a natural continuation of the Kama river Perm region. However, due to the unifying role for the Russian state, priorities have changed (the Kama is a tributary of the Volga, and nothing else).
The official source of the Volga is located in the Tver region. This is the village of Volgoverkhovye, where a spring of water breaks through to the surface, to the delight of numerous tourists.

It carries its waters through lakes Verkhit Maly and Verkhit Bolshoi, a system of large lakes in the upper reaches, and unites them in a reservoir all the way to the city of Rzhev.
The Volga is a river that unites four seas (Black, Azov, White and Baltic).
Vilyui
The most long tributary river Lena. Its length is two thousand six hundred and fifty kilometers.
The Yakuts have been using fish resources and water for decades. Ecological state gradually deteriorating due to the oil and gas industry. It is planned to build a hydrological power station.

The Vilyuisky basin is rich in fish resources and lakes, of which there are more than sixty-seven thousand. The source of the tributary is located on the plateau of the same name near Tunguska (Lower).
Gryazeva
The shortest river carries its waters over a distance of tens of kilometers. It starts a kilometer from the Mitovskaya station (Moscow railway).

Due to a historical inaccuracy, in the 20th century it changed places with Nakhabinka. The smallest river described.
Don
It takes its name from the languages: Scythians, Sarmatians and Aryans. From the same root word dānu (translated as “river, drops or dew”). Flows from the Central Russian Upland to a distance of one thousand eight hundred and seventy kilometers to Sea of Azov.

The Don is a winding river in the area of the Big Bend (Donskaya Luka). The bends bring the channel closer to the Volga already described above at a distance of sixty kilometers.

The Don is navigable due to the calm (slow) current that is typical for lowland rivers.
Northern Dvina
It was formed due to the union of two tributaries (Sukhona and Vychegda) with a delta of nine hundred square kilometers.

The trading history of the river begins in the fifteenth century. A lot of cargo was delivered to Europe.

The "status" changed in the nineteenth century, when the Dvina became an important military strategic site.
Yenisei
He is called “father” by analogy with Mother Volga. The deepest artery, running to the Arctic Ocean, crossing most of the climatic zones Siberia.

The mouth of the river (Yenisei basin) is fifty kilometers. On its banks you can meet a camel or a polar bear.

In terms of flow volume, the Yenisei is second only to the Tunguska (lower part), despite the fact that it is fed by half a thousand tributaries.
Irtysh
It received its letter designation on the map thanks to the Turkic-Iranian theory (“kara” means land, and “ircis” means a swift stream, fast).

The longest length, over 4 thousand kilometers, forced the residents of the coast to give the honorary name Black Irtysh to the section to Lake Zaisan (the synonym “kara” is used - black).
Ishim
It owes its appearance on the world map to the death of the Tatar Khan, who drowned in the left tributary of the Irtysh. “Took” a place in the Kazakh mountains of Iyaz.

Translated from Tatar language Ishim, and more specifically Ishimak, means “destroying.” According to a Russian laboratory, there are traces of pollution from the oil refining industry in its lower reaches.
Kuban
The beautiful river, glorified by more than one generation of Cossacks, did not immediately acquire its familiar name. Scholars suggest that there were at least three hundred different references to her. As a result, the Karachay-Balkar name “kuban” (stream, rising) remained.

Is born mountain river at the foot of Elbrus, after which it carries its waters through nine hundred kilometers and flows into the Sea of Azov.

On the banks of the great Russian Kuban there is a place for birds of prey and semi-aquatic birds, as well as wild boars and muskrats. And hundreds of species of fish found shelter in its waters.
Lena
In the first half of the seventeenth century, the Russian pioneer Pyande became acquainted with the life of the Kangalas Yakuts (now the city of Yakutsk). The largest river, the Lena (from the similar Even “yene”), became the first for the traveler to raft.

Has a length of over 4 thousand kilometers (the longest),

Surprisingly, the starting point of the Lena is a swampy area near Lake Baikal (ten kilometers to the west).
Neva
The only river flowing from Lake Ladoga. The uncontrollable and capricious “coquette river” constantly changes its channel depth and width.

It attracted the attention of Peter I both because of its picturesqueness and because it had the most water. The Tsar founded the most beautiful city of “drawbridges” (St. Petersburg) on its banks.
The total length is 74 kilometers.Its basin has 48 thousand lakes, and the volume of water is comparable to the Don and Dnieper combined.
After research in 2013, out of 24 places for swimming, one turned out to be suitable. After inspection, the pollution class was assigned to the third.
Ob
Leader in basin size (3 million km2) and water flow (12 thousand meters per second). The river stretches for 3.5 thousand km. and flows into the Kara Sea.

The widest in Russia. In the spring, a sixty-kilometer floodplain is formed at the confluence, and the flood itself lasts up to three months.

Russian travelers learned about the largest river in Russia from Komi guides (“obva” means “snow water”).
Ural
The original Yaik (Kazakh name) was renamed Ural by decree of the Russian Empress Catherine II. Many indigenous people in the Urals remember the former name.

The river originates in Uraltau (mountains Southern Urals) and flows into the Caspian Sea.

The Ural has a rather winding channel that often changes direction, leaving behind oxbow reservoirs.
Conclusion
Clean rivers are most often found in places devoid of constant human intervention. Drinking water from a source close to the city is dangerous. There is a possibility of industrial pollution.
IN Siberian taiga There were still springs with crystal clear moisture. Alas, technological progress makes environmental situation It gets more difficult every year.
Eat great way inspect water resources Russia, having taken a cruise along the most big rivers. This could be a great opportunity to understand the world of the Russian soul, known for its mystery.
Russia is the largest state in the world (its area is 17.12 million km 2, which is 12% of the earth's land), about 3 million rivers flow through its territory. Most are no different large sizes and has relatively short length, their total length is 6.5 million km.
The Ural Mountains and the Caspian Sea divide the territory of Russia into European and Asian parts. The rivers of the European part belong to the basins of such seas as the Black, Caspian, Baltic and the Arctic Ocean. Rivers of the Asian part - the basins of the Arctic and Pacific oceans.
Large rivers of Russia
The largest rivers of the European part are the Volga, Don, Oka, Kama, Northern Dvina, some originate in Russia, but flow into the seas in other countries (for example, the source of the Western Dvina River is the Valdai Upland, the Tver region of the Russian Federation, the mouth is the Gulf of Riga, Latvia). The Asian part is crossed by such large rivers as the Ob, Yenisei, Irtysh, Angara, Lena, Yana, Indigirka, and Kolyma.
The Lena River, 4400 km long, is one of the longest rivers on our planet (7th place in the world), its sources are located near the deep-water freshwater Lake Baikal in Central Siberia.
The area of its basin is 2490 thousand km². It has a western direction of flow, reaching the city of Yakutsk, it changes its direction to the north. Forming a huge delta at the mouth (its area is 32 thousand km2), which is the largest in the Arctic, the Lena flows into the Laptev Sea, the basin of the Arctic Ocean. The river is the main transport artery of Yakutia, its largest tributaries are the Aldan, Vitim, Vilyui, and Olekma rivers...
The Ob River passes through the territory of Western Siberia, its length is 3650 km, together with the Irtysh it forms a river system 5410 km long, and this is the sixth largest in the world. The area of the Ob River basin is 2990 thousand km².
It begins in the Altai Mountains, at the source of the confluence of the Biya and Katun rivers. In the southern part of Novosibirsk, a constructed dam forms a reservoir, the so-called “Ob Sea”, then the river flows through the Ob Bay (an area of more than 4 thousand km²) into the Kara Sea, basin of the Arctic Ocean. The water in the river has a high content organic matter and low oxygen levels. Used for commercial fish production ( valuable species- sturgeon, sterlet, nelma, muksun, broad whitefish, whitefish, peled, as well as small ones - pike, ide, burbot, dace, roach, crucian carp, perch), electricity production (Novosibirsk hydroelectric power station on the Ob, Bukhtarminskaya and Ust-Kamenogorskaya on the Irtysh) , shipping...
The length of the Yenisei River is 3487 km, it flows through the territory of Siberia, dividing it into Western and Eastern parts. The Yenisei is one of the largest rivers in the world, together with the tributaries Angara, Selenga and the Ider River, it forms a large river system 5238 km long, with a basin area of 2580 thousand km².
The river begins in the Khangai Mountains, on the Ider River (Mongolia), and flows into the Kara Sea in the Arctic Ocean basin. The river itself is called the Yenisei near the city of Kyzyl (Krasnoyarsk Territory, Republic of Tyva), where the confluence of the Big and Small Yenisei rivers occurs. It has a large number of tributaries (up to 500), about 30 thousand km long, the largest: Angara, Abakan, Lower Tunguska. Chicken. Dudinka and others. The river is navigable, this is one of the most important waterways in the Krasnoyarsk region of Russia, downstream there are such large hydroelectric power stations as Sayano-Shushenskaya, Mainskaya, Krasnoyarsk, timber rafting is carried out...
The Amur River, 2824 km long, with a basin area of 1855 thousand km², flows through Russia (54%), China (44.2%) and Mongolia (1.8%). Its sources are in the mountains of western Manchuria (China), at the confluence of the Shilka and Argun rivers. The current has an eastern direction and passes through the territory Far East, starting on the Russian-Chinese border, its mouth is located in the Gulf of Tatar (its northern part is called the Amur Estuary) of the Sea of Okhotsk, which belongs to the Arctic Ocean basin. Major tributaries: Zeya, Bureya, Ussuri, Anyui, Sungari, Amgun.
The river is characterized by sharp fluctuations in water level, which is caused by summer and autumn monsoon precipitation, with heavy downpours a wide spill of water up to 25 km is possible, which lasts up to two months. The Amur is used for navigation, large hydroelectric power stations have been built here (Zeyskaya, Bureyskaya), commercial fisheries are developed (the Amur has the most developed ichthyofauna among all the rivers of Russia, about 140 species of fish live here, 39 species of which are commercial)...
One of the most famous rivers flowing in the European part of Russia, for which the words from the song are composed "Toa folk beauty, like a deep sea" - Volga. Its length is 3530 km, the basin area is 1360 thousand km² (1/3 of the entire European part of Russia), most of it passes through the territory of Russia (99.8%), the smaller part passes through Kazakhstan (0.2%).
This is one of the largest rivers in Russia and throughout Europe. Its sources are located on the Valdai Plateau in the Tver region, it flows into the Caspian Sea, forming a delta, along the way receiving water from more than two hundred tributaries, the most significant of them is the left tributary of the Volga, the Kama River. The area around the river bed (15 constituent entities of the Russian Federation are located here) is called the Volga region, there are four large millionaire cities: Nizhny Novgorod, Kazan, Samara and Volgograd, 8 hydroelectric power stations of the Volga-Kama cascade...
The Ural River, 2428 km long (the third largest in Europe after the Volga and Danube) and a basin area of 2310 thousand km², is unique in that it divides the continent of Eurasia into two parts of the world, Asia and Europe, so one of its banks lies in Europe, the other - in Asia.
The river flows through the territory of Russia and Kazakhstan, begins on the slopes of Uraltau (Bashkortostan), flows from north to south, then changes direction several times to the west, then to the south, then to the east, forms a mouth with branches and flows into the Caspian Sea. The Urals are used to a small extent for shipping, Orenburg region The Iriklinskoye reservoir and hydroelectric power station have been built on the river, and commercial fishing is underway for fish (sturgeon, roach, bream, pike perch, carp, asp, catfish, Caspian salmon, sterlet, nelma, kutum)...
The Don River is one of the largest rivers in the European part of Russia, its length is 1870 km, its basin area is 422 thousand km², and in terms of volume of water it passes, it is the fourth in Europe after the Volga, Dnieper and Danube.
This river is one of the oldest, its age is 23 million years, its sources are located in the small town of Novomoskovsk ( Tula region), here begins the small river Urvanka, which gradually grows and absorbs water from other tributaries (there are about 5 thousand of them) spills into a wide channel and flows over large areas of southern Russia, flowing into the Taganrog Bay of the Sea of Azov. The main tributaries of the Don are the Seversky Donets, Khoper, and Medveditsa. The river is rapid and shallow, has a typical flat character, and such large million-plus cities as Voronezh and Rostov-on-Don are located here. The Don is navigable from its mouth to the city of Voronezh, there are several reservoirs, the Tsimlyansk hydroelectric station...
The Northern Dvina River, 744 km long and with a basin area of 357 thousand km², is one of the largest navigable rivers in the European part of Russia.
Its origins are the confluence of the Sukhona and Yug rivers near Veliky Ustyug ( Vologda Region), has a northern flow direction to Arkhangelsk, then northwest and again north, near Novodvinsk (a city in the Arkhangelsk region) it forms a delta consisting of several branches, its area is about 900 km², and flows into the Dvina Bay White Sea, Arctic Ocean basin. The main tributaries are the Vychegda, Vaga, Pinega, Yumizh. The river is navigable along its entire length; the oldest paddle steamer, built in 1911, N.V., plies here. Gogol"...
The Neva River flowing through the territory Leningrad region, connecting Lake Ladoga with the Gulf of Finland in the Baltic Sea, is one of the most picturesque and deep-flowing rivers in Russia. Length - 74 km, basin area of 48 thousand rivers and 26 thousand lakes - 5 thousand km². 26 rivers and rivulets flow into the Neva, the main tributaries are Mga, Izhora, Okhta, Chernaya Rechka.
Neva - the only river, flowing from the Shlisselburg Bay in Lake Ladoga, its bed flows through the territory of the Neva Lowland, the mouth is located in the Neva Bay of the Gulf of Finland, which is part of Baltic Sea. On the banks of the Neva there are cities such as St. Petersburg, Shlisselburg, Kirovsk, Otradnoye, the river is navigable along its entire length...
The Kuban River in the very south of Russia originates in Karachay-Cherkessia at the foot of Mount Elbrus ( Caucasus Mountains) and flows through the territory of the North Caucasus, forming a delta and flowing into the Sea of Azov. The length of the river is 870 km, the basin area is 58 thousand km², 14 thousand tributaries, the largest of them are Afips, Laba, Pshish, Mara, Dzheguta, Gorkaya.
The river is home to the largest reservoir in the Caucasus - Krasnodar, the Kuban cascade of hydroelectric power stations, the cities of Karachaevsk, Cherkessk, Armavir, Novokubansk, Krasnodar, Temryuk...













