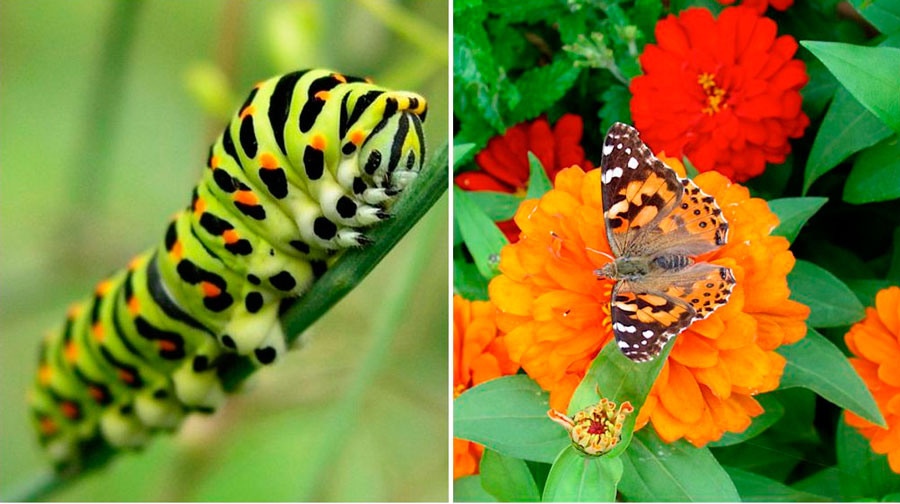
A yellow fluffy caterpillar with a red tail. Caterpillars and butterflies scoops, methods of dealing with them
The mesmerizing beauty and mystery of the appearance of a beautiful butterfly, as if from a dead sarcophagus - a cocoon, captures the minds of many people. The birth of a new creature is always a spectacle, but when for this it goes through 3 stages of changes, it calls for a process. Modern equipment allows you to trace how the caterpillar turns into butterflies.
A bit of history
The history of the appearance of butterflies has its roots in Jurassic era... It was at this time that floral plants received the greatest development, which caused the appearance of lepidoptera insects.
There are known species of butterflies found in amber from the Paleogene era. They are few
differ from modern species these insects, therefore, as a caterpillar turns into a butterfly today, so it happened millions of years ago.
Today, butterflies are the most numerous species of insects, they number about 160,000 species, and they inhabit the entire planet, except for Antarctica.
The first and second stages of butterfly development
Of this beautiful insect dedicated to finding a mate, mating and laying eggs. Each species of butterflies has its own time period for the transformation from a caterpillar into an adult insect; it can last for a maximum of three years.
Butterfly lays eggs not anywhere, but specially picks up a secluded leaf, where they will be safe. Moreover, they instinctively have plant species that are suitable for this. A caterpillar hatched from an egg is not "on its" leaf, it can pick and choose with food.
After the caterpillar gnaws the egg and gets out, all its actions are food. She starts from the sheet on which she was born, and then moves on. When the caterpillar population increases dramatically, they can cause irreparable damage to forests, fruit trees, and even grain crops.

During its existence in the body of a caterpillar, the insect rapidly gains weight, therefore it sheds its tight skin several times. After the last molt, most often the fourth or fifth, the caterpillar begins to prepare for "hibernation" in the cocoon. Some of them only have a few days to thoroughly nourish themselves, gain strength and and pack themselves into a cocoon.
Life in a cocoon
In order to survive during the period of "inactivity" and defenselessness, the caterpillars find a suitable leaf, branch, or to which they can imperceptibly "stick" with a strong silk thread, which they secrete from the abdomen.
To understand how a caterpillar turns into butterflies, one should delve into its ability to properly prepare oneself for this.
Having glued to the selected surface, the caterpillar hangs on a silk thread and begins to wrap itself around the little body with it. This happens gradually, but what is important, when wrapped, the caterpillar gives its cocoon the appearance of a leaf, bud or stem of the plant it has chosen.

The similarities are so obvious that only a very observant eye can detect a cocoon on its surface. This is done so that the defenseless caterpillar is not found and eaten.
How the caterpillar turns into a butterfly inside the cocoon can be seen only by making shooting with special equipment in laboratory conditions. This process is so slow and secretive that it is impossible to observe it in nature.
The reserves that the caterpillar managed to deposit in its body is quite enough for the strength to transform it into a butterfly.
The publication
The mystery of how the caterpillar turns into butterflies makes scientists study, shoot and record this moment every time for curious children and adults.
Usually, the moment of birth of a beautiful insect occurs at sunrise, when it is still not hot, and there is dew on the plants. The cocoon literally bursts, as if a ripe fruit, and a new creature is gradually selected from it, this caterpillar turns into a butterfly, the pictures clearly show this.

At first, the butterfly is very weak, its wings are crumpled and lacking elasticity and strength, so it clings to a stem, leaf or branch to "rest", to spread and dry its wings. As they straighten and dry, they become tighter and more elastic. Sometimes it takes a butterfly a couple of hours to do this.
After the caterpillar turns into butterflies, its "priorities" in life change. If at the larval stage the main need for its existence was food, now the insect's goal is to continue its genus and start the cycle again. The first thing a new creature does is find a partner for fertilization.
Interest in butterflies
Butterflies are deservedly recognized as one of the most beautiful insect species on the planet. Their amazing transformation from crawling and eternally chewing caterpillars into winged beauties especially fascinates children.
Filmed documentaries and cartoons on the theme "How a caterpillar turns into a butterfly" for children. Perhaps it is wonderful way wake up a child's genuine interest in the world around him.
Starting with an interest in butterflies, children subsequently take an interest in other species of fauna and flora. Thus, the child becomes familiar with the planet on which he lives and its inhabitants.
The caterpillar is the larva of a butterfly, moth or moth - insects from the order of Lepidoptera.
Caterpillar - description, characteristics, structure and photos. What does a caterpillar look like?
Torso
The length of the caterpillar, in accordance with the variety, varies from a few millimeters to 12 cm, as in individual specimens of the Saturnia butterfly (peacock eyes).
The body of a caterpillar consists of a well-defined head, thoracic, abdominal sections and several pairs of limbs located on the chest and abdomen.
Head

The caterpillar head is represented by six accrete segments that form a rigid capsule. Between the forehead and the eyes, the region of the cheeks is conventionally distinguished, at the bottom of the head is the occipital foramen, which looks like a heart.
A round head shape is typical of most caterpillars, although there are exceptions. For example, many hawk moths have a triangle-shaped head, while others have a rectangular head. The parietal parts can protrude strongly above the head, forming a kind of "horns". Small antennae-antennas, consisting of 3 successive articulations, grow on the sides of the head.
Oral apparatus
All caterpillars are distinguished by a gnawing type of mouth apparatus. The upper jaws of the insect are perfectly formed: their upper edge contains teeth intended for gnawing or tearing food. Inside there are bumps that perform the function of chewing food. The salivary glands are transformed into specific spinning (silk-separating) glands.
Eyes
The caterpillar's eyes are a primitive visual apparatus containing a single lens. Usually, several simple eyes are located one after another, in an arc, or they form 1 compound eye, merged from 5 simple ones. Plus 1 eye is located inside this arch. Thus, the caterpillars have 5-6 pairs of eyes in total.
Torso
The body of the caterpillar consists of segments separated by grooves, and is clothed in a soft shell, which provides the body with maximum mobility. The anal opening is surrounded by special lobes that have varying degrees development.
The organ of respiration of insects - spiracles, is a stigma located on the chest. Only in species living in water, spiracles are replaced by tracheal gills.
Most caterpillars have 3 pairs of thoracic limbs and 5 pairs of false abdominal legs. The abdominal limbs end in small hooks. On each thoracic limb there is a sole with a claw, which the caterpillar retracts or protrudes when moving.
Absolutely naked caterpillars do not exist: the body of each is covered with various formations - outgrowths, hairs or a well-grown cuticle. Cuticle growths are star-shaped, spikes or granules that look like fine hairs or bristles. Moreover, the bristles grow in a strictly defined way, characteristic of a particular family, genus, and even species. The outgrowths consist of raised skin formations, tubercles, similar to flat, round or oval warts and spines. Caterpillar hairs are represented by thin individual filaments or tufts.
Life in a cocoon

In order to survive during the period of "inactivity" and defenselessness, the caterpillars find a suitable leaf, branch or tree trunk, to which they can imperceptibly "stick" with a strong silk thread, which they secrete from the abdomen.
To understand how a caterpillar turns into butterflies, one should delve into its ability to properly prepare oneself for this.
Having glued to the selected surface, the caterpillar hangs on a silk thread and begins to wrap itself around the little body with it. This happens gradually, but what is important, when wrapped, the caterpillar gives its cocoon the appearance of a leaf, bud or stem of the plant it has chosen.
The similarities are so obvious that only a very observant eye can detect a cocoon on its surface. This is done so that the defenseless caterpillar is not found and eaten.
How the caterpillar turns into a butterfly inside the cocoon can be seen only by making shooting with special equipment in laboratory conditions. This process is so slow and secretive that it is impossible to observe it in nature.
The reserves that the caterpillar managed to deposit in its body is quite enough for the strength to transform it into a butterfly.
Types of caterpillars - photos and names
Among the great many different caterpillars, the following varieties are of greatest interest:

- Cabbage caterpillar or cabbage butterfly caterpillar (cabbage white) (lat.Pieris brassicae) lives throughout Eastern Europe, northern Africa to japanese islands, and also brought to South America. The caterpillar is 3.5 cm long, has 16 legs and is distinguished by a light green body covered with black warts and short black hairs. Depending on the weather, the caterpillar stage stays from 13 to 38 days. These caterpillars feed on cabbage, horseradish, radishes, turnips, turnips, and shepherd's purse. They are considered the main pest of cabbage.

- Caterpillar of the moth (surveyors)(lat. Geometridae) is characterized by a long thin body and undeveloped abdominal legs, due to which it differs in an original way of movement - it bends in a loop, while pulling the abdominal legs to the chest. The family unites more than 23 thousand species of moths distributed around the world. All types of caterpillars of this family have well-developed muscles, therefore, they are able to strengthen vertically on plants, perfectly imitating broken off branches and petioles. The color of the caterpillars is similar to the color of foliage or bark, which additionally is an excellent camouflage. They eat pine needles, currants and hazel.

- Great Harpy Caterpillar(lat.Cerura vinula = Dicranura vinula) lives throughout Europe, in Central Asia and in northern Africa. Adult caterpillars grow up to 6 cm and are distinguished by a green body with a purple diamond on the back, bordered by a white outline. In case of danger, the caterpillar inflates, assumes a threatening pose and sprays out a caustic substance. In the caterpillar stage, the insect stays from the beginning of summer to September, feeds on the leaves of plants from the willow and poplar families, including the common aspen.

- Red-tailed caterpillar(bashful woolfoot) (Latin Calliteara pudibunda) is found in the forest-steppe zone throughout Eurasia, as well as in Asia Minor and Central. Caterpillar up to 5 cm long is pinkish, brown or gray in color. The body is densely covered with individual hairs or tufts of hair, at the end there is a tail of protruding crimson hairs. This is a poisonous caterpillar: when it comes into contact with human skin, it causes painful allergies. These caterpillars eat the foliage of various trees and shrubs, especially hops.

- Caterpillar silkworm (Latin Bombyx mori) or silkworm. Lives in East Asia: in the north of China and in Russia, in the southern regions of Primorye. The length of the caterpillar is 6-7 cm, its wavy body is densely covered with blue and brown hairy warts. After 4 molts, completing a 32-day development cycle, the color of the caterpillar turns yellow. The food of the silkworm caterpillar is exclusively mulberry leaves. This insect has been actively used in sericulture since the 27th century BC. e.

- Corrosive Arboreal Caterpillar(lat.Zeuzera pyrina) from the carpenter family. Found on the territory of all European countries, except for the Far North, as well as in South Africa, Southeast Asia and North America. It hibernates twice, during this time it changes color from yellow-pink to yellow-orange with black, glossy warts. The length of the insect is 5-6 cm. Caterpillars live inside the branches and trunks of various trees, feeding on their juices.

- Lady Bear Caterpillar(Latin Callimorpha dominula) or female bear lives in the Eastern, Western Europe and in the southeast of Asia. It hibernates once, differs in black-blue color with yellow stripes and spots. Lives on nettles, geraniums, willows, raspberries, strawberries, and feeds on them.

- Swallowtail caterpillar(lat. Papilio machaon) lives throughout Europe, Asia, northern Africa and North America. One of the most colorful caterpillars: at first it is black, with scarlet warts, and as it grows, it becomes green with black transverse stripes. Each strip contains 6-8 red-orange spots. A disturbed caterpillar secretes an odorous orange-yellow liquid. It feeds on carrots, celery, wormwood, parsley, and sometimes alder leaves.

- The smallest caterpillar in the world Is a representative of the moth family. For example, the caterpillars of the clothing moth (Latin Tineola bisselliella), which have just emerged from the egg, reach a length of only 1 mm.

- The largest caterpillar in the world- this is a caterpillar of a peacock-eye atlas (lat.Attacus atlas). The bluish-green caterpillar, as if dusted with white dust, grows up to 12 cm in length.
Poisonous caterpillars - description, types and photos.
Among the caterpillars, there are quite poisonous specimens, so the bite of such a caterpillar or accidental touching it can cause unpleasant sensations. Usually, such contact ends with pain at the place of contact, redness and swelling of the skin, less often an itchy rash may appear. There are frequent cases of drowsiness, headache, gastrointestinal upset, increased blood pressure and temperature. In a word, do not be fooled by the bright and spectacular appearance of these creatures - sometimes they are dangerous.
The most famous poisonous caterpillars, ready to defend themselves from enemies and protect their food from encroachment with the help of a "poisonous cocktail", include:
- Caterpillar-coquette (lat.Megalopyge opercularis)
- Sibine stimulea
- Caterpillar "burning rose" (lat. Parasa indetermina)
- Spiny oak slug caterpillar (Latin Euclea delphinii)
- Caterpillar of the wild bears (lat.Tyria jacobaeae)
- Caterpillar of the marching silkworm (lat.Thaumetopoea pityocampa)
- Hickory bear caterpillar (lat.Lophocampa caryae)
- Caterpillar "lazy clown" (lat. Lonomia obliqua)
- Caterpillar Saturnia Maya (Latin Hemileuca maia)
- Volnyanka caterpillar (Latin Orgyia leucostigma)
Poisonous caterpillar-coquette(lat. Megalopyge opercularis) is an insect that looks pretty cute and resembles a miniature fur animal. However, this caterpillar is one of the most poisonous caterpillars living on the North American continent and in Mexico. The color of the "fur coat", under which there are poisonous thorns, varies from light gray to golden or red-brown. The length of the caterpillar does not exceed three centimeters, the width of the body is 1 cm, but even such modest dimensions make it very dangerous. After contact with an insect, after a couple of minutes, an acute throbbing pain and noticeable reddening of the integument of the skin, up to bruising, appear at the point of contact. Later, there is painful enlargement of the lymph nodes, shortness of breath and chest pain.

Saddle caterpillar(lat. Sibine stimulea) - the caterpillar is bright green, both ends of the calf are brown, the middle of the calf has a brownish spot enclosed in a white edging, which makes this area similar to a saddle. The length of the caterpillar inhabiting the North and South America, is 2-3 centimeters, two pairs of fleshy horn-appendages are equipped with hard hairs, which contain a fairly strong poison. The prick of these sting-hairs causes severe pain, skin swelling, rash and nausea lasting several days.

Poisonous caterpillar "lazy clown"(lat. Lonomia obliqua) - an insect that lives in large quantities in Uruguay and Mozambique, has the most powerful of all natural toxins known today. The caterpillar can reach 6-7 centimeters in length, has a greenish-brown color, the poison accumulates in herringbone-shaped spines. It loves shade, so the caterpillar usually lives in the foliage of trees, but it often moves to the courtyards of the residential sector. As a result of contact with this insect, painful hemorrhages appear on the skin, caterpillar venom can act on internal organs, causing renal colic, bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract, pulmonary edema and even disorders of the nervous system.

Fighting caterpillars: means and methods.
Many types of caterpillars are pests and eat fruit trees, fruits and vegetables.
There are many methods for dealing with caterpillars, combined into 3 main groups:
- mechanical means of struggle with caterpillars folk methods consist in manually collecting and shaking off caterpillars from plants, as well as cutting off wintering clutches. A proven method is trapping caterpillars using trapping glue belts and various traps with bait liquid.
- biological control methods aim to attract natural enemies caterpillars, primarily birds. For this, comfortable conditions are created in the gardens for their nesting (birdhouses, nest boxes, feeders) and with a small number of caterpillars are completely destroyed.
- chemical methods of control with caterpillars are considered the most effective, but addictive in caterpillars, therefore, poisonous drugs (biological and chemical) should be alternated. Rovikurt, Karbofos, Lepidotsid, Kilzar, Karate are considered to be well-proven means.
If the invasion of caterpillars is not significantly threatening, you can try decoctions and infusions of plants as a fight: black henbane (against the cabbage caterpillar), hemlock (against all leaf-eating caterpillars), as well as red elderberry and peppermint.

- Entomophagy, or insect eating, has flourished since prehistoric times. Caterpillars of more than 80 genera of butterflies occupy an honorable place in the gourmet menu. Caterpillars are eaten raw or fried, dried over hot coals, boiled, salted, added to omelets and sauces.
- The silkworm has a huge economic importance for a number of countries - silk producers. Indeed, from 100 kg of cocoons, 9 kg of silk thread can be isolated.
- The coloring of any caterpillar to one degree or another simulates the conditions environment and is the best remedy disguise and protection.
Video
Once in my childhood at my grandmother's in the village, I saw unusual caterpillar- a large bright green with orange horns. When I touched it with a twig, the caterpillar released its horns more strongly. I don’t know which of it later turned out to be a butterfly, but the caterpillar was very beautiful. Recently I remembered this episode from my childhood, and tried to search the Internet for this caterpillar. Maybe something was not so memorable, but I didn’t find one, but I did find many other interesting and unusual ones. By the way, most of the beautiful caterpillars have rather inconspicuous butterflies ...
Among the caterpillars, there are simply amazingly beautiful specimens, but the bright color most often indicates that these creatures are poisonous. This provides them with reliable protection from enemies, but people are curious, and just strive to hold these cuties in their hands. For example, a caterpillar butterflies-eucleids (Sibine stimulea) looks funny: she seems to be wearing a green vest with a hole in the back. At both ends of the body, the larva has a pair of horn-like processes. On these processes, there are many hairs-stings, touching which the offender will immediately be struck with poison. The sensations after contact with a caterpillar of eucleids are very painful: the affected area swells, a rash and nausea appear. A person can stay in this state for several days. living in North and South America.
2. Sibine stimulea
Butterfly caterpillar cross-bears resembles a zebra in color, only it is painted in black and orange stripes. These cute creatures have a truly brutal appetite, and they feed on plants of the genus of crossworms, most of which are poisonous. This species of butterflies was even specially distributed in New Zealand, Australia and North America in order to reduce the number of wild plants growing in the territory. Actually, thanks to such a diet, the caterpillars become poisonous.
3. Ursa rugus
Newly minted butterfly larva monarch so small that after hatching it can hardly be seen. True, it grows very quickly, feeding exclusively on plants of the genus Vatochnik, the milky sap of which is poisonous. Thanks to this, the larvae also become poisonous and inedible for predators. Very soon the caterpillar of the monarch's Danaid reaches 5 centimeters in length, and you can already clearly see their striped black-white-yellow color. By the way, the monarch is considered one of the most beautiful butterflies in the world. One of the most famous butterflies North America, in the 19th century, representatives of this species were found in New Zealand and Australia. In Europe, spread to Canary Islands and Madeira, during migrations were noted in Russia, on Azores, in Sweden and Spain, are found in northern Africa.
4. Monarch.

Caterpillar gypsy moth has five pairs of red and six pairs of blue spots on its body, covered with an unimaginable number of hairs. The hairs are mainly used for spreading - thanks to them, the larvae are easily picked up and carried away by the wind.
However, if the hairs are touched, then pain and skin irritation will occur. The unpaired silkworm is a real scourge of forest lands, especially maples, elms and oaks suffer from caterpillars. The unpaired silkworm is widespread almost throughout Europe, in North Africa, temperate latitudes Asia and North America, southern regions of Central Asia.
5. Gypsy moth.

Butterfly caterpillar Parasa indetermina of the family of tears is less than 1 inch in length, and is painted in longitudinal stripes of orange, yellow and brown, and a wide purple stripe runs along the back. On the body of the caterpillar, there are five pairs of massive horn-like processes, which are dotted with fine hairs with black tips. Touching the larva is very unpleasant, as the poisonous tips dig into the skin, causing rashes and itching. The caterpillar feeds on dogwood, maple, oak, cherry, apple, poplar and hickory leaves; it lives in North and South America.
6. Parasa indetermina
Lophocampa caryae - black and white caterpillar whose body is covered with many grayish-white hairs. However, these hairs do not pose any danger, since the larva's weapons are two pairs of black spines located in the front and back of the body, each of which is associated with a venom gland. On contact with the thorns, irritation and a rash appear on the skin of a person. These caterpillars are common in southern Canada and the northern regions of the United States and are found between June and September. The larvae live for about 8 weeks, feeding on hickory and walnut leaves.
7. Lophocampa caryae
Automeris io- very beautiful butterfly family of peacock eyes, found in North America. Its caterpillar begins its life with an orange coloration, but with age it changes its color to bright green with two stripes of red and white on the sides of the body.
The entire surface of the larva's body is dotted with bundles of hairs, when touched, the offender will be struck by two types of poison at once, causing severe pain, burning, and inflammation. This caterpillar feeds on the foliage of willow, maple, oak, elm, aspen, cherry and pear, and is found from February to September.
8. Automeris io
Another representative of the slug family - Euclea delphinii... Its body, flattened at the top, does not exceed one inch in length, and is colored mostly green, with two longitudinal orange-red stripes. Like other slugs, this caterpillar's weapon is poisonous hairy spikes in the back of its body. On contact, they dig into the skin, and without medical care the person will be tight. The species inhabits the United States, feeding on the leaves of ash, oak, chestnut and some other trees.
9. Euclea delphinii
A few more caterpillars and their butterflies, which I found in the bowels of the Internet))
Butterflies from the squad bluebirds quite often found on the territory of Russia, including Siberia. These butterflies are rather small, but so cute, and the caterpillars are quite ordinary.
10. Cupido arjades 
11. Lucaena dispar

Peacock eye- a butterfly, which can also be often found in our area. A beautiful butterfly, and its caterpillar is also quite interesting.
12. Peacock eye.
Swallowtail considered one of the most beautiful butterflies in Europe ( perhaps I saw a similar caterpillar in my childhood). In total, there are 550 species of this beautiful family in the world fauna, inhabiting the temperate zone of Asia, north africa, North America, throughout Europe (absent only in Ireland, and in England it lives only in Norfolk County). Swallowtail was once one of the most common butterflies in Europe, and now it belongs to a rare, shrinking species and is listed in the Red Book. The decrease in the number of this beautiful butterfly is associated, first of all, with the change or complete destruction of its habitats through the use of pesticides and other toxic substances, as well as in connection with the capture.
13. Sailboat - swallowtail

Kaya dipper (Arctia caja) distributed throughout Europe, as well as in Siberia, to Far East, in Central and Asia Minor, in China, Korea and Japan, in North America. Inhabits gardens, wastelands and other open places.
14. Arctia caja 
The silver hole (Phalera bucephala) is found in all countries of the middle and of Eastern Europe, Scandinavia, the Baltic states, the European part of Russia and Turkey.
15. Phalera bucephala .jpg)
Small peacock eye, or night peacock (Saturnia pavonia)... The wingspan of these butterflies is 50 - 70 mm. Sexual dimorphism is pronounced: in females, the background of the hind wings is gray, and in the male - orange. The butterfly is distributed over most of Europe, in Asia Minor, through the whole forest zone Eurasia to Japan, in the European part of Russia, in the Caucasus, in Siberia, in the Far East. It inhabits heather wastelands, as well as mountainous, rocky steppes and deciduous forests.
16. Saturnia pavonia 
Helikonida Julia (Dryas Julia) has a bright orange color of the wings, at rest it folds them and becomes like a dry leaf. Distributed in Central and South America. Meets all year round, sometimes in large quantities.
17. Dryas Julia

Peacock-eye Atlas (Attacus atlas)- a butterfly from the Peacock Eyes family is considered one of the largest butterflies in the world; wingspan up to 26 cm, females are noticeably larger than males. Found in tropical and subtropical forests South-East Asia, South China and from Thailand to Indonesia, Borneo, Java.
18. Attacs atlas. 
Butterfly Heliconius melpomene belongs to the Heliconidae family; distributed over a vast area from Mexico to Brazil. Dwells in wet forests, flies through the copses, but avoids sunny places.
19. Heliconius melpomene![]()
Junonia orithya; the halo of its habitat - Africa, South and Southeast Asia, India, Australia.
20. Jinonia orithya 
And some more caterpillars ...
21.


23.

24.

25.

The insect class is one of the most diverse and numerous representatives of living creatures inhabiting Earth... The most beautiful representatives of the family are butterflies, which differ from each other in the most diverse and intricate patterns located on their wings. Caterpillars are integral natural purpose formation of butterflies. They also differ in a variety of shapes and colors.

The birth of a butterfly is associated with a certain stage of insect development. After an adult has laid eggs in some secluded place, larvae appear from them, in the form of small worms. These worms are quite voracious creatures. They eat a lot of greens in order to move to another stage of development.
These larvae are called caterpillars. An insect caterpillar can be either several days, or several years, depending on the species. Typically, each type of caterpillar eats a specific type of plant. Often they become pests of any crops, fruit trees, berries, vegetables, fruits, etc. After a certain time, the caterpillar turns into a cocoon, which is called a pupa. Then an adult emerges from the cocoon, which is called a butterfly.
Interesting to know! The larger the butterfly, the larger the caterpillar, and vice versa.
All types of caterpillars may differ in their size, development periods, colors, habitats, but they all have the same body structure. The structure of the caterpillar's body consists of:
- From a well-defined head of a regular rounded shape, mouth apparatus, organs of vision and horn-like antennae.
- Breasts.
- Abdominal region.
- Several pairs of limbs.
As a rule, a caterpillar has at least 5-6 pairs of eyes located side by side. There are several small teeth in the mouth, with the help of which they gnaw plants. On the body there are small hairs or outgrowths that look like thorns. Typically, the caterpillar moves quickly over leaves, branches, and other surfaces.
Types of caterpillars with photos and names

Each type of butterfly has its own caterpillar. At the same time, the color of the caterpillar does not always correspond to the color of the butterfly. In most cases, caterpillars are herbivores, although there are also predatory species... Depending on the food consumed, caterpillars are:
- Polyphages... These are caterpillars that indiscriminately eat any plants. This species includes moths such as wine hawk, ocellated hawk moth, blind hawk moth, kaya bear, moths, peacock eyes and others.
- Monophages represent caterpillars that feed on one a certain kind plants. These are cabbage, apple moth, silkworm and others.
- Oligophages- These are caterpillars that prefer to feed on one species of plants belonging to the same species of the family or type. These are swallowtail butterflies, pine scoop, polyxena, etc.
- Xylophages refers to a type of caterpillar that feeds on wood or bark. These include leaf rollers, woodworms and others.
Certain species of caterpillars inhabit the subtropical regions, the tropics, and also the northern regions. On the territory of each country, there are hundreds of species of such insects. Caterpillars don't get their names by accident. As a rule, they receive their names depending on the main source of food. Some of the caterpillars were named so because they have a very interesting and intricate pattern on the wings.
Among all types of caterpillars, there are also valuable ones, such as silkworms. Many caterpillars have this property. In the course of its movement, a thin thread remains behind the caterpillar. This thread serves as a kind of insurance in the event of an insect falling.
Interesting to know! From the cocoon of a silkworm butterfly, a silk thread is obtained, after which a silk cloth is woven from it, and then various products are sewn.
There are caterpillars up to 1 mm in size, as well as caterpillars more than 12 cm long. Among them there are quite beautiful specimens, completely nondescript, hairy, poisonous, and also those that can change their color during their development.
On the territory of Russia, the following types are widespread:
- Cabbage white (cabbage).
- Peacock eye.
- A moth (land surveyor).
- Hawk moth.
- Admiral.

This is the most common type of caterpillar inhabiting European part Russia. The caterpillar is different in green and the body length is within 3-4 cm. On the body of the caterpillar there are black growths and hairs. It got its name due to the fact that it appears mainly on cabbage. In addition to cabbage, he can feast on such crops as:
- Radish.
- Turnip.
- Turnips.
- Horseradish, etc.
In the caterpillar stage, the insect can stay from 2 to 5 weeks. Depending on weather conditions. Despite such a short period of time, the cabbage manages to cause serious damage to the crop.

This caterpillar is also called a land surveyor, because of original way movement. This is due to the underdevelopment of the anterior false legs... Due to its brown color, it manages to reliably camouflage itself among the vegetation. In addition, due to the developed muscular system, the caterpillar can be in an extended motionless state for a long time, depicting a broken off twig or twig. This type of caterpillar feeds on the needles of trees, currant foliage, hazel, etc. The moth butterfly has a slender, elongated body and wide, delicate wings. Butterflies fly mostly at night. They can be easily recognized by their slow and uneven flight.

This caterpillar can be found throughout the forest-steppe zone of our continent. It feeds on the foliage of various shrubs. These are fluffy caterpillars, the body of which is covered with brown or gray hairs. The end of the body is distinguished by a bright scarlet color, which served as the basis for such a name.
Interesting to know! The bright red tail of the insect indicates that the caterpillar is poisonous. Contact with the human body may cause an allergic reaction.
Butterfly years are celebrated in the month of May and June. Redtail is quite fertile, as one female is capable of laying up to 1000 eggs per tree. With the arrival of autumn, all caterpillars leave the tree and the pupation process begins.
Redtail is considered a pest of fruit trees such as apple, plum, mountain ash, pedunculate oak, hornbeam, elm, etc.

Differs quite large size... The caterpillar is widespread almost throughout Europe, Asia, North America, as well as in the north African continent... The caterpillar is quite beautiful, like the butterfly itself. At the same time, at its stage of development, the caterpillar changes its color. At first, the caterpillar is almost black with bright red spines. Over time, it turns green with black stripes, interspersed with brown spots. This caterpillar can feed on:
- Carrots.
- Parsley.
- Celery.
- Wormwood.
- Alder.

The hawk moth caterpillar can be found both in central Russia and in Siberia and the Far East. Prefers to eat birch, willow, poplar leaves. The caterpillar is distinguished by its green body color, which allows it to perfectly camouflage itself among the leaves. The body is painted with diagonal thin stripes that resemble leaf veins. On the tail of this caterpillar, you can see a kind of horn.

This is a fairly beautiful butterfly, which differs comparatively large size: its length reaches 10 cm, or even more. There are 2 types of these butterflies: the day peacock eye and the night peacock eye. In addition, there is also a large peacock's eye butterfly, which has insignificant differences from the first two species. The butterfly caterpillar is also large and green in color. The peacock's eye lives in the western part of Russia, in the Caucasus and in the Crimea. Prefers the following fruit trees for food:
- Apple tree.
- Pear.
- Walnut.
- Plum.
- Cherries.
Interesting to know! In the process of development, the larva of the butterfly peacock eye changes its color. Before pupation begins, it turns yellow, and the pupa itself has a brown tint.

Who has not met a clothes moth in their life? It is difficult to find such a person, since everyone knows the results of her life: the larvae of the clothes moth spoil the personal belongings of people. A caterpillar white in color with a brown head eats natural wool, furs and cotton. Here she lays eggs.
Butterfly larvae - caterpillars - differ in a variety of shapes and colors. And anyone who does not have a disgust for caterpillars can enjoy observing these amazing creatures and, perhaps, learn something new for themselves. This is especially true of pupation, because it is one thing to just know about life cycle insects, and another - to see firsthand the process of transformation of one creature into another.
Hawkers
Hawkers (Sphingidae) is a family of large or medium sized butterflies. The body is powerful, often cone-shaped; wings - narrow, elongated wingspan from 30 to 175 mm.
For some unknown reason, with a filing aunt, he called hawkers most of his life bob a mi... What the bobs such - it is incomprehensible, except for the aunt this word from anyone's lips did not hear, and Yandex for such a request finds only the story of the same name by Dostoevsky.
Caterpillars are large, beautiful, usually brightly colored with contrasting stripes and false eyes. The tail has a characteristic horn.
The pupae of most hawk moths also have horns.
Next, we will talk about the history of pupation of two caterpillars found simultaneously on our site and identified as larvae hawkers: wine and fake... Actually, it was not difficult to identify them, since it is known that the caterpillars of the hawk moths are very picky and selective towards their food plants, therefore, if the caterpillar is found on grapes, then it is possible with a high probability that it should turn out to be a wine hawk moth.
So, the first story, happy ...
Wine hawk moth (Deilephila elpenor)
The caterpillar was found eating grape leaves. She was fat, springy and green, with a horn and four false eyes in the front.
Friends! This is not just an advertisement, but mine, personal request... Please join ZooBot group in VK... This is nice to me and useful to you: there will be a lot that will not get to the site in the form of articles.
She behaved actively, did not refuse food in captivity. I didn't mind taking pictures in different poses either. Click on the pictures - they have a lot of details!
But a couple of days later, she disappeared from sight. Carefully turning over the leaves piled on the bottom of the aquarium, I discovered a certain conglomerate: the leaves were clearly glued together. In the depths of the shelter, the strangely altered body of the caterpillar, covered with mucus, lay motionless.
After a day or two, I decided to see what had happened in the leaf house. As soon as I started to rake them, I felt something inside jerk vigorously. The leaves were glued together wonderfully, but what can one poor caterpillar oppose to the destructive power of the human mind?
For no one, I think, will be a discovery that the leaves were hiding chrysalis.
The anterior part of the pupa is completely rigid, the posterior part consists of three movably connected segments and ends in a horn. When the pupa is nervous, it can beat intensely, frightening the offender and jumping from place to place:
And here is what struck me the most. A blackened and dried head and front of the body lay in the leaves next to the pupa. former caterpillar with six horny paws. I never thought about the fact that when it turns into a chrysalis, the caterpillar discards head!("And what does she think ???" - this begs an idiotic question, from which, however, follows another: "Do caterpillars think in principle?"
An idea for a demotivator is born by itself: “Don't be a maggot! Don't lose your head! "
Now all that remains is to put the chrysalis in a secluded cool place, and perhaps in the spring I will be able to observe the most exciting stage of transformation: the birth of a butterfly.
Added after six months: it was possible to observe the birth of a butterfly, however, somewhat earlier than expected. Details and photos - by clicking on the picture:

Medium wine hawk moth is the one that I hatched six months later.
And now the second story, tragic ...
Linden hawk moth (Mimas tiliae)
This caterpillar was caught on a linden tree, and when caught, it was about the same green color as our previous hero. However, by the time of the photo session, she noticeably changed color to green-yellow. If I had read about this caterpillar earlier, I would have understood that it was already about to pupate - in the linden hawk moth, this is preceded by a change in color.
 If the caterpillar was immediately planted in the leaves and no longer touched, then, perhaps, I would still have a chrysalis of the lime hawk moth. But I did not let the poor creature carry out my biological program calmly. While replanting, while photographing ...
If the caterpillar was immediately planted in the leaves and no longer touched, then, perhaps, I would still have a chrysalis of the lime hawk moth. But I did not let the poor creature carry out my biological program calmly. While replanting, while photographing ...