General characteristics of the suborder lizards (SAURIA). The names and characteristics of different types of lizards What type of development in a lizard
Lizards are reptiles with a variety of species. You can find out photos of various lizards and a description of their life by reading this article.
To date, scientists have established that lizards are the largest group among the Reptiles (Reptiles) class. Very often we call those who are not lizards at all. We are used to the fact that lizards are all representatives of reptiles who run on four legs and have a long tail. But you will be surprised to learn that scientists refer to lizards, basically only representatives of the family Real lizards, and the rest like them: agamas, skinks, monitor lizards, and geckos are a completely different group.
Let's take a closer look at real lizards. These reptiles are of medium size, although there are also very small species among them. Basically, the body length of lizards reaches from 20 to 40 cm. And only a pearl lizard can grow up to 80 centimeters. But a separate group in the family of real lizards, called the lizard, has a size of about 10 centimeters.
Real lizards differ from their own kind (other reptiles) by their mobile eyelids. For example, snakes cannot boast of such an eye device, because their eyelids are fused. All lizards have an oblong body and a long, narrow tail. Another distinctive feature of lizards is their natural ability to autotomy. What it is? This is the famous one that even young children know about! In general, the scientific substantiation of the term autotomy sounds like a disposition to "self-mutilation", i.e. deliberate self-harm.

No, do not think, lizards perform such tricks not out of idle life and boredom! Only hopelessness and approaching death when meeting an enemy can make the lizard break its spine and throw off its tail, which, by the way, will wriggle for some time, as if alive, distracting the predator and misleading it. At this time, the lizard itself, almost intact, but alive, quickly disappears out of sight.
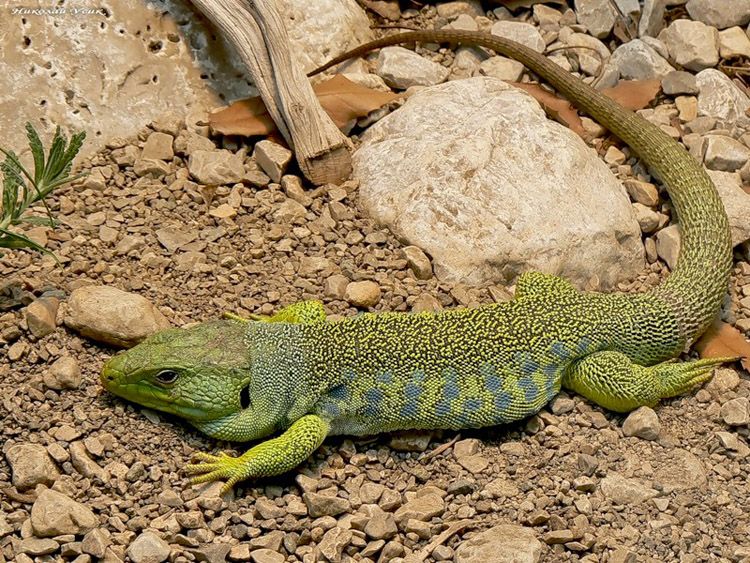

The color of lizards is always a combination of several shades: brown, green and gray. But depending on habitat and climatic zones, lizards can have skin, for example, yellow. And some species are even decorated with incredibly bright shades: red, azure, blue.
Sexual dimorphism in these reptiles is very weak, so it is almost impossible to distinguish a male lizard from a female lizard with the naked eye, unless you are a professional zoologist. Scientists have established that lizards do not have vocal cords and therefore are always silent, but in nature there are no exceptions, right? Therefore, there is a "vociferous" lizard on Earth, which is called the Lizard of Stechlin and Simon, this reptile lives in the Canary Islands. When danger overtakes her, she emits something like a squeak.

Today, representatives of real lizards inhabit Europe, Africa and partly Asia. But they will not be found in Madagascar, in the southern regions of Asia and on the island territories in the Indian Ocean. But, being once introduced to the lands of the United States, the lizards happily took root there and bred successfully. Real lizards prefer forests, shrub thickets, steppes, semi-deserts, meadows, highlands, gardens, river banks and even cliffs as biotopes. They are not afraid of the height and steep slopes, because these reptiles move equally well both horizontally and vertically.
Lizards are most active during daylight hours. Their food is made up of invertebrates, but sometimes a lizard can encroach on a small rodent or a snake, and the most desperate even eat birds' eggs. But most often these reptiles eat spiders, butterflies, locusts, snails, slugs, worms, grasshoppers and other small inhabitants of our fauna.
Pets living with us in the same apartment or house are becoming more sophisticated and interesting. The classic ones are less and less common: cats, dogs and birds. Increasingly, people are settling various insects, arachnids and reptiles. All sorts of lizards are especially common, and this is not surprising, because many of them are very cute and friendly, which allows each of them to become a replacement for the notorious kitty or puppy.
There are a lot of lizards suitable for home living. This material contains some of the most popular of them. With a description of their features, as well as photo materials for each species.
Chameleons
- Yemeni chameleon Is a fairly popular species, often found as a pet. The reason for such love for the Yemeni chameleon was its unpretentiousness in terms of maintenance and nutrition. Appearance: adults often reach up to 60 centimeters in length (females are slightly inferior). A chameleon's color changes during periods of stress and pregnancy. Conditions of detention: it is necessary to keep this species alone, having allocated a large terrarium to the lizard, with ventilation. The chameleon feeds on small insects.
- Three-horned chameleon- not yet so widespread, but very bright and noticeable representative of lizards. Appearance: the chameleon justifies its name by its extraordinary appearance, the three-horned chameleon has a bright green color. There are three horns on the head, one straight and two curved. A curved tail used as a hook. Conditions of detention: the individual should be kept in the same conditions as other chameleons: a large, vertical terrarium, with good ventilation, while being solitary.
Agamaceae
Monitor lizards
- Black and white tegu- a typical representative of the lizards of South America. Appearance: this individual often reaches sizes up to one and a half meters. This representative of monitor lizards is a predator that gets out of the hole during the day, eating small and large animals, which can catch up. Conditions of detention: to keep such in captivity, you will need a truly gigantic terrarium, or better a whole corral. Chicks, locusts, and rats must be included in the lizard's diet. It is enough to look at the photo of this “dinosaur” to understand that everything is serious.
Geckos
- The fat-tailed gecko is a very small and even cute representative of the lizard family. In nature, it leads a rather secretive lifestyle. It is found throughout West Africa. Appearance: The size of a gecko rarely exceeds 30 centimeters. Due to its "compactness", the fat-tailed gecko easily fits even in a small terrarium. Conditions of detention: hundreds of liters are enough to seat three females and one male there. You cannot put two males in one terrarium. This will lead to a constant struggle for territory. These lizards feed on small insects and artificial, vitamin-rich food for reptiles.
- Leopard lizard- another representative of geckos. Larger, but at the same time more popular among exotic lovers. Appearance: This lizard is not easily called the namesake of the leopard. It is a similar spotted color that causes similar associations and sets it apart from other geckos. The spotted gecko reaches an average of 30 centimeters in length. The gecko fascinates at first sight, take a look at the photo below to see for yourself. Housing conditions: as in the case of the fat-tailed gecko, you can get by with a small terrarium of 60-90 liters and safely plant a couple of geckos there. These lizards do not need soil.
Iguanas

Skinks
- Blue-tongued skink- a very patient and domestic lizard, which, despite its "angry" appearance, can be the best choice for beginners. Appearance: large animal of light color with large scales. A distinctive feature, as the name suggests, is the blue language. Conditions of detention: this species lives in Australia and it is forbidden to export it from there. At the same time, the lizard is on sale with us, and it feels great at home. A terrarium 100 centimeters long and 50 centimeters wide is perfect.
Domestic lizards
















Squamata Oppel Squad = Scaly
Suborder taxonomy: Lacertilia Owen = Lizards
Family: Agamidae Gray, 1827 = Agamas, agamas (lizards)
Family: Anelytropsidae Boulenger = American worm-like lizards
Family: Anguidae Gray, 1835 = Spindle-shaped, spindle-shaped
Family: Anniellidae Cope = Legless lizards
Family: Chamaeleonidae Gray, 1825 = Chameleons
Family: Cordylidae Mertens, 1937 = Belt-tails
Family: Dibamidae Boulenger = Worm-like lizards
Family: Gekkonidae Gray, 1825 = Geckos, [chain-toed] lizards
Family: Helodermatidae Gray, 1837 = Venomtooth
Family: Iguanidae Gray, 1827 = Iguanas, iguanas
Family: Lacertidae Fitzinger, 1826 = Real lizards, Lacertids
Family: Lanthanotidae Gray, 1825 = Earless Monitor Lizards
Family: Pygopodidae Gray, 1845 = Scalelegs
Family: Scincidae Gray, 1825 = Skinks, skinks
Family: Teiidae Gray, 1827 = Teiidae, American monitor lizards
Genus: Ameiva Meyer = Ameives
Species: Ameiva ameiva = Giant, or North American ameiva
Species: Ameiva polops = Island Ameiva
Family: Varanidae Gray, 1827 = Monitor lizards
Family: Xantusiidae Baird, 1858 = Night lizards
Family: Xenosauridae Cope, 1827 = Xenosaurs
Brief description of the detachment
Most lizards are tetrapods, whose oblong body is covered with horny scales, scutes, or grains.... Sizes from 3.5 cm to 4 m (weight up to 150 kg). Among the modern representatives of the suborder, forms with both well-developed five-fingered limbs and those without them are widely represented; there are transitions between these two extremes, and the loss of the legs is usually accompanied by a significant lengthening of the trunk. In species devoid of limbs, rudiments of the sternum or other bones of the anterior girdle are always preserved.
Eyes in most species they are equipped with movable eyelids, but in geckos, gologlazes and some other lizards, they grow together and turn into transparent films before the eyes. In some species, the eyes are completely hidden under the skin, through which they shine through in the form of dark spots. There are eardrums. The bladder is usually present. The anterior part of the cerebral box is not completely ossified. The right and left branches of the lower jaw are fixedly connected to each other. There is one (superior) temporal arch, formed by the scaly, forehead or postorbital bones. In some lizards, for example, in a number of species of the skink family, this arch is directly adjacent to the parietal bone, as a result of which the superior temporal foramen may be absent; in others, for example in all geckos, the temporal arch is absent at all, the postorbital arch is usually developed. The pterygoids are connected anteriorly with the palatines, by which they are thus separated from the vomer. The cranial column is present in most lizards, but in some agamids it is greatly reduced. The square bone is usually mobile. The teeth are attached to the outer edge of the jaws (acrodontic) or to the inner side (pleurodont). Often teeth are also present on the palatine, pterygoid and some other bones.
About 3500 species, 20 families and almost 370 genera are known. The CIS is home to 77 species belonging to 6 families and 18 genera.
Peculiarities scaly cover lizards are of great importance in identifying. The body scales in most groups differ significantly in shape, structure and size. The dorsal scales are smooth, tuberous, conical, ribbed, etc. Very small scales are called grains, large scales are called scutes. The shields on the head, where each of them has its own name, reach a significant variety in shape, size and location. In some species, the neck is separated from the body by a series of enlarged scales - a collar, in front of which is a more or less pronounced transverse throat fold. In a number of lizard species, in addition to large scutes, on the head there are small scales located between the upper ciliary and supraorbital, frontal and supraorbital, as well as in front and behind the supraorbital scutes. In other cases, the head is covered from above with numerous small irregularly polygonal scutes or scales.
In some lizards, the scales of the back almost do not differ from the abdominal, but in most, the lower surface of the body is covered with enlarged shields. On the chest, the shields are usually arranged in a triangle or in another order; the abdominal ones run in more or less regular rows, parallel or somewhat inclined in relation to each other. In front of the cloacal fissure, many lizards have an anal plate, in front of which there are sometimes comparatively large preanal ones.
Representatives of some families have special formations on the lower surface of the thigh, the so-called femoral pores; each pore pierces one scale, and all together they are grouped in a row along the thigh. During the breeding season, columns of keratinized cells emerge from the femoral pores, the role of which is not entirely clear. If the row is shortened to 1-3 pores, then they are called inguinal. Some geckos have so-called anal pores, which are an extension of the femoral pores in the lower abdomen. Geckos also have post-cloacal pores, one on each side of the lower surface of the tail base; the opening of such a pore leads into a small sac, in the front wall of which in males lies a small curved bone.
The tail scales are located in more or less irregular oblique or regular transverse rows (rings). In some cases, the number of scales around the ninth to tenth ring is used as a sign that allows you to determine the type of lizard. The rings should be counted on the lower surface of the tail from the first row of large lower caudal scales located immediately behind the small scales of the precloacal fold.
Vision, especially in diurnal forms, well developed; some species are able to distinguish colors; in this regard, the color acquires a signal value. Most have a developed parietal eye, which is usually regarded as a receptor for light regime and its seasonal changes. Hearing is well developed; the middle ear has a tympanic membrane; in some species, it can be covered with skin. Some lizards make sounds. Modes of movement range from swimming (marine iguanas), climbing trees and gliding (flying dragon) to moving over loose sands and sheer cliffs and walls (geckos).
According to the degree of development of the femoral and anal pores in many lizards, it is possible determine gender... The easiest way to determine the sex is in geckos, the females of which are completely devoid of pores. Determining the sex of most other lizard species takes some practice. So, in males of the family Lacertidae, especially childbirth Lacerta and Eremias, the femoral pores are better developed than in females, and have a slightly different shape, occupying almost the entire scale, in which each individual pore is cut. Agamas do not have such pores, but there are shallow so-called pre-cloacal pores, which occupy almost the entire surface of the scales, located immediately in front of the cloacal fissure; the secretions of these pores give the scales the appearance of a kind of callus. There are other secondary sex characteristics for sex determination. Thus, the base of the tail in males gradually becomes thinner towards the rear, while in females this transition is much more pronounced. The sex of freshly sacrificed lizards can be easily determined by the presence or absence of the characteristic male genitalia, which usually twist outward immediately upon pressure on the base of the tail. In fixed animals, a short longitudinal incision must be made to find them, starting from the lower surface of the base of the tail downward. In a number of species, sex differences in color are observed.
Many lizards, being captured, discard their tail... Subsequently, a new tail of a slightly altered shape grows in place of the fallen one. The restored (regenerated) tail is usually easy to recognize by slightly different scales, and often by the color of the regenerated part.
Most lizards reproduce, laying eggs, but some species are ovoviviparous (spindle, viviparous lizard). Nutrition varied: from small invertebrates to large prey (giant monitor lizard from Komodo Island hunts wild pigs and deer). Food specialization is expressed in marine iguanas (they eat algae) and some lizards, which feed mainly on either termites or slugs. Feeding on a variety of harmful insects and shellfish, benefits agriculture and forestry. There are no poisonous species among the lizards of our fauna.
A large number of lizard species are found in the CIS, most of which live in the south of the country. But some of them, such as viviparous and quick lizards ( Lacerta vivipara, L. agilis), are distributed far to the north. In the deserts of Central Asia, roundheads are common ( Phrynocephalus), characterized by a rounded head on a mobile neck, their body is covered with small horny tubercles. In the houses and among the rocks of the southern regions of the USSR at night you can meet peculiar geckos ( Geckonidae), dexterously running along the walls, and even on the ceiling. A large lizard lives in the deserts of Central Asia - the gray monitor lizard ( Varanus griseus), the length of which reaches 1.5 m.The monitor lizards living on Komodo Island (Indonesia) reach 3 m.
When identifying lizards, the features of the scaly body cover are of great importance, in particular the number and location of individual large head shields.
Literature:
1. Keys to amphibians and reptiles of the fauna of the USSR. Textbook. textbook for students of biol. specialties ped. in-tov. M., "Education", 1977.415 p. with ill .; 16 l. silt
2. The course of zoology. B. A. Kuznetsov, A. 3. Chernov, L. N. Katonova. Moscow, 1989
3. A.G. Bannikov, I.S. Darevsky, A.K. Rustamov. Amphibians and reptiles of the USSR. Publishing house "Mysl", Moscow, 1971
4. Naumov NP, Kartashev NN Zoology of vertebrates. - Part 2. - Reptiles, birds, mammals: A textbook for a biologist. specialist. un-tov. - M .: Higher. school, 1979. - 272 p., ill.
- Lizards (Lacertilia, formerly Sauria) are a suborder from the squamous order. The suborder of lizards includes all those species that do not belong to the other two suborders of scaly - and two-walkers.
- Lizards are widespread throughout the world. They are found on all continents except Antarctica.
- They are, as a rule, small animals with well-developed limbs.

- About 3800 modern species of lizards are known, which are united in 20 families.
- The smallest species of lizards - the round-footed one from the West Indies - is only 33 mm long and weighs about 1 g, and the largest is the Komodo lizard from Indonesia, which, with a mass of 135 kg, can reach 3 m in length.
- Despite the widespread belief that many lizards are venomous, there are only two such species - an escorpion from Mexico and a related dwelling from the southwestern United States.
- Most lizards are carnivores.
- Small and medium-sized species feed mainly on various:,.
- Large predatory lizards (tegu, monitor lizards) attack small vertebrates: other lizards, snakes, and small mammals, and also eat birds' eggs, etc.
- The Moloch lizard feeds only.
- Some large agamic, iguana, and skink lizards are wholly or nearly wholly herbivorous. Such species eat leaves, young shoots, fruits and flowers.
- In addition to insects, Madagascar day geckos willingly eat the nectar and pollen of flowers and the pulp of juicy ripe ones.
- Lizards have lived on Earth for more than one hundred million years. The oldest fossil lizard, called the Lizzie lizard, lived about 340 million years ago. She was found in Scotland in March 1988.
- Some extinct lizard species were huge in size. A species of lizard like Megalania, which lived in Australia about 1 million years ago, reached a length of about 6 m.
- The humerus and thigh bones of lizards are parallel to the surface of the earth. Therefore, when moving, the body sags and adjoins the ground with its back - it reptiles, which gave the name to the class - Reptiles.
- The eyes of most lizards are protected by movable, opaque eyelids. They also have a transparent nictitating membrane - the third eyelid, with which the surface of the eye is moistened.
- Gecko lizards have no eyelids, so they are forced to periodically wet a special transparent membrane in front of their eyes with their tongue.
- In the recess behind the eyes is the tympanic membrane, followed by the middle and inner ear in the bones of the skull. The lizard hears very well. The organ of touch and taste is a long, thin, forked at the end of the tongue, which the lizard often sticks out of the mouth.
- The scaly cover of the body protects against water loss and mechanical damage, but interferes with growth, and therefore several times during the summer the lizard sheds, shedding its skin in parts.
- What makes all lizards UNIFORMALLY different from snakes? If we talk about limbs that snakes do not have, then there are also legless lizards. Most lizards have visible openings of the external auditory canal, which snakes do not have, the eyes of lizards, as a rule, are equipped with movable separate eyelids, while in snakes the eyelids have grown together, forming transparent "lenses" in front of the eyes. However, some lizards do not have these signs. It is therefore safer to focus on the peculiarities of the internal structure. For example, all lizards, even legless ones, retain at least the rudiments of the sternum and shoulder girdle (skeletal support of the forelimbs); in snakes, both are completely absent.
- In diurnal lizards, color vision is a rarity in the animal kingdom.
- Many lizard species are capable of shedding part of their tail (autotomy). The lizard has a lot of enemies, but only nimble legs and a tail can protect it, with which it can, after assessing the degree of danger, part. The enemy sees a wriggling tail, this distracts his attention, and the animal has been gone for a long time. If a person grabbed the tail, then the tail remains in his fingers. In a number of species capable of augotomy, the tail is very brightly colored, and the lizard itself is much more modest in color, which allows it to quickly hide. After a while, the tail is restored, but in a shortened form. During autotomy, special muscles constrict the blood vessels in the tail, and there is hardly any bleeding.
- A lizard without a tail is no longer so fast and nimble, it can lose the ability to reproduce, climbs and runs poorly due to the lack of a "rudder". In many lizards, the tail serves to accumulate fat and nutrients, which means that all their energy is concentrated in the tail. The animal after its separation can die of exhaustion. Therefore, the often escaped lizard tries to find its tail and eat it in order to restore the lost strength. There is no complete regeneration. The new tail is always worse than the original. It has poor flexibility, shorter length and less agile movement.
- Sometimes the tail of a lizard does not come off completely and gradually recovers. But the tear-off plane is damaged, which gives an impetus to the formation of a new tail. This is how a lizard with two tails appears.
- In many climbing forms, such as geckos, anoles and some skinks, the lower surface of the fingers is expanded into a pad covered with bristles - hair-like branched outgrowths of the outer layer of the skin. These bristles catch on the slightest irregularities in the substrate, which allows the animal to move on a vertical surface and even upside down.
- Most often, lizards live in pairs. For the winter and at night they hide in burrows, under stones and in other places.
- Most lizards lay eggs. Lizard eggs have a thin leathery shell, less often, as a rule, in geckos, they are calcareous, dense. In different species, the number of eggs can range from 1-2 to several dozen.
- They always lay eggs in the most secluded places - in cracks, under driftwood, etc.
- Some geckos stick their eggs to tree trunks and branches, on rocks.
- As a rule, after laying eggs, lizards no longer return to them.
- Only a few species, for example, the female yellow toddler, guard the clutch and take care of it, and after the appearance of young jaundice, they continue to protect them and even feed them.
- Fewer lizards are ovoviviparous. Their eggs, devoid of a dense membrane, develop inside the mother's body, and the young are born alive, freeing themselves from the thin film that covers them even in the oviducts or immediately after birth.
- True viviparity has been established only in American night lizards, xanthusia, and in some skinks.
- Viviparity during reproduction is usually associated with harsh living conditions, for example, with living in the far north or high in the mountains.
- The largest lizard was the monitor lizard, exhibited in 1937 at the St. Louis Zoo, Missouri, USA. Its length was 3.10 m, and its mass was 166 kg.
- The longest lizard is Salvador's thin-bodied monitor lizard, or musk deer (Varanus salvadorii), from Papua New Guinea. It, according to accurate measurements, reaches a length of 4.75 m, but about 70% of its total length falls on the tail.
- The fastest lizard is the iguana. The highest speed of movement on land - 34.9 km / h - was recorded in the black iguana (Ctenosaura), which lives in Costa Rica.
- The longest-lived is the fragile lizard. A male fragile lizard (Anguis fragilis) lived in the Zoological Museum of Copenhagen, Denmark for over 54 years, from 1892 to 1946.
- The toad lizard belongs to the family of iguanas that live in the deserts of America. Therefore, the color of the lizards is either sand or stone, so that it is easy to mask. Toad-like lizards live in open areas; over the years of their existence, they have developed many methods of defense. First of all, they will try to freeze in place, hoping that the camouflage coloring will hide them from the predator, then they will be in jerks. If it is impossible to hide, the lizard begins to attack, at first it will stretch out on its paws and swell like a toad, from this comes its name, its size at the same time increases 2 times, but if this does not scare off the enemy, the lizard goes to extreme measures: it shoots blood from his eyes, aiming at the face of the predator. Its blood contains poisonous and toxic substances, which forces the predator to retreat.
- Lizard two-headed short-tailed skink
Lizards are reptiles. Most of them have a long tail and 4 legs. But there are also types of lizards that have no legs at all. Only specialists can distinguish them from snakes. The species diversity of this group of reptiles is enormous. They differ not only in size, body structure and color, but also in habits. Moreover, it is not uncommon for people to call lizards reptiles that are not. In order not to make mistakes, it is useful to know what lizards are.
Data lives especially in many places
general description
These reptiles thrive in forests, mountains, steppes and deserts. Some species of lizards have adapted to live in water.
Most of the reptiles are small in size from 20 to 40 cm, but there are also very large lizards, for example, the pearl. Its body length exceeds 80 cm. Giant lizards also live on our planet. These are Komodo dragons. Their growth can reach 3 meters.
We should also mention very small lizards. On average, their height barely reaches 10 cm. The smallest of them are South American geckos - their body length with a tail rarely exceeds 4 cm.
The color of reptiles is varied. Most often, their scales are painted in those colors that allow them to better camouflage themselves on the ground: green, brown and gray.
Some representatives of this group of reptiles have a very bright color, consisting of red or blue.
They have no voice
Lizards have several characteristics:
- They have highly mobile eyelids, for example, in snakes, which are their closest relatives, the eyelids are fused, so they practically cannot move their eyeballs.
- These reptiles can get rid of their tail if necessary. When attacked by a predator, the animal breaks its spine and discards the organ, which wriggles for some time, distracting the enemy's attention.
- Lizards do not have vocal cords, so they do not make sounds.
- They have small ears. You can find them on both sides of the head.
Scientists know only one species that makes at least some sounds - this is the lizard of Shtekhlin and Simon. In case of danger, it is capable of emitting a thin squeak.
Breeding features
The number of mates in lizards depends on their size. Large reptiles reproduce only once a year, while small reptiles are able to mate several times per season.
Males often fight for females. If one of them is larger, then the small one will soon leave the battlefield. When both fighters are in equal weight classes, then it can get to serious bloodshed. The victorious male receives the female as a reward.
Can lay up to 18 eggs
In some species, the sex ratio is disturbed, but the lizards do not disappear. The fact is that females begin to lay eggs without the participation of males - this is the so-called parthenogenesis.
Lizards reproduce in two ways: with the help of eggs and live birth. Small species lay up to 18 eggs at a time. Large reptiles lay only a few pieces.
In most cases, females hide the clutch in the ground, sand, under stones or in the holes of the rodents they kill. The ripening period for eggs lasts from several weeks to 1.5 months. After the appearance of the babies, the female loses all interest in them. Young lizards begin to live an independent life.
Pregnancy in viviparous species lasts 3 months. As a rule, the gestation period is in the winter. Young growth is born in winter.
In this video, you will learn more about lizards:
Reptile squads
Biologists divide all lizards into 6 orders, each of which includes about thirty families. The reptile orders are:
- Skink-like. The order is distinguished by a rich species diversity. It includes real lizards, widely represented in Russia, but most of the species live in tropical regions of the planet. Skink reptiles are found in South America and Africa, Madagascar and Cuba. Certain species have been discovered by scientists in the Sahara Desert.
- Iguaniformes. This order includes 14 families of reptiles. The most famous of these is the chameleon, found in South America and Madagascar.
- Gecko-like. Reptiles belonging to this order are considered rare. It includes lizards that do not have legs. They are found in Australia.
- Fusiform. These include monitor lizards.
- Worm-like lizards. These are the so-called worms. Outwardly, reptiles look more like huge earthworms. They can be found in the rainforests of Indochina, Indonesia, and Mexico.
- Lizard-like. These lizards are very large. Their weight often exceeds 5 kg. There are many legends about them.
There is only one type of venomous lizard - gila moth. During an attack on their victim, they not only bite it, but also inject dangerous poison under the skin.
Some species can be pets
Pets
Increasingly, people have unusual pets in their homes. These can be insects, spiders and reptiles. Lizards make up the lion's share of this list. The reason for such popularity of reptiles lies in their cute appearance, calm demeanor and relative friendliness. Lizards may well replace a cat or dog.
Panther chameleon
Furcifer pardalis is native to Madagascar. The lizard looks very bright, and its color depends largely on the place where it was born. Males can reach a length of 50 cm, but only in natural conditions. When kept at home, their body length rarely exceeds 25 cm. Females are even shorter. The life span of a panther chameleon does not exceed 6 years.
Females have a less bright color, which is practically the same in different regions of their habitat. Males, on the other hand, are very bright and very different from each other. By their appearance, experienced specialists can determine where this or that individual appeared. The most popular varieties are:
- Chameleon ambilobe. Born in the northern part of the island between two villages.
- Sambava. Lives in the northeastern part of Madagascar.
- The chameleon tamatave is an inhabitant of the coastal area in the east of the island.
Easy to feed from human hands
At home, the panther chameleon should be kept in a terrarium. In the first months of life, a lizard needs a small dwelling measuring 30x30x50 cm, but then it will need a larger house.
To approximate the living conditions of the pet to natural, branches, artificial and live plants are laid inside the terrarium. Of the latter, dracaena and ficuses should be distinguished. Chameleons love to climb steep surfaces, which means that snags and vines should be in the serpentarium. The top of the dwelling should be tightly closed. If the lid is removed, the chameleons, despite their slowness, will quickly flee.
The panther and other types of chameleons do not like human contact. They love peace. If you take a reptile in your arms, then you need to do this only from below. Seeing movement from above, the reptile will regard it as a threat. Over time, chameleons get used to their owners and even begin to recognize them. They willingly approach people during feeding.
This reptile prefers to live in close proximity to water bodies, on the banks of which there are large stones or branches. The agama is basking on them on sunny days.
The lizard has strong legs with large claws, which are not a weapon, but a tool for convenient movement on various surfaces. The strong and wide tail allows the reptile to swim quickly.
The water agama is considered a large lizard. Taking into account the tail, the length of the female can reach 60 cm. Males are even larger - up to 1 meter. Males differ from females not only in size, but also in color. Moreover, these differences in young lizards are rather weak.
A very large terrarium is needed for keeping a water agama at home. Young individuals can huddle in a 100-liter aquarium for some time, but then the living space for them will have to be significantly expanded.
No wonder Agamu is called water - she loves to be in the water
It is imperative to put thick branches inside the terrarium. You can use paper and coconut as a backing. But the sand will not work - the lizard will eat it.
The terrarium must have a heating zone with a constant air temperature of +35 ° C. It is better to provide heating with the help of lamps, since lizards spend most of their time climbing on driftwood.
Agamas love to swim, so you need to place a pond inside the terrarium. In addition, you will have to maintain a humidity of at least 60%. This can be done with a spray bottle.
There should not be 2 males in one terrarium. They will not be able to get along and will definitely fight.
The eublefar or spotted gecko is perhaps the most popular species among those who like to keep exotic at home. This lizard is very calm and peaceful. She feels great in small terrariums. The gecko is easy to care for. In addition, this type of reptile is distinguished by a variety of colors.
In nature, eublefar lives in dry steppes and rocky semi-deserts of Afghanistan, Iran and Pakistan. The lizard is active at dusk and early morning. At this time, the air temperature is most comfortable for her.
Spotted geckos prefer to live alone. They guard their territory jealously. Males prefer to communicate with females only during the mating season.
One gecko will feel great in a 50 liter terrarium. However, if the owner plans to breed these reptiles, then he will have to buy a larger terrarium.
Eublefar cannot walk on smooth terrain
cannot climb smooth surfaces, therefore, the dwelling does not need to be covered with a lid. But if there are other pets at home, especially cats, then it is better to close the terrarium.
In one house, you can safely keep several females at once, if they are of the same age and size. There will be no enmity between them. But the males will certainly fight. Moreover, males do not get along with females. They will take food from females and kill them, so males should be kept alone.
Spotted geckos should have hot and cold temperatures in the terrarium. The maximum temperature indicators are +32 ° C, the minimum is not lower than +22 ° C. This parameter must be monitored with two thermometers. Overheating or hypothermia will lead to illness of the pet.
Collared iguana
This medium-sized lizard is native to the southeastern United States. Its maximum length, including the tail, is 35 cm.Under natural conditions, it lives for about 8 years, and in captivity - no more than 4.
The collar iguana is a very strong and fast predator. According to biologists, if its size were comparable to the size of monitor lizards, it would easily displace the latter. This reptile effectively preys on other reptiles and rodents. She does not disdain insects either.
The iguana moves very fast. Accelerating to a speed of 26 km / h, it attacks prey and kills it with powerful jaws in several movements.
The lizard has a high metabolism, so keeping it at home is not easy, since you have to feed it often. Large cockroaches, beetles, mice serve as food.
An iguana needs a spacious aviary with an ultraviolet heater. You can keep it in the terrarium, but then it must be very large. The temperature in the lizard's dwelling should be maintained at + 27 ° C, and in the heating zone - up to + 41-43 ° С. It is not necessary to make a separate reservoir, it is enough to put a drinker. Spray water from a spray bottle from time to time.
Be careful when dealing with iguanas. They are hard to get used to human hands and, if handled carelessly, can injure their jaws.